Abstract
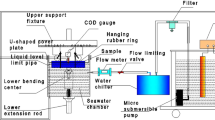
The fatigue strength of a web stiffener corner welded joint of the type found in ships was investigated in synthetic seawater using a steel beam specimen and a small-scale specimen. Both specimens incorporated the same weld detail, representing the end of the web stiffener where fatigue cracking occurs. The beam specimens contained tensile residual stresses of yield strength magnitude and they were fatigue tested at R = 0. Residual stresses were lower in the small-scale specimen, and they were fatigue tested with σmax = σy to establish if this testing technique simulated the effect of high tensile residual stresses. This was confirmed since the results obtained from the two types of test were in good agreement. The automatic detection of fatigue crack initiation was performed with an eddy current type detector. This method was effective even in synthetic seawater. It was found that the fatigue crack initiation, defined as the formation of a 1mm deep crack, occupied 20% of the life in synthetic seawater, compared with only 10% in air. If this is generally the case, it may be possible to reduce the cost of corrosion fatigue tests.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fisher, J.W., Fatigue Strength of Welded A514 Steel Beams, Fatigue of Welded Structures 1, The Welding Institute (1971), 135–148.
Gurney, T.R. and Maddox, S.J., A Re-Analysis of Fatigue Data for Welded Joint in Steel, Welding Research International 3 (1973), 1–54.
Gurney, T.R., Fatigue Design Rules for Welded Steel Joints, Welding Institute Research Bulletin 17 (1976), 115–124.
Ohta, A., Maeda, Y., Mawari, T., Nishijima, S. and Nakamura, H., Fatigue Strength Evaluation of Welded Joints Containing High Tensile Residual Stresses, Int. J. Fatigue 8 (1986), 147–150.
Nakamura, H., Nishijima, S., Ohta, A., Maeda, Y., Uchino, K., Kohno, T., Toyomasu, K., and Soya, I., A Method for Obtaining Conservative S-N Data for Welded Structures, J. Testing & Evaluation 16 (1988), 280–285.
Ohta, A., Maeda, Y., Machida, S. and Yoshinari, H., Fatigue Crack Propagation in Welded Joints under Random Loadings in the Splash Zone, Welding in the World 35 (1995), 391–394.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ohta, A., Maeda, Y. & Suzuki, N. Fatigue Strength of Corner Welded Web Stiffeners Joints in Synthetic Seawater Obtained by σmax = σy Testing. Weld World 47, 25–30 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03266375
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03266375