Abstract
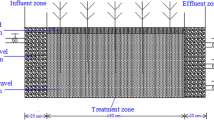
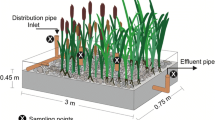
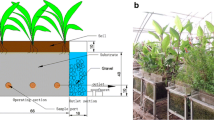
The influent concentration has a great effect on nutrients removal efficiency in vertical subsurface flow constructed wetland systems, but treatment performance response to different C: N: P ratios in the influent are unclear at present. At the first growing seasons, the effects of the plants present or not, season, the different C: N: P ratio in influent condition and their interaction on treatment performances were studied in the planted or the unplanted wetlands in greenhouse condition. Each set of units was operated at hydraulic loading rates of 40 L/d. Low, medium and high-strength (100, 200, 400 mg/L of chemical oxygen demand or 20, 40, 80 mg/L total nitrogen) synthetic sewage were applied as influent. According to the first growing season results, the average removal efficiencies for the unplanted and the planted wetlands were as follows: chemical oxygen demand (44–58 % and 55–61 % respectively), total nitrogen (26–49% and 31–54 %) and total phosphorus (36–64 % and 70–83 %). The both wetlands system was operated as an efficient treatment system of highest average removal rates of both chemical oxygen demand and total phosphorus when medium-strength synthetic sewage were applied. When high strength synthetic sewage was applied, the planted wetlands usually had a higher nutrients removal rates than the unplanted over the study period. The plants grew well under any high loading treatment over the study period. Anyhow, it also proved that the wetland systems have a good capacity to treat different strength wastewater in greenhouse condition.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdel-Ghani, N. T.; Elchaghaby, G. A., (2007). Influence of operating conditions on the removal of Cu, Zn, Cd and Pb ions from wastewater by adsorption. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Tech. 4(4), 451–456 (6 pages).
Abdel-Ghani, N. T.; Hegazy, A. K.; El-Chaghaby, G. A., (2009). Typha domingensis leaf powder for decontamination of aluminium, iron, zinc and lead: Biosorption kinetics and equilibrium modeling.. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Tech., 6(2), 243–248 (6 pages).
Akratos, C. S.; Tsihrintzis, V. A., (2007). Effect of temperature, HRT, vegetation and porous media on removal efficiency of pilot-scale horizontal subsurface flow constructed wetlands. Ecol. Eng., 29(2), 173–191 (19 pages).
Alam, Md. J. B.; Islam, M. R.; Muyen, Z.; Mamun, M.; Islam, S., (2007).Water quality parameters along rivers. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Tech., 4(1), 159–167 (9 pages).
Baptista, J. D. C.; Davenport R. J.; Donnelly, T.; Curtis, T. P.; Rayne, D., ( 2008). The microbial diversity of laboratory-scale wetlands appears to be randomly assembled. Water. Res., 42(12), 3182–3190 (9 pages).
Baptista, J. D. C.; Donelly, T.; Rayne, D.; Davenport, R. J., (2003). Microbial mechanisms of carbon removal in subsurface flow wetlands. Water Sci. Tech., 48(5), 127–134 (8 pages).
Brix, H.; Arias, C. A.; Del Bubba, M., (2001). Media selection for sustainable phosphorus removal in subsurface flow constructed wetlands. Water Sci. Tech., 44(11-12), 47–54 (8 pages).
Brix, H.; Arias, C. A., (2005). The use of vertical flow constructed wetlands for on-site treatment of domestic wastewater. New Danish guidelines., Ecol. Eng., 25(5), 491–500 (10 pages).
Calheiros, C. S. C.; Rangel, A. O. S. S.; Castro, P. M. L., (2009). Treatment of industrial wastewater with two-stage constructed wetlands planted with Typha latifolia and Phragmites australis. Bioresour. Tech., 100(13), 3205–3213 (9 pages).
Cooper, P. F., (1999). A review of the design and performance of a vertical-flow and hybrid reed bed treatment systems. Water Sci. Tech., 40(3), 1–9 (9 pages).
Coveney, M. F.; Sites, D. L.; Lowe, E. F; Battoe, L. E.; Conrow, R., (2002). Nutrient removal from eutrophic lake water by wetland filtration. Ecol. Eng., 19(2), 141–159 (19 pages).
Edwards, K. R.; Cizkova, H.; Zemanova, K.; Santruckova, H., (2006). Plant growth and microbial processes in a constructed wetland planted with Phalaris arundinacea. Ecol. Eng., 27(2), 153–165 (9 pages).
Enriquez, S.; Duarte, C. M.; Sand-Jensen, K., (1993). Patterns in decomposition rates among photosynthetic organisms: the importance of detritus C: N: P content. Oecologia, 94(4), 457–471 (15 pages).
Harikumar, P. S.; Nasir, U. P.; Mujeebu Rahman, M. P., (2009). Distribution of heavy metals in the core sediments of a tropical wetland system. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Tech., 6(2), 225–232 (8 pages).
Igbinosa, E. O.; Okoh, A. I., (2009). Impact of discharge wastewater effluents on the physico-chemical qualities of a receiving watershed in a typical rural community. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Tech. 6(2), 175–182 (8 pages).
Juang, D. F.; Chen, P. C., (2007). Treatment of polluted river water by a new constructed wetland. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Tech., 4(4), 481–488 (8 pages).
Kayser, K.; Kunst, S., (2005). Processes in vertical-flow reed beds — nitrification, oxygen transfer and soil clogging. Water Sci. Tech., 51(9), 177–184 (8 pages).
