Abstract
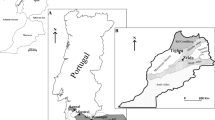
The degree of contamination by heavy metals (arsenic, copper, lead, tin and zinc) in soil and transfer to plants has been studied. Specimens of plant species from five locations in an area of 10 × 10 m were sampled with their corresponding soils. Thirty six plant species including two shallow water aquatic plants were identified. Soil and plant specimens were analyzed by using inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectrometry. It was found that metal concentration in soil was highly variable while concentration of metals in plants directly depends on the concentration of metals it was rooted. Roots showed highest metal concentration followed by leaves, shoots and flowers. Bioconcentraion factor and translocation factor were calculated, representing Cyperus rotundus L. as a potential tin-hyperaccumulator plant, previously not reported in literature. Plant Species Imperata cylindrica, Lycopodium cernuum, Melastoma malabathricum, Mimosa pudica Linn, Nelumbo nucifera, Phragmites australis L., Pteris vittata L. and Salvinia molesta, were metal accumulator while Acacia podalyriaefolia G. Don, Bulb Vanisium, Dillenia reticulate King, Eugenia reinwardtiana, Evodia roxburghiania Hk. f. clarke, Gleichenia linearis, Grewia erythrocarpa Ridl., Manihot esculenta Crantz, Paspalum conjugatum Berguis, Passiflora suberosa, Saccharum officinarum, Stenochlaena palustris (Burm.) Bedd. and Vitis trifolia Linn. were tolerated plant species. All other studied plants were excluders. Identified plant species could be useful for revegetation and erosion control in metals contaminated ex-mining sites. Morphological changes such as reduction in size, change in color and deshaping have also been observed in plant species with high metal values.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alvarez, E.; Fernández Marcos, M. L.; Vaamonde, C.; Fernández-Sanjurjo, M. J., (2003). Heavy metals in the dump of an abandoned mine in Galicia (NWSpain) and in the spontaneously occurring vegetation. Sci. Total Environ., 313(1–3), 185–197 (13 pages).
Ashraf, M. A.; Maah, M. J.; Yusoff, I., (2010). Study of water quality and heavy metals in soil and water of ex-mining area Bestari Jaya, Peninsular Malaysia, Int. J. Basic. Appl. Sci., 10(3), 7–27 (21 pages).
Atafar, Z.; Mesdaghinia, A.; Nouri, J.; Homaee, M.; Yunesian, M.; Yunesian, M.; Ahmadimoghaddam, M.; Mahvi, A. H., (2010). Effect of fertilizer application on soil heavy metal concentration. Environ. Monitor. Assess. 160(1–4), 83–89 (7 pages).
Ayari, F.; Hamdi, H.; Jedidi, N.; Gharbi, N.; Kossai, R., (2010). Heavy metal distribution in soil and plant in municipal solid waste compost amended plots. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Tech., 7(3), 465–472 (8 pages).
Baker, A. J. M., (1981). Accumulators and excluders strategies in the response of plants to heavy metals. J. plant nutr. 3(1–4), 643–654(12 pages).
Baker, A. J. M.; Brooks, R. R., (1989). Terrestrial higher plants which hyperaccumulate metallic elements. A review of their distribution, ecology and phytochemistry. Biorecovery, 1, 81–126 (36 pages).
Baker, A. J. M.; Reeves, R. D.; Hajar, A. S. M., (1994). Heavy metal accumulation and tolerance in British populations of the metallophyte Thlaspi cearulescens J. and C. Presl. (Brasicaceae)., New Phytol. 127(1), 61–68 (8 pages).
Baker, A. J. M., (1995). Metal hyperaccumulation by plants: our present knowledge of the ecophysiological phenomenon. In: Will Plants Have a Role in Bioremediation? 14th Annual Symp. Current Topics in Plant Biochemistry, Physiology and Molecular Biology, 19–22 April, 7–8, Columbia, MO.
Batty, L. C.; Baker, A. J. M.; Wheeler, B. D.; Curtis, C. D., (2000).The Effect of pH and plaque on the uptake of Cu and Mn in Phragmites australis(Cav.) Trin ex. Steudel. Ann. Bot., 86(3), 647–653 (7 pages).
