Abstract
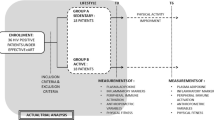
We examined the influence of physical activity (PA) and acute resistance exercise on insulin-like growth factor I (IGF-I) in 39 healthy, independent, community-dwelling elderly volunteers (14 men and 25 women) aged from 66 to 84. In a longitudinal non-interventional study, we compared the fluctuations in IGF-I levels and changes in habitual PA over a 6-month period. PA was evaluated by a questionnaire QAPSE (Questionnaire d’Activité Physique Saint-Etienne), and expressed by two activity indices: mean habitual daily energy expenditure (MHDEE), and daily energy expenditure corresponding to leisure time sports activities (sports activity index). In an experimental design we compared IGF-I levels before, at 1 and 15 minutes after short quadriceps muscle exertion (10 consecutive repetitions) carried out with optimal muscle power development. Changes in IGF-I levels over a 6-month period were positively related to changes in MHDEE (r=0.41; p<0.01), and sports activity (r=0.40; p<0.02). When analyzed by gender, these correlations were still statistically significant in women (r=0.39; p=0.05 and r=0.41; p<0.05), but not in men (r=0.36; p=0.21 and r=0.20; p=0.50). No changes (p=0.17) were observed in serum IGF-I concentrations after the acute exercise protocol. These findings indicate that IGF-I levels are positively related to fluctuations in habitual PA, at least in women. Further research is needed to establish the best intensity and duration of exercise training to induce these changes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbasi A.A., Drinka P.J., Mattson D.E., Rudman D.: Low circulating levels of insulin-like growth factors and testosterone in chronically institutionalized elderly men. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 41: 975–982, 1993.
Borst S.E., Millard W.J., Lowenthal D.T.: Growth hormone, exercise, and aging: the future of therapy for the frail elderly. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 42: 528–535, 1994.
Thompson J.L., Butterfield G.E., Marcus R., Hintz R.L., van Loan M., Ghiron L., Hoffman A.R.: The effects of recombinant human insulin-like growth factor-I and growth hormone on body composition in elderly women. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 80: 1845–1852, 1995.
Sullivan D.H., Carter W.J., Warr W.R., Williams L.H.: Side effects resulting from the use of growth hormone and insulin-like growth factor-I as combined therapy to frail elderly patients. J. Gerontol. Med. Sci. 53A: M183–M187, 1998.
Kelly P.J., Eisman J.A., Stuart M.C., Pocock N.A., Sambrook P.N., Gwinn T.H.: Somatomedin-C, physical fitness, and bone density. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 70: 718–723, 1990.
Poehlman E.T., Copeland K.C.: Influence of physical activity on insulin-like growth factor-I in healthy younger and older men. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 71: 1468–1473, 1990.
Toth M.J., Gardner A.W., Ades P.A., Poehlman E.T.: Contribution of body composition and physical activity to agerelated decline in peak VO2 in men and women. J. Appl. Physiol. 77: 647–652, 1994.
Cappon J., Brasel J.A., Mohan S., Cooper D.M.: Effect of brief exercise on circulating insulin-like growth factor I. J. Appl. Physiol. 76: 2490–2496, 1994.
Hornum M., Cooper D.M., Brasel J.A., Buneo A., Sietsema K.E.: Exercise-induced changes in circulating growth factors with cyclic variation in plasma estradiol in women. J. Appl. Physiol. 82: 1946–1951, 1997.
Kraemer W.J., Gordon S.W., Fleck S.J., Marchitelli L.J., Mello R., Dziados J.E., Friedl K., Harman E., Maresh C., Fry A.C.: Endogenous anabolic hormonal and growth factor responses to heavy resistance exercise in males and females. Int. J. Sports Med. 12: 228–235, 1991.
Poehlman E.T., Rosen C.J., Copeland K.C.: The influence of endurance training on insulin-like growth factor-1 in older individuals. Metabolism. 43: 1401–1405, 1994.