Kantawanichkul, S.; Kladprasert, S.; Brix, H., (2009). Treatment of high-strength wastewater in tropical vertical flow constructed wetlands planted with Typha angustifolia and Cyperus involucratus. Ecol. Eng., 35(2), 238–247 (10 pages).
Konnerup, D.; Thammarat Koottatep, T.; Brix, H., (2009). Treatment of domestic wastewater in tropical subsurface flow constructed wetlands planted with Canna and Heliconia. Ecol. Eng., 35(2), 248–257 (10 pages).
Koottatep, T.; Polprasert, C.; Oanh, N. T. K.; Heinss, U.; Montangero, A.; Strauss, M., (2001). Septage dewatering in vertical-flow constructed wetlands located in the tropics. Water Sci. Tech., 44(2-3), 181–188 (8 pages).
Korkusuz, E. A.; Beklioglu, M.; Demirer, N.G., (2005). Comparison of the treatment performances of blast furnace slag-based and gravel-based vertical flow wetlands operated identically for domestic wastewater treatment in Turkey. Ecol. Eng., 24(3), 187–200 (14 pages).
Li, L. F.; Li, Y. H.; Biswas, D. K.; Nian, Y. G.; Jiang G., (2008). Potential of constructed wetlands in treating the eutrophic water: Evidence from Taihu Lake of China., Bioresource Tech., 99(6), 1656–1663 (8 pages).
Lin, Y. F.; Jing, S. R.; Lee, D. Y.; Wang, T. W., (2002). Nutrient removal from aquaculture wastewater using a constructed wetlands system. Aquaculture, 209(1-4), 169–184 (16 pages).
Lu, X. M.; Huang, M. S., (2010). Nitrogen and phosphorus removal and physiological response in aquatic plants under aeration conditions. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Tech., 7(4), 665–674 (10 pages).
Luederitz, V.; Eckert, E.; Lange-Weber, M.; Lange, A.; Gersberg, R. M., (2001). Nutrient removal efficiency and resource economics of vertical flow and horizontal flow constructed wetlands. Ecol. Eng., 18(2), 157–171 (15 pages).
Mahvi, A.H., (2008). Application of agricultural fibers in pollution removal from aqueous solution. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Tech., 5(2), 275–285(11 pages).
Merlin, G.; Pajean, J. L.; Lissolo, T., (2002). Performances of constructed wetlands for municipal wastewater treatment in rural mountainous area. Hydrobiologia, 469(1-3), 87–98 (12 pages).
Nameni, M.; Alavi, Moghadam M. R.; Arami, M., (2008). Adsorption of hexavalent chromium from aqueous solutions by wheat bran. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Tech., 5(2), 161–168 (8 pages).
Nouri, J., Danehkar, A., Sharifipour, R., (2008). Evaluation of ecotourism potential in the northern coastline of the Persian Gulf. Environ. Geo., 55(3) 681–686 (6 pages).
Nwuche, C. O.; Ugoji, E. O, (2008). Effects of heavy metal pollution on the soil microbial activity. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Tech., 5(3), 409–414 (6 pages).
Nwuche, C. O.; Ugoji, E. O, (2010). Effect of co-existing plant specie on soil microbial activity under heavy metal stress. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Tech., 7(4), 697–704 (8 pages).
OECD., (1996). Guideline for testing of chemicals simulation test-aerobic sewage treatment. technical report. Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD), Paris, France.
Okafor, E.C.; Opuene, K., (2007). Preliminary, assessment of trace metals and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the sediments. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Tech., 4(2), 233–240 (8 pages).
Prochaskaa, C. A.; Zouboulisa, A. I.; Eskridgeb, K. M., (2007). Performance of pilot-scale vertical-flow constructed wetlands, as affected by season, substrate, hydraulic load and frequency of application of simulated urban sewage. Ecol. Eng., 31(1), 57–66 (10 pages).
Prochaska, C. A.; Zouboulis, A. I., (2009). Treatment performance variation at different depths within vertical subsurface-flow experimental wetlands fed with simulated domestic sewage. Desalination, 237(1-3), 367–377 (11 pages).
Seo, D. Ch.; Cho, J. S.; Lee, H. J.; Heo, J. S., ( 2005). Phosphorus retention capacity of filter media for estimating the longevity of constructed wetland. Water Res. 39(11), 2445–2457 (13 pages).
Stottmeister, U.; Wiessner, A.; Kuschk, P.; Kappelmeyer, U.; Kappstner, M.; Bederski, O.; Muller, R.A.; Moormann, H., (2003). Effects of plants and microorganisms in constructed wetlands for wastewater treatment. Biotechnol. Adv., 22(1-2), 93–117 (25 pages).
Tang, X. Q.; Huang, S. L.; Fciwem, M.S., (2009). Comparison of phosphorus removal between vertical subsurface flow constructed wetlands with different substrates. Water Environ. J. 23(3), 180–188 (9 pages).
Tsihrintzis, V. A.; Akratos, C. S.; Gikas, G. D.; Karamouzis, D.; Angelakis, A.N., (2007). Performance and cost comparison of a FWS and a VSF constructed wetland systems. Environ. Tech., 28(6), 621–628 (8 pages).
Zurita, F.; De, A.J.; Belmont, M.A., (2006). Performance of laboratory-scale wetlands planted with tropical ornamental plants to treat domestic wastewater. Water Qual. Res. J. Can., 41(4), 410–417 (8 pages).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cheng, B., Hu, C.W. & Zhao, Y.J. Effects of plants development and pollutant loading on performance of vertical subsurface flow constructed wetlands. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 8, 177–186 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03326207
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03326207