Baudo, R.; Canzian, E.; Galanti, G.; Guilizzoni, P.; Rapetti, G., (1985). Relationships between heavy metals and aquatic organisms in Lake Mezzola hydrographc system (Northern Italy) Hydrochemestry. Mem. Ist. Ital. Idrobiol., 43, 161–180 (19 pages).
Bischof, C., (1996 ). Effects of heavy metal stress on free amino acids in the haemolymph and proteins in haemolymph and total body tissue of Lymantria dispar larvae parasitized by Glyptapanteles liparidis., Entomol. Experimental. et Appl., 79 ( 1) 61–68 (8 pages).
Boularbah, A.; Bitton, G.; Morel, J. L.; Schwartz, C., (2000). Assessment of metal accumulation in plants using MetPAD, a toxicity test specific for metal toicity. Environ. Toxicol., 15(5), 449–455 (7 pages).
Boularbah, A.; Schwartz, C.; Bitton, G.; Morel, J. L., (2006). Heavy metal contamination from mining sites in south Morocco: 1. Use of a biotest to assess metal toxicity of tailings and soils. Chemosphere, 63(5), 802–810 (9 pages).
Bradshaw, A. D.; Humphreys, M. O.; Johnson, M. S., (1978). The value of heavy metal tolerance in the revegation of metalliferous mine wastes, in: Goodman, G. T., Chadwick, M. J. (Eds.), Environmental management of mineral wastes. Sitjhoff and Noordhoff, The Netherlands, 311–314(4 pages).
Brooks, R. R., (2000). Plants that Hyperaccumulate Heavy Metals. CAB International, Cambridge, UK, 380–385 (6 pages).
Brotheridge, R. M.; Newton, K. E.; Taggart, M. A.; McCormick, P. H.; Evans S. W., (1998). Nickel, cobalt, zinc and copper levels in brown trout (Salmo trutta) from the river Otra, Southern Norway., Analyst, 123(1), 69–72 (4 pages).
Camel, V., (2000). Microwave-assisted solvent extraction of environmental samples. TrAC Trends in Anal. Chem., 19(4), 229–248 (20 pages).
Carpena-Ruiz, R.; Sopeña, A.; Ramon, A. M., (1989). Extraction of free amino acids from tomato leaves. Plant Soil., 119(2), 251–254 (4 pages).
Charles, C. W.; Glenn, S. R., (1953). The composition of plant fractions extracted with 80 % alcohol. Plant Physiol., 28(3), 535–538 (4 pages).
Conesa, H. M.; Faz, A.; Arnaldos, R., (2006). Heavy metal accumulation and tolerance in plants from mine tailings of the semiarid Cartagena-La Union mining district. Sci. Total Environ., 366(1), 1–11 (11 pages).
Deng, H.; Ye, Z. H.; Wong, M. H., (2004). Accumulation of lead, zinc, copper and cadmium by 12 wetland plant species thriving in metal-contaminated sites in China. Environ. Pollut., 132(1), 29–40 (12 pages).
Dowdy, D. L.; McKone, T. E., (1997). Predicting plant uptake of organic chemicals from soil or air using octanol/water and octanol/air partitioning ratios and a molecular connectivity index. Environ. Toxicol. Chem., 16(12), 2448–2456 (8 pages).
Dudka, S.; Adriano, D. C., (1997). Environmental impacts of metal ore mining and processing: A review. J. Environ. Qual., 26(3), 590–602 (13 pages).
Fayiga, A. O.; Ma, L. Q.; Cao, X.; Rathinasabapathi, B., (2004). Effects of heavy metals on growth and arsenic accumulation in the arsenic hyperaccumulator Pteris vittata L. Environ. Poll., 132(2), 289–296 (8 pages).
Freitas, H.; Prasad, M. N. V.; Pratas, J., (2004). Plant community tolerance and trace elements growing on the degraded soils of Sao Domingos mine in the south east of Portugal: Environmental implications. Environ. Int., 30(1), 65–72 (8 pages).
