Abstract
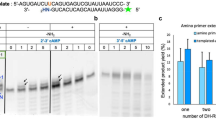
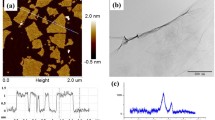
Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is a useful technique for in vitro amplification of a DNA fragment. In this paper, a PCR procedure using Au nanoparticle (AuNP) -bound primers was systemically studied. The 5′-SH-(CH2)6-modified primers were covalently attached to the AuNP surface via Au-S bonds, and plasmid pBluescript SK was used as a template. The effects of the concentration of AuNP-bound primers, annealing temperature and PCR cycles were evaluated, respectively. The results indicate that PCR can proceed successfully under optimized condition, with either forward or reverse primers bound to the AuNP surface or with both the two primers bound to the AuNP surface. Development of PCR procedure based on AuNPs not only makes the isolation of PCR products very convenient, but also provides novel methods to prepare AuNP-bound ssDNA and nanostructured material.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Shen, H. B., Wang, Y. B., Yang, H. F. et al., Covalent immobilization of oligoDNA on the surface of magnetic nanoparticles and surface-enhanced Raman scattering study, Chinese Science Bulletin, 2003, 48(n24): 2698–2702.
Katz, E., Willner, I., Integrated nanoparticle-biomolecule hybrid systems: synthesis, properties, and applications, Angew. Chem., 2004, 43: 6042–6108.
Mirkin, C. A., Letsinger, R. L., Mucic, R. C. et al., A DNA-based method for rationally assembling nanoparticles into macroscopic materials, Nature, 1996, 382(n6592): 607–609.
Alivisatos, A. P., Johnsson, K. P., Peng, X. G. et al., Organization of ‘nanocrystal molecules’ using DNA, Nature, 1996, 382 (6592): 609–611.
Daniel, M. C., Astrucm, D., Gold nanoparticles: assembly, supramolecular chemical, quantum-size-related properties, and applications toward biology, catalysis, and nanotechnology, Chem. Rev., 2004, 104(n1): 293–346.
Glynou, K., Ioannou, P. C., Christopoulos, T. K. et al., Oligonucleotide-functionalized gold nanoparticles as probes in a dry-reagent strip biosensor for DNA analysis by hybridization, Anal. Chem., 2003, 75(n16): 4155–4160.
Naik, R. R., Jones, S. E., Murray, C. J. et al., Peptide templates for nanoparticle synthesis derived from polymerase chain reaction-driven phage display, Advanced Functional Materials, 2004, 14(n1): 25–30.
Holzel, R., Gajovic-Eichelmann, N., Bier, F. F., Oriented and vectorial immobilization of linear M13 dsDNA between interdigitated electrodes-towards single molecule DNA nanostructures, Biosensors and Bioelectronics, 2003, 18 (5-6): 555–564.
Li, H. X., Rothberg, L. J., Label-Free colorimetric detection of specific sequences in genomic DNA amplified by the Polymerase Chain Reaction, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2004, 126(n35): 10958–10961.
Turner, M. S., Penning, S., Sharp, A. et al., Solid-phase amplification for detection of C282Y and H63D hemochromatosis (HFE) gene mutations, Clinical Chemistry, 2001, 47(n8): 1384–1389.
Adessi, C., Matton, G., Ayala, G. et al., Solid phase DNA amplification: characterization of primer attachment and amplification mechanisms, Nucleic Acids Res., 2000, 28: 20e87.
Huber, M., Losert, D., Hiller, R. et al., Detection of single base alterations in genomic DNA by solid phase polymerase chain reaction on oligonucleotide microarrays, Analytical Biochemistry, 2001, 299: 24–30.
Lockley, A. K., Jones, C. G., Bruce, J. S. et al., Colorimetric detection of immobilised PCR products generated on a solid support, Nucleic Acids Res., 1997, 25: 1313–1314.
Frens, G., Controlled nucleation of the regulation of the particle size in monodisperse gold solution, Nat. Phys. Sci., 1973, 241: 20–22.
Nicewarner Pena, S. R., Raina, S., Goodrich, G. P. et al., Hybridization and enzymatic extension of Au nanoparticle-bound oligonucleotides, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2002, 124(n25): 7315–7323.
Poddar, S. K., Symmetric vs asymmetric PCR and molecular beacon probe in the detection of a target gene of adenovirus, Molecular and Cellular Probes, 2000, 14: 25–32.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Shen, H., Hu, M., Yang, Z. et al. Polymerase chain reaction of Au nanoparticle-bound primers. Chin.Sci.Bull. 50, 2016–2020 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03322794
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03322794