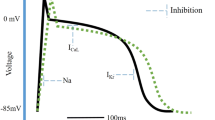
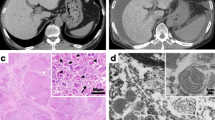
Summary
Amiodarone is an extremely effective antiarrhythmic agent for the treatment of both life-threatening ventricular arrhythmias and refractory supraventricular tachyarrhythmias. Subjective minor side effects are common with amiodarone but rarely require discontinuation of therapy and are often handled by dose reduction. Serious end-organ toxicity, including pulmonry fibrosis and drug-induced hepatitis, have been the most common indications for discontinuing amiodarone therapy in these patients.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Burger A, Dinichett C, Nicod P, Jenny N, LeMarchand BP, et al. Effect of amiodarone on serum triiodothyronine, reverse triiodothyronine, thyroxin and thyrotropin: a drug influencing peripheral metabolism of thyroid hormones. Journal of Clinical Investigation 58: 255–259, 1976
Greene HL, Graham EL, Werner JA, et al. Toxic and therapeutic effects of amiodarone in the treatment of cardiac arrhythmias. Journal of the American College of Cardiology 2: 1114–1128, 1983
Hamer A, Peter T, Mandel WJ, Scheinman MM, Wales D. The potentiation of warfarin anticoagulation by amiodarone and anticoagulant treatment. Circulation 65: 1025–1029, 1982
Harris L, McKenna WJ, Rowland E, Krikler DM. Side effects and possible contraindications of amiodarone use. American Heart Journal 106: 916–921, 1983
Heger JJ, Prystowsky EN, Jackman WM, et al. Amiodarone: clinical efficacy and electrophysiology during long-term therapy for recurrent ventricular tachycardia or ventricular fibrillation. New England Journal of Medicine 305: 539–545, 1981
Heger JJ, Prystowsky EN, Miles WM, Zipes DP. Clinical use and pharmacology of amiodarone. Medical Clinics of America 68: 1339–1366, 1984
Ingram DV. Ocular effects in long-term amiodarone therapy. American Heart Journal 106: 902–940, 1983
Kaplan LJ, Cappaert WE. Amiodarone keratopathy: correlation to dosage and duration. Archives of Ophthalmology 100: 601–620, 1982
Kerin NZ, Blevins RD, Kerner N, Faitel K, Frumin H, et al. A low incidence of proarrhythmia using low-dose amiodarone. Journal of Electrophysiology 2: 289–295, 1988
Magro SA, Lawrence EC, Wheeler SH, Krafchek J, Lin HT, et al. Amiodarone pulmonary toxicity: prospective evaluation of serial pulmonary function tests. Journal of the American College of Cardiology 12: 781–788, 1988
Marchlinski FE, Gansler S, Waxman HL, Josephson ME. Amiodarone pulmonary toxicity. Annals of Internal Medicine 97: 839–845, 1982
Marcus FI. Drug interactions with amiodarone. American Heart Journal 106: 924–929, 1983
Marcus FI, Fontaine GH, Frank R, Grosgogeat Y. Clinical pharmacology and therapeutic applications of the antiarrhythmic drug amiodarone. American Heart Journal 101: 480–493, 1981
Marpinowitz U, Rabinovici J, Goldfarb D, Many A, Bank H. Interaction between warfarin sodium and amiodarone. Correspondence. New England Journal of Medicine 304: 671–672, 1981
Martino E, Safran M, Aghini-Lombardi F, et al. Environmental iodine intake and thyroid dysfunction during chronic amiodarone therapy. Annals of Internal Medicine 101: 28–34, 1984
McGovern B, Garan H, Kelly E, Ruskin JN. Adverse reactions during treatment with amiodarone hydrochloride. British Medical Journal 287: 175–180, 1983
McKenna WJ, Harris L, Rowland E, Whitelaw A, Storey G, et al. Amiodarone therapy during pregnancy. American Journal of Cardiology 51: 1231–1233, 1983
Meier C, Bauer B, Muller U, Ludin HP. Neuropathy during chronic amiodarone therapy. Journal of Neurology 220: 231–239, 1979
Moysey JO, Jaggarao NSV, Grundy EM, Chamberlain DA. Amiodarone increases plasma digoxin concentrations. British Medical Journal 282: 272, 1981
Naccarelli GV, Rinkenberger RL, Dougherty AH, Giebel RA. Amiodarone: pharmacology and antiarrhythmic and adverse effects. Pharmacotherapy 5: 298–313, 1985
