Abstract
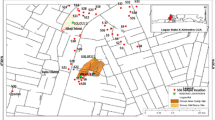
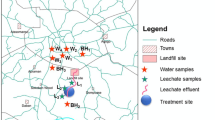
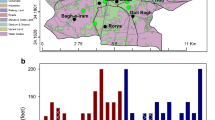
Geochemical analyses of groundwater and streams flowing around abandoned and active dumpsites in Lagos, Southwestern Nigeria were carried out. Results show that water samples have generally low total dissolved solids with average values of 163.75 and 153.4 for abandoned and active dumpsites, respectively. pH ranges from 3.96-8.34 while total hardness varies from 10–220 mg/L calcium carbonate (soft to slightly hard). Average concentrations of the dominant ions for abandoned and active dumpsites were 57.8 and 25.86 mg/L (Na) representing 40.7 and 46.3 % of the total cations respectively and Nitrate (av. 96.89 and 61.51 mg/L) representing 49.1 % and 40 %, respectively of the total anions. The pH, coliform count and concentrations of nitrate iron, manganese and sodium in most of the water samples were above the national drinking water standards proposed by the United States Environmental Protection Agency. Trace elements like silver, arsenic, beryllium, bismuth, cerium, cobalt, chromium, lithium selenium, tellurium, titanium, uranium, vanadium, tin and yttrium were below detection level for all the water samples while tungsten, thallium, molybdenum and lead were only present in surface and groundwater close to the dumpsites and also display values higher than recommended standards while cupper, zinc, aluminum, barium and strontium were present in most of the samples. The pollution index among all sites varied from 0.009 to 1.26 and 0.106 to 6.25 for abandoned and active dumpsites, respectively while the water around most of the dumpsite areas exceeded the acute and chronic effect levels proposed by the United States Environmental Protection Agency in 2007.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdel-Ghani, N. T.; Elchaghaby, G. A., (2007). Influence of operating conditions on the removal of Cu, Zn, Cd and Pb ions from wastewater by adsorption. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Tech., 4 (4), 451–456 (6 pages).
Abdel-Ghani, N. T.; Hegazy, A. K.; El-Chaghaby, G. A., (2009). Typha domingensis leaf powder for decontamination of aluminium, iron, zinc and lead: Biosorption kinetics and equilibrium modeling. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Tech., 6 (2), 243–248 (6 pages).
Adams, W. J.; Kimerle, R. A.; Barnet, J. W., (1992). Sediment quality and aquatic life assessment. Environ. Sci. Tech., 26 (10), 1865–1875 (11 pages).
Adeniyi, A. A.; Yusuf, O. O.; Okedeyi, O. O., (2008); Assessment of the exposure of two fish species to metals pollution in the Ogun river catchments, Ketu, Lagos, Nigeria. Environ. Monit. Assess., 137 (1-3), 451–458 (8 pages).
Akcay, H.; Oguz, A.; Karapire, C., (2003). Study of heavy metal pollution and speciation in Buyak Menderes and Gediz river sediments. Water Res., 37 (4), 813–822 (10 pages).
Altindag, A.; Yigit, S., (2005). Assessment of heavy metal concentrations in the food web of lake Beysehir, Turkey. Chemosphere, 60 (4), 552–556 (5 pages).
Arienzo, M.; Adamo, P.; Bianco, M. R.; Violante, P., (2001). Impact of land use and urban run-off on the contamination of the Samo river basin in southwestern Italy. Water Air Soil Pollut., 131 (1-4), 349–366 (18 pages).
Awofolu, O. R.; Du Plessis, R.; Rampedi, I., (2007). Influence of discharged effluent on the quality of surface water utilized for agricultural purposes. Afr. J. Biotech., 6 (19), 2251–2258 (8 pages).
Awofolu, O. R.; Mbolekwa, Z.; Mtshemla, V.; Fatoki, O. S.; (2005). Levels of trace metals in water and sediment from Tyume river and its effects on an irrigated farmland. Water S. Afr., 31 (1), 87–94 (8 pages).
Campbell, N. A., (1996). Biology, 4th. Ed. The Benjamin/ cummings publishing company Inc., University of California, USA.
Chon, H. T.; Ahn, J. S.; Jung, M. C., (1991). Environmental contamination of toxic heavy metals in the vicinity of some Au-Ag mines in Korea. Proc. of the 4th. Biennial SGA Meeting, Truku: Finland, 891.
Daka, E. R.; Molson, M.; Ekeh, C. A.; Ekweozor, I. K. E., (2007). Sediment quality status of two creeks in the upper bonny estuary, Niger delta, in relation to urban/industrial activities. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol., 78 (6), 515–521 (7 pages).