Gardea-Torresdey, J. L.; Peralta-Videa, J. R.; de la Rosa, G.; Parsons, J. G., (2005). Phytoremediation of heavy metals and study of the metal coordination by X-ray absorption spectroscopy. Coordin. Chem. Rev., 249(17–18), 1797–1810 (14 pages).
Gee, G. W.; Bauder, J. W., (1986). Particle soil analysis. in: Klute, A. (Ed.), Methods for soil analysis. Part 1: Physical and mineralogical methods. Soil Science Society of America. American Society of Agronomy, Madison, Wisconsin, USA., 383–411 (39 pages).
Gibbs, M. I., (1951). The position of C14 in sunflower leaf metabolites after exposure of leaves to short period photosynthesis and darkness in an atmosphere of C1402., Plant Physiol. 26(3), 549–556 (8 pages).
Goyal, P.; Sharma, P.; Srivastava, S.; Srivastava, M. M., (2008). Saraca indica leaf powder for decontamination of Pb: Removal, recovery, adsorbent characterization and equilibrium modeling. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Tech., 5(1), 27–34 (8 pages).
Griepink, B.; Muntau, H., (1988). The Certification of the Contents (Mass Fractions) of As, B, Cd, Cu, Hg, Mn, Mo, Ni, Pb, Sb, Se and Zn in Rye Grass—CRM 281. Office for Official Publications of the European Communities, Luxembourg.
Hall, W. S.; Pulliam, G. W., (1995), An assessment of metals in an estuarine wetlands ecosystem. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol., 29(2), 164–173 (8 pages).
Henriques, F. S.; Fernandes, J. C., (1991). Metal uptake and distribution in rush (Juncus conglomeratus L.) plants growing in pyrites mine tailings at Lousal, Portugal. Sci. Total Environ., 102, 253–260 (8 pages).
Johansen, P.; Asmund, G., (2001). Pollution from mining in Greenland—a review, in: Olsen, H. K., Lorentzen, L., Rendal, O. (Eds.), Mining in the arctic. The Netherlands: A. A. Balkema Publishers, 29–36 (8 pages).
Johnson, D. B.; Hallberg, K. B., (2005). Acid mine drainage remediation options: A Rev., Sci. Total Environ. 338(1–2), 3–14 (12 pages).
Keller, B. E. M.; Lajtha, K.; Cristofor, S., (1998). Trace metal concentrations in the sediments and plants of the Danube Delta, Romania., Wetlands. 18, 42–50 (9 pages).
Ling, T.; Guanghua, Z.; Jun, R., (2009). Effects of chromium on seed germination, root elongation and coleoptile growth in six pulses. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Tech., 6(4), 571–578 (8 pages).
Malakootian, M.; Nouri, J.; Hossaini, H., (2009). Removal of heavy metals from paint industry’s wastewater using Leca as an available adsorbent. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Tech., 6(2) 183–190 (8 pages)
Mateo, R.; Taggart, M.; Green, A. J.; Cristòfol, C.; Ramis, A.; Lefranc, H.; Figuerola, J.; Meharg, A. A., (2006). Altered porphyrin excretion and histopathology of greylag geese (Anser anser) exposed to soil contaminated with lead and arsenic in the Guadalquivir Marshes, SW Spain. Environ. Toxicol. Chem., 25(1), 203–212 (10 pages).
Mattina, M. I.; Lannucci-Berger, W.; Musante, C.; White, J. C., (2003). Concurrent plant uptake of heavy metals and persistent organic pollutants from soil. Environ. Pollut., 124(3), 375–378 (4 pages).
McNeill, J., (2006). International Code of Botanical Nomenclature (VIENNA CODE), adopted by the 17th International Botanical Congress Vienna, Austria.
McGrath, S. W.; Zhao, F. J.; Lombi, E., (2001). Plant and rhizosphere processes involved in phtoremediation of metal-contaminated soils. Plant and Soil, 232(1–2), 207–214 (8 pages).
Mickel, J. T., (1992). Pteridophytes, in: McVaugh, R. (Ed.), Flora Novo-Galiciana. A descriptive account of the vascular plants of Western Mexico, vol. 17. University of Michigan Herbarium, Ann Arbor, 120–431 (12 pages).
