Summary
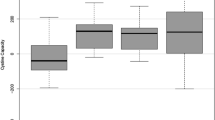
Mesna, the sodium salt of 2-mercaptoethanesulphonic acid (MES), is a uroprotective agent used to prevent oxazaphosphorine-induced haemorrhagic cystitis during cancer chemotherapy. Oral administration of mesna is frequently associated with nausea and vomiting secondary to its unpleasant taste. Argimesna, a newly synthesised salt of MES in which sodium is replaced by arginine, has not been associated with similar adverse effects. In this study, the urinary excretion of the two salts of MES was compared after oral administration of either mesna 800mg or argimesna 1800mg (equivalent to 920mg of mesna). The 2 drugs exhibited almost identical urinary excretion patterns. Percentage recoveries 12 hours after drug administration were 14.8 and 13.2% of the dose for mesna and argimesna, respectively. Maximum urinary concentrations of free thiols were observed with both drugs during the 0- to 4-hour urine collection, and were 3.9 mmol/L for mesna and 3.3 mmol/L for argimesna. Since 0.61 mmol/L is considered the minimum free thiol concentration required to confer uroprotection, it is concluded that argimesna ensures a uroprotective activity equivalent to that of mesna and may be advantageously substituted for mesna in oral therapeutic regimens.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Burkert H. Clinical overview of mesna. Cancer Treatment Reviews 10 (Suppl. A): 175–181, 1983
Burkert H, Lucker PW, Wetzelsberger N, Breuel HP. Bioavailability of orally administered mesna. Arzneimittel-Forschung 34: 1597–1600, 1984
Dechant KL, Brogden RN, Pilkington T, Faulds D. Ifosfamide/mesna: a review. Drugs 42: 428–467, 1991
Hilgard P, Pohl J. Oxazaphosphorine toxicity reduction by mesna. Cancer Treatment Reviews 17: 217–220, 1990
James CA, Mant TG, Rogers HJ. Pharmacokinetics of intravenous and oral sodium 2-mercaptoethanesulfonate (mesna) in normal subjects. British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 23: 561–568, 1987
Ormstad K, Orrenius S, Lastborn T, Uehara N, Pohl J, et al. Pharmacokinetics and metabolism of sodium 2-mercaptoethanesulfonate in the rat. Cancer Research 43: 333–338, 1983
Shaw IC, Graham MI. Mesna — a short review. Cancer Treatment Reviews 14: 67–86, 1987
Stekar J. Photometric determination of mesna and dimesna in blood plasma and urine. Das Ärztliche Laboratorium 28: 187–191, 1982
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Miglioli, P.A., Pea, F., Mazzo, M. et al. A Comparative Analysis of the Urinary Excretion Profiles of Mesna and Argimesna Following Oral Administration to Healthy Volunteers. Drug Invest 4, 391–394 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03258416
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03258416