Abstract
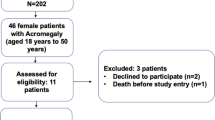
In some acromegalic patients medical treatment does not succeed in normalizing GH/IGF-I values. Data showing IGF-I suppression in acromegaly by estrogen and by tamoxifen use prompted us to reevaluate the effects of estro-progestins (EP) supplementation on GH/IGF-I levels in acromegalic women resistant or only par-tially sensitive to medical treatment. Eight active acromegalic women (30–52 yr, 4 with regular menses) entered a prospective open pilot study. Three of them, resistant to medical treatment, were off therapy; the remaining five, partially sensitive, maintained it at the maximally effective dosages throughout the study. Patients were treated with a triphasic pill (ethynil-estradiol 30–40–30 μg/day and desogestrel 50–70–100 mg/day) for 13±7 months. IGF-I levels fell from 512 (median, interquartile 436–657) μg/l to 282 (244–526) μg/l (p=0.0414); the decrease was observed in 6 patients (75%), and normal values were reached in 4 (50%). GH levels did not change [basal 7.6 (6.2–8.6) μg/l, final 7.6 (6.5–8.3) μg/l]. Effectiveness of treatment was not dependent on concomitant anti-GH treatment or gonadal status. In all patients IGF-I levels re-increased after EP withdrawal. This pilot study shows a marked IGF-I lowering effect of pill in acromegalic women, and warrants a prospective randomized study in patients resistant or partially sensitive to other medical treatments.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Melmed S., Jackson I., Kleinberg D., et al. Current treatment guidelines for acromegaly. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1998, 83: 2646–2652.
Clemmons D.R., Underwood L.E., Ridgway E.C., et al. Estradiol treatment of acromegaly. Reduction of immunoreactive somatomedin-C and improvement in metabolic status. Am. J. Med. 1980, 69: 571–575.
Cozzi R., Attanasio R., Oppizzi G., et al. Effects of tamox-ifen on GH and IGF-I levels in acromegaly. J. Endocrinol. Invest. 1997, 20: 445–451.
Heaney A.P., Manory F., Melmed S. Functional role of estrogen in pituitary tumor pathogenesis. J. Clin. Invest. 2002, 109: 277–283.
Anderson S.M., Shah N., Evans W.S., et al. Short-term estradiol supplementation augments growth hormone (GH) secretory responsiveness to dose-varying GH-releasing peptide infusions in healthy postmenopausal women. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2001, 86: 551–560.
Bellantoni M.F., Harman S.M., Cho D.E., et al. Effects of progestin-opposed transdermal estrogen administration on growth hormone and insulin-like growth factor-I in postmenopausal women of different ages. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1991, 72: 172–178.
Weissberger A.J., Ho K.K., Lazarus L. Contrasting effects of oral and transdermal routes of estrogen replacement therapy on 24-hour growth hormone (GH) secretion, insulinlike growth factor I, and GH-binding protein in postmenopausal women. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1991, 72: 374–381.
Hartmann B., Kirchengast S., Albrecht A., et al. Effects of hormone replacement therapy on growth hormone secretion patterns in correlation to somatometric parameters in healthy postmenopausal women. Maturitas 1995, 22: 239–246.
Bellantoni M.F., Vittone J., Campfield A.T., et al. Effects of oral versus transdermal estrogen on the growth hormone/insulin-like growth factor I axis in younger and older postmenopausal women: a clinical research center study. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1996, 81: 2848–2853.
Friend K.E., Hartman M.L., Pezzoli S.S., et al. Both oral and transdermal estrogen increase growth hormone release in postmenopausal women — A clinical research center study. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1996, 81: 2250–2256.
Malarkey W.B., Burleson M., Cacioppo J.T., et al. Differential effects of estrogen and medroxyprogesterone on basal and stress-induced growth hormone release, IGF-1 levels, and cellular immunity in postmenopausal women. Endocrine 1997, 7: 227–233.
Moe K.E., Prinz P.N., Larsen L.H., et al. Growth hormone in postmenopausal women after long-term oral estrogen replacement therapy. J. Gerontol. 1998, 53: B117–B124.
Shah N., Evans W.S., Veldhuis J.D. Actions of estrogen on pulsatile, nyctohemeral, and entropic modes of growth hormone secretion. Am. J. Physiol. — Regul. Integr. & Compar. Physiol. 1999, 276: R1351–R1358.
Shah N., Evans W.S., Bowers C.Y., et al. Oral estradiol administration modulates continuous intravenous growth hormone (GH)-releasing peptide-2-driven GH secretion in postmenopausal women. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2000, 85: 2649–2659.
Heald A., Selby P.L., White A., et al. Progestins abrogate estrogen-induced changes in the insulin-like growth factor axis. Am. J. Obstetr. Gynecol. 2000, 183: 593–600
Veldhuis J.D., Evans W.S., Bowers C.Y., et al. Interactive regulation of postmenopausal growth hormone insulin-like growth factor axis by estrogen and growth hormone-releasing peptide-2. Endocrine 2001, 14: 45–62.