Roelen C.A.M., deVries W.R., Koppeschaar H.P.F., Vervoom C., Thijssen J.H.H., Blankenstein M.A.: Plasma insulin-like growth factor-I and high affinity growth hormone-binding protein levels increase after two weeks of strenuous physical training. Int. J. Sports Med. 18: 238–241, 1997.
Di Luigi L., Conti F., Casini A., Guidetti L., Zezze G., Pigozzi F., Spera G., Fortunio G., Romanelli F.: Growth hormone and insulin-like growth factor I responses to moderate submaximal acute physical exercise in man: effects of octreotide, a so-matostatin analogue, administration. Int. J. Sports Med. 18: 257–263, 1997.
Kraemer W.J., Aguilera B.A., Terada M., Newton R.U., Lynch J.M., Rosendaal G., McBride J.M., Gordon S.W., Häkkinen K.: Responses of IGF-I to endogenous increases in growth hormone after heavy-resistance exercise. J. Appl. Physiol. 79: 1310–1315, 1995.
McCall G.E., Byrnes W.C., Fleck S.J., Dickinson A., Kraemer W.J.: Acute and chronic hormonal responses to resistance training designed to promote muscle hypertrophy. Can. J. Appl. Physiol. 24: 96–107, 1999.
Niclas B.J., Ryan A.J., Treuth M.M., Harman S.M., Blackman M.R., Hurly B.F., Rogers M.A.: Testosterone, growth hormone and IGF-I responses to acute and chronic resistive exercise in men aged 50-70 years. Int. J. Sports Med. 16: 445–450, 1995.
Bonnefoy M., Kostka T., Patricot M.C., Berthouze S.E., Mathian B., Lacour J-R.: Physical activity and dehydroepiandros-terone sulfate, insulin-like growth factor-I and testosterone in healthy active elderly people. Age Ageing 27: 745–751, 1998.
Hagberg J.M., Seals D.R., Yerg J.E., Gavin J., Gingerich R., Premachandra B., Holloszy J.O.: Metabolic responses to exercise in young and old athletes and sedentary men. J. Appl. Physiol. 65: 900–908, 1988.
Horber F.F., Kohler S.A., Lippuner K., Jaeger P.: Effect of regular physical training on age-associated alteration of body composition in men. Eur. J. Clin. Invest. 26: 279–285, 1996.
Papadakis M.A., Grady D., Tierney M.J., Black D., Wells L., Grunfeld C.: Insulin-like growth factor 1 and functional status in healthy older men. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 43: 1350–1355, 1995.
Rudman D., Mattson D.E.: Serum insulin-like growth factor I in healthy older men in relation to physical activity. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 42: 71–76, 1994.
Vitiello M.V., Wilkinson C.W., Merriam G.R., Moe K.E., Prinz P.N., Ralph D.D., Colasurdo E.A., Schwartz R.S.: Successful 6-month endurance training does not alter insulin-like growth factor-I in healthy older men and women. J. Gerontol. 52A: M149–M154, 1997.
Berthouze S.E., Minaire P., Chatard J-C., Boutet C., Castells J., Lacour J-R.: A new tool for evaluating energy expenditure: the “QAPSE” development and validation. Med. Sci. Sports Ex-erc. 25: 1405–1414, 1993.
Berthouze S.E., Minaire P.M., Castells J., Busso T., Vico L., Lacour J.R.: Relationship between mean habitual daily energy expenditure and maximal oxygen uptake. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 27: 1170–1179, 1995.
Bonnefoy M., Kostka T., Berthouze S.E., Lacour J-R.: Validation of physical activity questionnaire (QAPSE) in healthy elderly volunteers. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 74: 528–533, 1996.
Sidney K.H., Shephard R.J.: Maximum and submaximum exercise tests in men and women in the seventh, eighth and ninth decades of life. J. Appl. Physiol. 43: 280–287, 1977.
Durnin J.V., Womersley J.: Body fat assessed from total body density and its estimation from skinfold thickness: measurements on 481 men and women aged from 16 to 72 years. Br. J. Nutr. 32: 77–97, 1974.