Min, Y.; Boquing, T.; Meizhen, T.; Aoyama, I., (2007). Accumulation and uptake of manganese in a hyperaccumulator Phytolacca americana. Miner. Eng., 20(2), 188–190 (3 pages).
Mizell, M.; Sidney, B.; Simpson, Jr., (1961), Paper chromatographic separation of amino acids: A solvent to replace phenol. J. Chromatograph. A(5), 157–160 (4 pages).
Monni, S.; Uhlig, C.; Hansen, E.; Magel, E., (2001). Ecophysiological responses of Empertrum nigrum to heavy metal pollution. Environ. Poll., 112(2), 121–129 (9 pages).
Moran, R. C.; Riba, R., (1995). Psiolotaceae and Salviniaceae. Flora Mesoamericana, vol. 1. Universidad Nacional Autónoma de México, México, DF.
Morel, J. L.; Bitton, G.; Schwartz, C.; Schiavon, M., ( 1997). Bioremediation of soils and waters contaminated with micropollutants: With role of plants, in: Zelikoff, J. J., Lynch, J. M., Sheppers, J., Eds., Ecotoxicology: Responses, Biomarkers and risk assessment OECD, 1–38 (38 pages).
Nelson, D. W.; Sommers, L. E., (1982). Total carbon, organic carbon and organic matter, in: Page, L. (Ed.), Methods of soil analysis. Part 2. Agronomy 9. American Society of Agronomy, Madison, WI. 539–279 (41 pages).
Norland, M. R.; Veith, D. L., (1995). Revegetation of coarse taconite iron ore tailing using municipal waste compost. J. Hazard. Mater., 41(2–3), 123–134 (12 pages).
Nouri, J., (1980). Heavy metals in sewage sludge, soils amended with sludge and their uptake by crop plants. Ph.D. thesis, University of London, London, UK.
Nouri, J.; Karbassi, A. R.; Mirkia, S., (2008). Environmental management of coastal regions in the Caspian Sea. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Tech., 5(1), 43–52 (10 pages).
Nouri, J.; Khorasani, N.; Lorestani, B.; Yousefi, N.; Hassani, A. H.; Karami, M., (2009). Accumulation of heavy metals in soil and uptake by plant species with phytoremediation potential. Environ. Earth Sci., 59(2), 315–323 (9 pages).
Nouri, J.; Lorestani, B.; Yousefi, N.; Khorasani, N.; Hasani, A. H.; Seif, S.; Cheraghi, M., (2011). Phytoremediation potential of native plants grown in the vicinity of Ahangaran lead-zinc mine Hamedan, Iran. Environ. Earth Sci., 62(3), 639–644 (6 pages).
Nwuche, C. O.; Ugoji, E. O., (2008). Effects of heavy metal pollution on the soil microbial activity. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Tech., 5(3), 409–414 (6 pages).
Prasad, M. N. V.; Strzalka, K., (2002). Physiology and Biochemistry of Metal Toxicity and Tolerance in Plants. 1st Ed., Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht, 330–432 (103 pages).
Peverly, J. H.; Surface, J. M.; Wang, T., (1995). Growth and trace metal absorption by Phragmites australis in wetlands constructed for landfill leachate treatment. Ecol. Eng., 5(1), 21–35 (15 pages).
Reeves, R. D.; Baker, A. J. M., (2000). Metal-accumulating plants, in: Raskin, I., Ensley, B. D. (Eds.), Phytoremediation of toxic metals: using plants to clean up the environment. John Wiley and Sons Inc., New York, USA, 193–230 (38 pages).
Rout, G. R.; Das, P., (2003). Effect of metal toxicity on plant growth and metabolism: I. Zinc., Agron., 23(1), 3–11 (9 pages).
Rowell, D. J., (1994). Soil Science. Methods and Applications, Longman, Essex, England, 149–150 (12 pages).
Santillan, L. F. J.; Constantino, C. A. L.; Rodriguez, G. A. V.; Ubilla, N. M. C.; Hernandez, R. I. B., (2010). Manganese accumulation in plants of the mining zone of Hidalgo, Mexico. Biores. Tech., 101(15), 5836–5841 (6 pages).