Chapman I.M., Hartman M.L., Straume M., et al. Enhanced sensitivity growth hormone (GH) chemilumi-nescence assay reveals lower post-glucose nadir GH concentrations in men than in women. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1994, 78: 1312–1319.
Kam G.Y., Leung K.C., Baxter R.C., et al. Estrogens exert route- and dose-dependent effects on insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-binding protein-3 and the acid-labile subunit of the IGF ternary complex. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2000, 85: 1918–1922.
Cano A., Castelo-Branco C., Tarin J.J. Effect of menopause and different combined estradiol-progestin regimens on basal and growth hormone-releasing hormone-stimulated serum growth hormone, insulin-like growth factor-1, insulin-like growth factor binding protein (IGFBP)-1, and IGF-BP-3 levels. Fertil. Steril. 1999, 71: 261–267.
Paassilta M., Karjalainen A., Kervinen K., et al. Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-1 (IGFBP-1) and IGF-I during oral and transdermal estrogen replacement therapy: Relation to lipoprotein(a) levels. Atherosclerosis 2000, 149: 157–162.
Cardim H.J.P., Lopes C.M.C., Giannella-Neto D., et al. The insulin-like growth factor-I system and hormone replacement therapy. Fertil. Steril. 2001, 75: 282–287.
Raudaskoski T., Knip M., Laatikainen T. Plasma insulin-like growth factor-I and its binding proteins 1 and 3 during continuous nonoral and oral combined hormone replacement therapy. Menopause 1998, 5: 217–222.
Garnero P., Tsouderos Y., Marton I., et al. Effects of intranasal 17beta-estradiol on bone turnover and serum insulin-like growth factor I in postmenopausal women. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1999, 84: 2390–2397.
Helle S.I., Omsjo I.H., Hughes S.C., et al. Effects of oral and transdermal oestrogen replacement therapy on plasma levels of insulin-like growth factors and IGF binding proteins 1 and 3: a cross-over study. Clin. Endocrinol. (Oxf.) 1996, 45: 727–732.
Lawrence A.M., Kirsteins L. Progestins in the medical management of active acromegaly. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1970, 30: 646–652.
Parkinson C., Ryder W.D.J., Trainer P.J., et al. The relationship between serum GH and serum IGF-I in acromegaly is gender-specific. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2001, 86: 5240–5244.
Eden Engström B., Burman P., Karlsson F.A. Men with acromegaly need higher doses of octreotide than women. Clin. Endocrinol. (Oxf.) 2002, 56: 73–77.
Cook D.M., Ludlam W.H., Cook M.B. Route of estrogen administration helps to determine growth hormone (GH) replacement dose in GH-deficient adults. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1999, 84: 3956–3960.
Wolthers T., Hoffman D.M., Nugent A.G., et al. Oral estrogen antagonizes the metabolic actions of growth hormone in growth hormone-deficient women. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2001, 281: E1191–1196.
Shupnik M.A., Pitt L.K., Soh A.Y., et al. Selective expression of estrogen receptor alpha and beta isoforms in human pituitary tumors. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1998, 83: 3965–3972.
Chaidarun S.S., Swearingen B., Alexander J.M. Differential expression of estrogen receptor-beta (ERbeta) in human pituitary tumors: Functional interactions with ERalpha and a tumor-specific splice variant J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1998, 83: 3308–3315.
Huynh H., Pollak M. Enhancement of tamoxifen-induced suppression of insulin-like growth factor I gene expression and serum level by a somatostatin analogue. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Comm. 1994, 203: 253–259.
Fournier B., Gutzwiller S., Dittmar T., et al. Estrogen receptor (ER)-alpha, but not ER-beta, mediates regulation of the insulin-like growth factor I gene by antiestrogens. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276: 35444–35449.
Bates A.S., Van’t Hoff W., Jones J.M., et al. An audit of outcome of treatment in acromegaly. Q. J. Med. 1993, 86: 293–299.
Rajasoorya C., Holdaway I.M., Wrightson P., et al. Determinants of clinical outcome and survival in acromegaly. Clin. Endocrinol. (Oxf.) 1994, 41: 95–102.
Swearingen B., Barker F.G., Katznelson L., et al. Long-term mortality after transsphenoidal surgery and adjunctive therapy for acromegaly. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1998, 83: 3419–3426.
Le Roith D., Bondy C., Yakar S., et al. The Somatomedin Hypothesis: 2001. Endocr. Rev. 2001, 22: 53–74.
Scheidegger K.J., Cenni B., Picard D., et al. Estradiol decreases IGF-1 and IGF-1 receptor expression in rat aortic smooth muscle cells: Mechanisms for its athero-protective effects. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275: 38921–38928.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cozzi, R., Barausse, M., Lodrini, S. et al. Estroprogestinic pill normalizes IGF-I levels in acromegalic women. J Endocrinol Invest 26, 347–352 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03345183
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03345183