Abstract
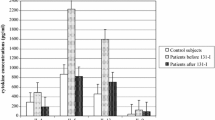
In order to examine whether serum soluble lnterleukin-2 Receptors (sIL-2R) could be used as a marker of the biological effects of the thyroid hormones, we measured the sIL-2R, sex hormone binding globulin and beta-2 microglobulin levels in thirty-three hyperthyroid patients (14 with Graves’ disease, 17 with Toxic Nodular Goiter and 2 with toxic adenoma) before and during treatment with antithyroid drugs. We found that serum sIL-2R concentrations of the patients, at diagnosis, were significantly higher compared with normal controls (2424±1447 vs 459±184 U/ml). All hyperthyroid patients had sIL-2R levels > mean + 2SD of normal controls, with 28 of the 33 patients having sIL-2R concentrations higher than 1011 U/ml (mean + 3SD of normal controls). Only 15 patients had SHBG levels higher than 3SD above the mean for the normal controls and 28 had SHBG levels 2SD above the mean for the normal controls. Three of the 5 hyperthyroid patients with normal SHBG levels at presentation had abnormally high sIL-2R levels. In all patients sIL-2R levels decreased gradually during therapy down to normal levels when euthyroidism was achieved. A strong positive correlation was found between slL-2R, SHBG and T3 and T4 concentrations. Serum B2-microglobulin (B2-m) levels were higher than the upper normal limit only in 9 patients, but a significant decrement was observed in all patients when euthyroidism was achieved. The above results indicate that serum sIL-2R levels could be a useful marker of the in vivo biological effects of the thyroid hormones on lymphocytes in hyperthyroid patients.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Makenzie K., Zakarijia M. Hyperthyroidism. In: De Groot L.J. (Ed.), Endocrinology. WB Saunders, Philadelphia, 1989, p. 646.
Studer H., Gerber H., Peter H.J. Multinodular goiter. In: DeGroot L.J. (Ed.), Endocrinology. WB Saunders, Philadelphia, 1989, p. 722.
Cantrell D.A., Smith K.A. Transient expression of IL-2 receptors. Consequences for T cell growth. J. Exp. Med. 158: 1895, 1983.
Rubin L.A., Nelson D.L. The soluble interleukin-2 receptor: biology, function and clinical application. Ann. Intern. Med. 113: 619, 1990.
Pui C.H. Serum interleukin-2 receptor: clinical and biological implications. Leukaemia 3: 323, 1989.
Koukkou E., Panayiotidis P., Alevizou-Terzaki V., Thalassinos N. High levels of serum soluble interleukin-2 receptors in hyperthyroid patients: correlation with serum thyroid hormones and independence from the etiology of the hyperthyroidism. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 73: 771, 1991.
Mariotti S., Caturegli P., Barbesino G., Del Prete G.E., Chiovato L., Pinchera A. Circulating soluble interleukin 2 receptor concentrations is increased in both immunogenic and nonim-munogenic hyperthyroidism. J. Endocrinol. Invest. 14: 777, 1991.
Mariotti S., Caturegli P., Barbesino G., Marino M., Del Prete G.F., Chiovato L., Tonacchera M., De Carli M., Pinchera A. Thyroid function and thyroid autoimmunity independently modulate serum concentration of soluble interleukin 2 (IL-2) receptor (sIL-2R) in thyroid diseases. Clin. Endocrinol. (Oxf.) 37: 417, 1992.
Nakanishi K., Taniguchi Y., Ohta Y. Increased soluble interleukin-2 receptor levels in autoimmune thyroid disease. Acta Endocrinol. (Copenh.) 125: 253, 1991.
Anderson D.C. Sex hormone binding globulin. Clin. Endocrinol. (Oxf.) 3: 69, 1974.
Caron P., Bennet A., Barousse C., Nisula B.C., Louvet J.P. Effect of hyperthyroidism on binding proteins for steroid hormones. Clin. Endocrinol. (Oxf.) 31: 219, 1989.
Ford H.C., Cooke R.R., Keightley E.A., Feek C.M. Serum levels of free and bound testosterone in hyperthyroidism. Clin. Endocrinol. (Oxf.) 36: 187, 1992.
De Nayer P., Lambot M.P., Desmons M.C., Rennotte B., Malvaux P., Beckers C. Sex hormone-binding protein in hyperthyroxinemic patients: A discriminator for thyroid status in thyroid hormone resistance and familial dysalbuminemic hyperthyroxinemia. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 62: 1309, 1986.
Beck-Peccoz P., Roncoroni R., Mariotti S., Medri G., Marcocci C., Brabant G., Forloni E.., Pinchera A., Faglia G. Sex hormone-binding globulin measurement in patients with inappropriate secretion of thyrotropin (IST): Evidence against selective pituitary thyroid hormone resistance in nonneoplastic IST. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 71: 19, 1990.
Rubin L.A., Kurman C.C., Fritz M.E., Biddison W.E., Boutin B., Yarchoan R., Nelson D.L. Soluble interleukin-2 receptors are released from activated human lymphoid cells in vitro. J. Immunol. 735: 3172, 1985.
Lervang H.H., Moller-Petersen J., Ditzel J. Serum beta-2 microglobulin levels in thyroid diseases. J. Intern. Med. 226: 261, 1989.
Roiter I., DaRin G., DeMenis E., Foscolo G.C., Legovini P., Conte N. Increased serum beta-2 microglobulin concentrations in hyperthyroid states. J. Clin. Pathol. 44: 73, 1991.
Hofmann B., Bass H., Nishanian P., Faisal M., Figlin R.A., Sarna G.P., Fahey J.L. Different lymphoid cell populations produce varied levels of neopterin, beta-2 microglobulin and soluble interleukin-2 receptors when stimulated with IL-2, interferon-gamma or tumor necrosis factor-alpha. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 88: 548, 1992.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Supported by a grant from the Greek Ministry of Health.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Koukkou, E., Panayiotidis, P. & Thalassinos, N. Serum soluble Interleukin-2 receptors as an index of the biological activity of thyroid hormones in hyperthyroidism. J Endocrinol Invest 18, 253–257 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03347809
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03347809