Abstract
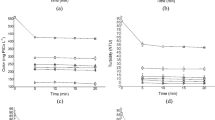
In this study acrylic water base color was removed from synthetic wastewater using coagulation process. Experiments were conducted on the sample containing 100 mg/L and 400 mg/L of acrylic water base color. Destruction of color by means of coagulation/flocculation techniques using ferrous sulfate, alum, lime and polyelectrolyte (cationic, anionic and non ionic). The study was performed in a systematic approach searching optimum values of alum and FeSO4 concentration, pH and temperature. All the experiments were run in a laboratory scale.The obtained results show that treatment with alum and ferrous sulfate alone proved to be very effective in removing the color (> 99 %) and part of COD (60–70 %) from aqueous solution. Lime alone did not significant change on COD and color removal.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anamaria, B. A., (2000). Ultra filtration for color removal of tannery dyeing waste waters. J. Desalination, 130, 147–157.
Anonymous, SAPHA., AWWA., WPCF., (1998). Standard methods for water and wastewater examination, 20th. Ed.
Azbar, N. and Tonar, T., (2004). Comparison of various advanced oxidation processes and chemical treatment methods for COD and color removal from a polyester and acetate fiber dyeing effluent. J. Chemosphere, 55, 35–43.
Costa, A. P., (2004). Bleaching and photo degradation of textile dyes by H2O2 and solar or ultraviolet radiation. J. Solar E., 77, 29–35.
Gallely, A. G. and Forster, E.F., (1979). Treatment of industrial effluent, 154–159.
Georgiou, D., Aivazidis, A., Hatiras, J. and Gimouhopoulos, K., (2003). Treatment of cotton textile wastewater using lime and ferrous sulfate. J. Water Res., 37, 2248–2250.
Georgiou, D., and Melidis, P., (2002). Degradation of azoreactive dyes by ultraviolet radiation in the presence of hydrogen peroxide. J. Dyeand Pigm., 52, 69–78.
Kang, S., (2000). Decolonization of textile waste water by photo-fenton oxidation technology. J. Chemosphere, 41, 1287–1294.
Kardag, A. and Saraydin, D., (1998). Removal of some cationic dyes from aqueous solution by Acrylamid/Itaconic acid hydro gel water, air. Soil Poll., 106, 369.
Konstantinou, I., K., (2004). TiO2-assisted photocatalytic degradation of azo dyes in a queous solution: kinetic and mechanistic investigation. A review J. Appl. Catalysis B: Environmental, 49, 1–14.
Kusvuran, E., (2004). Comparison of several advanced oxidation processes for the decolorization of Reactive Red 120 azo dye in aqueous solution. J. Hazard. Mater., 109, 85–93.
Lin, S, H. and Jiang, C., (2003). Fenton oxidation and sequencing batch reactor (SBR) treatment of high-strength semiconductor waste water. J. Desalinat., 154, 107–116.
Liu, S. and Liang, S., (2000). Return sludge employed in enhancement of color removal in the integrally industrial wastewater treatment Plant. J. Water Res., 38, 103–110.
Marcucc, M. and Nosenzo, G., (2001). Treatment and reuse of textile effluents based on new ultrafiltration and other membrane. J. Desalinat., 138, 75–82.
Pala, A., (2002). Color removal from cotton textile industry waste water in an activated sludge system with various additives. J. Water Res., 36, 2920–2925.
Porter, J. J. and Sinder, E., (1979). Biodegradability of textile chemical, J. WPCF., 48(9), 48–52.
Selcuk, H., (2005). Decolonization and detoxification of textile waste water by ozonation and coagulation processes. J. Dye. Pig., 64, 217–222.
Sostar, S., and Simonic, M., (2000). Waste water treatment after reactive printing, J. Dye. Pig., 24, 147–152.
Sungkpet, A., (2004). Treatment of effluents from textile rinsing, Operations by thermally stable nanofiltration membranes. J. Desalinat., 160, 75–81.
Supalanuttapun, J. K., (2004). Microbial decolorization of reactive azo dyes in a sequential anaerobic-aerobic system. J. Chemical Eng., 99, 169–176.
Sureyya, M., Kaptan, D. and Tugba, O., (2004). Color and COD removal from wastewater containing Reactive Black 5 using fenton's oxidation process. J. Chemosphere, 106, 435–441.
Swaminatan, K., and Sandhya, S., (2003). Decolorizaton and degradation of H-acid and other dyes using ferrous-hydrogen peroxide system, J. Chemosphere, 50, 619–625.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Asilian, H., Moradian fard, S., Rezaei, A. et al. The removal of color and COD from wastewater containing water base color by coagulation process. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 3, 153–157 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03325919
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03325919