Abstract
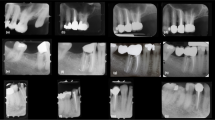
AIM: To compare the efficacy of three caries removal techniques namely: Papacarie®, calcium hydroxide and rotary instruments by SEM analyses of the micro-morphology of residual dentine and resin tags at resin-dentine interface. METHODS: 45 extracted human permanent molar teeth, with occlusal caries extending up to dentine, were divided into two groups (Group 1 and 2) and each group was subdivided into three subgroups: subgroup A included teeth treated with conventional rotary method, subgroup B and C included those treated with calcium hydroxide and Papacarie® respectively. Group 1 samples were prepared for viewing the micro-morphology of residual dentine (2000x and 5000x) and Group 2 samples were filled with composite resin and analysed for resin tag formation (1000x) under SEM. RESULTS: Papacarie® showed minimal smear layer and open dentinal tubules. Calcium hydroxide and rotary instruments showed a typical smear layer and occluded dentinal tubules. Resin tags obtained with Papacarie® were the longest and significantly superior to those obtained with rotary and calcium hydroxide. CONCLUSIONS: Papacarie® exhibited better bonding characteristics of residual dentine than calcium hydroxide and rotary method of caries removal. Thus, Papacarie® is a suitable alternative to conventional method of caries removal, especially in paediatric patients.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andersen M, Lund A, Andreasen JO, Andreasen FM. In vitro solubility of human pulp tissue in calcium hydroxide and sodium hypochlorite. Endodontics and Dent Traumatol 1992; 8:104–108.
Banerjee A, Kidd EAM, Watson TF. Scanning electron microscopic observations of human dentine after mechanical caries excavation. J Dent 2000; 28:179–186.
Beeley JA, Yip HK, Stevenson AG. Chemochemical caries removal: a review of the techniques and latest developments. Br Dent J 2000; 188:427–430.
Bussadori S.K, Castro L.C, Galvao A.C. Papain Gel: A new chemo-mechanical caries removal agent. J Clin Ped Den 2005; 30:115–120.
Bystrom A, Claesson R, Sundqvist G. The antibacterial effect of camphorated paramonochlorophenol, camphorated phenol and calcium hydroxide in the treatment of infected root canals. Endod Dent Traumatol 1985; 1:170–175.
Carrillo CM, Tanaka MH, Cesar MF et al. Use of papain gel in disabled patients. J Dent Child 2008; 75:222–228.
Correa FNP, Rocha RDO, Filho LER, Muench A, Rodrigues CRMD. Chemical vs conventional caries removal techniques in primary teeth: a microhardness study. J Clin Ped Dent 2007a; 31:189–194.
Correa FNP, Filho LER, Rodrigues CRMD. Evaluation of residual dentine after conventional and chemo-mechanical caries removal using SEM. J Clin Ped Dent 2007b; 32:115–120.
Dammaschke T, Eickmeier M, Schafer E, Danesh G, Ott KHR. Effectiveness of Carisolv compared with sodium hypochlorite and calcium hydroxide. Acta Odont Scand 2005; 63:110–114.
Elkholany NR, Abdelaziz KM, Zaghloul NM, Aboulenine N. Chemo-mechanical method: A valuable alternative for caries removal. Dent Update 2002; 9:16–22.
Fava LRG, Saunders WP. Calcium hydroxide pastes: classification and clinical indications. Int Endod J 1999; 32:257–282.
Ferrari M, Grandini S, Simonetti M, Monticelli F, Goracci C. Influence of a microbrush on bonding fiber post into root canals under clinical conditions. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 2002; 94:627–631.
Foreman PC, Barnes F. A review of calcium hydroxide. Int Endod J 1990; 23:283–297.
Ganesh M, Parikh D. Chemo-mechanical caries removal agents: review and clinical application in primary teeth. Journal of Dentistry & Oral Hygiene 2011; 3:34–45.
Hasselgren G, Olsson B, Cvek M. Effects of calcium hydroxide and sodium hypochlorite on the dissolution of necrotic porcine muscle tissue. J Endod 1988; 14:125–127.
Hosoya Y, Shinkawa H, Marshall GW. Influence of Carisolv on resin adhesion for two different adhesive systems to sound human primary dentine and young permanent dentine J Dent 2001; 33:283–291.
Kotb RMS, Abdella AAH, El Kateb MA, Ahmed AM. Clinical evaluation of Papacarie in primary teeth. J Clin Ped Dent 2009; 34:117–123.
Martins MD, Fernandes KPS, Motta LJ et al. Biocompatibility analysis of chemo-mechanical caries removal material Papacarie on cultured fibroblasts and subcutaneous tissue. J Dent Child 2009; 76:123–129.
Pashley DH, Kalathoor S, Burnham D. The effects of calcium hydroxide on dentine permeability. J Dent Res 1986; 65:417–420.
Peric T, Markovic D. In vitro effectiveness of a chemo-mechanical method for caries removal. Eur J Paed Dent 2007; 2:61–67.
Piva E, Ogliari FA, de Moraes RR et al. Papain-based gel for biochemical caries removal: influence on microtensile bond strength to dentin. Braz Oral Res 2008; 22:364–370.
Sivapathasundharam B and Raghu AR. Shafer’s textbook of oral pathology. Ed. 5th Elsevier; 2006: pg 567–658.
Splieth C, Rosin M, Gellissen B. Determination of residual dentine caries after conventional mechanical and chemo-mechanical caries removal with Carisolv. Clin Oral Inves 2001; 5:250–253.
Tonami KI, Araki K, Mataki S, Kurosaki N. Effect of chloramines and sodium hypochlorite on carious dentin. J Med Dent Sci 2003; 50:139–146.
Tronstad L. Root resorption etiology, terminology and clinical manifestations. Endod Dent Traumatol 1988; 4:241–52.
Yazici AR, Atilla P, Ozgunaltay G, Muftuoglu S. In vitro comparison of the efficacy of Carisolv™ and conventional rotary instrument in caries removal. J Oral Rehab 2003; 30:1177–1182.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Arora, R., Goswami, M., Chaudhary, S. et al. Comparative evaluation of effects of chemo-mechanical and conventional caries removal on dentinal morphology and its bonding characteristics — An SEM study. Eur Arch Paediatr Dent 13, 179–184 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03262867
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03262867