Daughaday E., Rotwein P.: Insulin-like growth factor I and II. Peptide, messenger ribonucleic acid and gene structures, serum and tissue concentrations. Endocr. Rev. 10: 68–91, 1989.
Bosco C., Belli A., Astrua M., Tihanyi J., Pozzo R., Kellis S., Tsarpela O., Foti C., Manno R., Tranquilli C.: A dynamometer for evaluation of dynamic muscle work. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 70: 379–386, 1995.
Blair S.N., Haskell W.L., Ho P., Paffenbarger R.S., Vranizan K.M., Farquhar J.W., Wood P.D.: Assessment of habitual physical activity by a seven-day recall in a community survey and controlled experiments. Am. J. Epidemiol. 122: 794–804, 1985.
Goran M.I., Poehlman E.T.: Total energy expenditure and energy requirements in healthy elderly persons. Metabolism 41: 744–753, 1992.
Seals D.R., Hagberg J.M., Hurley B.F., Ehsani A.A., Holloszy J.O.: Effects of endurance training on glucose tolerance and plasma lipid levels in older men and women. JAMA 252: 645–649, 1984.
Ambrosio M.R., Valentini A., Trasforini G., Minuto F., Ghigo E., Cella S., Margutti A., Pansini R., Degliuberti E.C.: Function of the GH/IGF-I axis in healthy middle-aged male runners. Neuroendocrinology 63: 498–503, 1996.
Nelson M.E., Meredith C.N., Dawson-Hughes B., Evans W.: Hormonal and bone mineral status in endurance-trained and sedentary post-menopausal women. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 66: 927–933, 1988.
Porch J.V., Jain K., Reilly A., Valdez C., Mazariegos M., Ziegler T.R., Solomons N., Smith R.J.: Aging, physical activity, insulin-like growth factor I, and body composition in Guatemalan women. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 66: 874–879, 1997.
Taaffe D.R., Pruitt L., Reim J., Hintz R.L., Butterfield G., Hoffman A.R., Marcus R.: Effect of recombinant human growth hormone on the muscle strength response to resistance exercise in elderly men. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 79: 1361–1366, 1994.
Kraemer R.R., Kilgore J.L., Kraemer G.R., Castracane V.D.: Growth hormone, IGF-I, and testosterone responses to resistive exercise. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 24: 1346–1352, 1992.
Goodman-Gruen D., Barrett-Connor E.: Epidemiology of insulin-like growth factor-I in elderly men and women. The Rancho Bernardo Study. Am. J. Epidemiol. 145: 970–976, 1997.
Italian Association for Research on Brain Aging (AIRIC) Multicenter Study Group: function of GH/IGF-I axis in aging: Multicenter study in 152 healthy elderly subjects with different degrees of physical activity. Aging Clin. Exp. Res. 9: 185–192, 1997.
Jahreis G., Kauf E., Frohner G., Schmidt H.: Influence of intensive exercise on insulin-like growth factor 1, thyroid and steroid hormones in female gymnasts. Growth Regul. 1: 95–99, 1991.
Skelton D.A., Young A., Greig C.A., Malbut K.E.: Effects of resistance training on strength, power, and selected functional abilities of women aged 75 and older. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 43: 1081–1087, 1995.
Young A., Skelton D.A.: Applied physiology of strength and power in old age. Int. J. Sports Med. 15: 149–152, 1994.
Cuttica C.M., Castoldi L., Gorrini G.P., Peluffo F., Delitala G., Filippa P., Fanciulli G.: Effects of six-month administration of recombinant human growth hormone to healthy elderly subjects. Aging Clin. Exp. Res. 9: 193–197, 1997.
Czerwinski S.M., Martin J.M., Bechtel P.J.: Modulation of IGF mRNA abundance during stretch-induced skeletal muscle hypertrophy and regression. J. Appl. Physiol. 76: 2026–2030, 1994.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bonnefoy, M., Kostka, T., Patricot, M.C. et al. Influence of acute and chronic exercise on insulin-like growth factor-I in healthy active elderly men and women. Aging Clin Exp Res 11, 373–379 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03339815
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03339815