Nademanee K, Kannan R, Hendrickson J, Ookhtens M, Kay I, et al. Amiodarone-digoxin interaction: clinical significance, time course of development, potential pharmacokinetic mechanisms and therapeutic implications. Journal of the American College of Cardiology 4: 111–116, 1984
Nademanee K, Singh BN, Hendrickson JA, Reed AW, Melmed S. et al. Pharmacokinetic significance of serum reverse T3 levels during amiodarone treatment: a potential method for monitoring chronic drug therapy. Circulation 62: 202–221, 1982
Poucell S, Ireton J, Valencia-Mayoral P, et al. Amiodarone-associated phospholipidosis and fibrosis of the liver. Gastroenterology 86: 926–936, 1984
Raeder EA, Podrid PJ, Lown B. Side effects and complications of amiodarone therapy. American Heart Journal 109: 975–983, 1985
Rakita L, Sobol SM, Mostow N, Vrobel T. Amiodarone pulmonary toxicity. American Heart Journal 106: 906–914, 1983
Rees A, Dalal JJ, Reid PG, Henderson AH. Dangers of amiodarone and anticoagulant treatment. British Medical Journal 282: 1756–1757, 1981
Rinkenberger RL, Prystowsky EN, Jackman WM, Naccarelli GV, Heger JJ, et al. Drug conversion of nonsustained to sustained ventricular tachycardia during serial electrophysiologic studies: identification of drugs that exacerbate tachycardia and potential mechanisms. American Heart Journal 103: 177–184, 1982
Rosenbaum MB, Chiale PA, Haedo A, Lazzari JO, Elizari MV. Ten years of experience with amiodarone. American Heart Journal 106: 957–964, 1983
Rotmensch HH, Belhassen B, Swanson BN, et al. Steady-state serum amiodarone concentrations: relationships with antiarrhythmic efficacy and toxicity. Annals of Internal Medicine 101: 462–469, 1984
Saal AK, Warner JA, Greene HL, Sears GK, Graham EL. Effect of amiodarone on serum quinidine and procainamide levels. American Journal of Cardiology 53: 1264–1267, 1984
Sanmarti A, Permanyer-Miralda G, Castellanos JM, Fos-Sala M, Galard RM, et al. Chronic administration of amiodarone and thyroid function: a follow-up study. American Heart Journal 108: 1262–1268, 1984
Sclarovsky S, Lewin RF, Kracoff O, Strasberg B, Arditta A, et al. Amiodarone-induced polymorphous ventricular tachycardia. American Heart Journal 105: 6–12, 1983
Shea P, Lal R, Kim SS, Schechtman K, Ruffy R. Flecainide and amiodarone interaction. Journal of the American College of Cardiology 7: 1127–1130, 1986
Simon JB, Manley PN, Brien JF, Armstrong PW. Amiodarone hepatotoxicity simulating alcoholic liver disease. New England Journal of Medicine 311: 167–172, 1984
Singh BN, Nademanee K. Amiodarone and thyroid function: clinical implications during antiarrhythmic therapy. American Heart Journal 106: 857–868, 1983
Soussi A, Colonna D. Troubles du rythme auriculaire et amiodarone. Journal des Agreges 7: 43, 1974
Tartini R, Kappenberger L, Steinbrunn W, Mayer UA. Dangerous interactions between amiodarone and quinidine. Lancet 1: 1327–1330, 1982
Van Roojj WJ, Van der Meer SC, Van Rayen EA, Van Zandwijk N, Darmanata JI. Pulmonary gallium-67 uptake in amiodarone pneumonitis. Journal of Nuclear Medicine 25: 211–213, 1984
Vos AK, Van Ramstrost AGS, Grosfeld JCM, Goossens JP. A peculiar cutaneous pigmentation from Cordarone. Dermatologica 145: 297–303, 1972
Westveer DC, Gadowski GA, Gordon S, Timmis GC. Amiodarone-induced ventricular tachycardia. Annals of Internal Medicine 97: 561–562, 1982
Wilson FM, Schmitt TE, Grayson M. Amiodarone-induced cornea verticillata. Annals of Ophthalmology 12: 657–660, 1980
Zipes DP, Prystowsky EN, Heger JJ. Amiodarone: electrophysiologic actions, pharmacokinetic and clinical effects. Journal of the American College of Cardiology 3: 1059–1071, 1984
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Naccarelli, G.V., Rinkenberger, R.L., Dougherty, A.H. et al. Adverse Effects of Amiodarone. Med Toxicol Adverse Drug Exp 4, 246–253 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03259911
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03259911