Emoyan, O. O; Ogban, F. E.; Akarah, E., (2005). Evaluation of Heavy metals loading of River Ijana, Nigeria. J. Appl. Sci. Environ. Manag., 10 (2), 121–7 (7 pages).
Grimanis, A. P.; Zafiropoulos, D.; Vassilaki, R.; Grimanis, M., (1978). Trace elements in the flesh and liver of two fish species from polluted and unpolluted areas in the Aegean Sea. Environ. Sci. Tech., 12 (6), 723–726 (4 pages).
Hem, J. D., (1985). Study and interpretation of the chemical characteristics of natural water. USGS. 3rd. Ed., Water supply paper, 2254.
Jenkins, P.; Southern, T.; Truesdale, V.; Jeary, A., (1996). Waters. Watts S., Halliwell L., (Eds.). Essential environmental science. Methods and Techniques London: Routledge, 336-350.
Kaonga, C. C.; Kumwenda, J.; Mapoma, H. T., (2010). Accumulation of lead, cadmium, manganese, copper and zinc by sludge worms; Tubifex tubifex in sewage sludge. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Tech., 7 (1), 119–126 (8 pages).
Kim, K. W.; Lee, H. K.; Yoo, B. C., (1998). The environmental impact of gold mines in the Yugu- Kwangcheon Au-Ag metallogenic province Republic of Korea. Environ. Tech., 19, 291.
Kloke, A., (1979). Content of arsenic, cadmium, chromium, fluorite, lead, mercury and nickel in plants grown on contaminated soil. United Nations ECE Symp.
Lee, J. S.; Chon, H. T.; Kim, J. S.; Kim, K. W.; Moon, H. S., (1998). Enrichment of potentially toxic elements in areas underlain by black shales and slates in Korea. Environ Geochem. Hlth., 20 (30), 135–147 (13 pages).
Manjunatha, B. R.; Balakrishna, K.; Shanker, R.; Mahalingam, T. R., (2001). Geochemistry and assessment of metal pollution in soils and river India components of a monsoon-dominated environment near Karwar, southwest Coast. Environ. Geol., 40 (11-12), 1462–1470 (9 pages).
Manly, R., (1996). Biological indicators. Fifield, F. W., Haines, P. J. (Eds.). Environmental analytical chemistry. Black Academic and Professional, Oxford, London.
Mohiuddin, K. M.; Zakir, H. M.; Otomo, K.; Sharmoh, S.; Shikazono, N., (2010). Geochemical distribution of trace metal pollutants in water and sediments of downstream of an Urban river. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Tech., 7 (1) 17–28 (12 pages).
Nier, (2007). Investigation of the impact of mine discharges on Han-river watershed. 1st. year’s report.
Nishida, H.; Miyai, M., Tada, F.; Suzuki, S., (1982). Computation of the index of pollution caused by heavy metals in river sediment. Environ. Poll. Ser. B4: 241.
Olobaniyi, S. B., Owoyemi, F. B., (2006). Characterization by factor analysis of the chemical facies of ground water in the deltaic plain sands aquifer of Warri, Western Nigerdelta, Nigeria. Afr. J. Sci. Tech., 7 (1), 73–81 (9 pages).
Samarghandi, M. R.; Nouri, J.; Mesdaghinia, A. R.; Mahvi, A. H.; Naseri, S.; Vaezi, F., (2007). Efficiency removal of phenol, lead and cadmium by means of UV/TiO2/H2O2 processes. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Tech., 4 (1), 10–25 (16 pages).
Todd, D. K., (1980). Groundwater hydrogeology. John Willey and sons Inc., New York.
Usepa, (2007). Recent recommended water quality criteria. United States Environmental Protection Agency, http://www.epa.gov/waterscience/criteria/wqcriteria.html
Usepa, (2009). National Drinking water standards. United States Environmental Protection Agency,http://www.epa.gov/safewater/
Wang, X.; Zhuo, Q., (2005). Ecotoxicological effects of cadmium on three ornamental plants. Chemosphere, 60 (1), 16–21 (6 pages).
Woodwell, G. M., (1972). A watch on the earth; Man’s home series. United Nations Conference on the Human Environment. Stockholm, Sweden.
Zvinowanda, C. M.; Okonkwo, J. O.; Shabalala, P. N.; Agyei, N. M., (2009). A novel adsorbent for heavy metal remediationin aqueous environments. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Tech., 6 (3), 425–434 (11 pages).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Odukoya, A.M., Abimbola, A.F. Contamination assessment of surface and groundwater within and around two dumpsites. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 7, 367–376 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03326146
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03326146