Scholes, L. N. L.; Shutes, R. B. E.; Revitt, D. M.; Purchase, D.; Forshaw, M., (1999). The removal of urban pollutants by wetlands during wet weather. Wat Sc. Tech., 40(3), 333–340 (8 pages).
Singh, A. N.; Zeng, D. H.; Chen, F. S., (2005). Heavy metals concentration in re-developing soil of mine spoil under plantation of certain native woody species in dry tropical environment, India. J. Environ. Sci., 17(1), 168–174 (7 pages).
SISS, (1985). Metodi normalizzati per l’analisi del suolo. Societa’ Italiana per la Scienza del Suolo, Edagricole, Bologna.
Shah, B. A.; Shah, A. V.; Singh, R. R., (2009). Sorption isotherms and kinetics of chromium uptake from wastewater using natural sorbent material. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Tech., 6(1), 77–90 (14 pages).
Sheldon, A. R.; Menzies, N. W., (2005). The Effect of copper toxicity on the growth and root morphology of Rhodes Grass (Chloris gayana Knuth.) in resin buffered solution culture. Plant and Soil, 278(1–2), 341–349 (9 pages).
Sun, Q.; Ye, Z. H.; Wang, X. R.; Wong, M. H., (2005). Increase of glutathione in mine population of Sedum alfredii: A Zn hyperaccumulator and Pb accumulator. Phytochem., 66(21), 2549–2556 (8 pages).
Thomas, G. W., (1996). Soil pH and soil acidity, in: Sparks, D. L. (Ed.), Methods for soil analysis. Part 3: Chemical methods. Soil Science Society of America. American Society of Agronomy, Madison, Wisconsin. USA, 475–490 (16 pages).
Tordoff, G. M.; Baker, A. J. M.; Willis, A. J., (2000). Current approaches to the revegetation and reclamation of metalliferous mine wastes. Chemosphere, 41(1–2), 219–228 (10 pages).
Wilson, B.; Pyatt, F. B., (2007). Heavy metal dispersion, persistance, and bioccumulation around an ancient copper mine situated in Anglesey, UK. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Safety, 66(2), 224–231 (8 pages).
Wong, J. W. C.; Ip, C. M.; Wong, M. H., (1998). Acid-forming capacity of lead-zinc mine tailings and its implications for mine rehabilitation. Environ. Geochem. Health, 20(3), 149–155 (7 pages).
Wong, M. H., (2003). Ecological restoration of mine degraded soils, with emphasis on metal contaminated soils. Chemosphere, 50(6), 775–780 (6 pages).
Yanqun, Z.; Yuan, L.; Schvartz, C.; Langlade, L.; Fan, L., (2004). Accumulation of Pb, Cd, Cu and Zn in plants and hyperaccumulator choice in Lanping lead-zinc mine area, China. Environ. Int., 30(4), 567–576 (10 pages).
Ye, Z. H.; Baker, A. J. M.; Wong, M. H.; Willis, A. J., (1997). Zinc, lead and cadmium tolerance, uptake and accumulationby the common reed, Phragmites australis (Cav.) trin. ex steudel. Ann. Bot., 80(3), 363–370 (8 pages).
Younger, P. L., (2001). Mine water pollution in Scotland: Nature, extent and preventative strategies. Sci. Total Environ., 265(1–3), 309–326 (18 pages).
Zhang, W.; Cai, Y.; Tu, C.; Ma, L. Q., (2002). Arsenic speciation and distribution in an arsenic hyperaccumulating plant. Sci. Total Environ., 300(1–3), 167–177 (11 pages).
Zvinowanda, C. M.; Okonkwo, J. O; Shabalala, P. N.; Agyei, N. M., (2009). A novel adsorbent for heavy metal remediation in aqueous environments. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Tech., 6(3) 425–434 (10 pages).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ashraf, M.A., Maah, M.J. & Yusoff, I. Heavy metals accumulation in plants growing in ex tin mining catchment. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 8, 401–416 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03326227
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03326227