Abstract
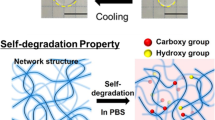
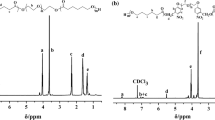
Several kinds of biodegradable hydrogels were prepared viain situ photopolymerization of Pluronic F127/poly(ε-caprolactone) macromer and acrylic acid (AA) comonomer in aqueous medium. The swelling kinetics measurements showed that the resultant hydrogels exhibited both thermo- and pH-sensitive behaviors, and that this stimuli-responsiveness underwent a fast reversible process. With increasing pH of the local buffer solutions, the pH sensitivity of the hydrogels was increased, while the temperature sensitivity was decreased.In vitro hydrolytic degradation in the buffer solution (pH 7.4, 37 °C), the degradation rate of the hydrogels was greatly improved due to the introduction of the AA comonomer. Thein vitro release profiles of bovine serum albumin (BSA)in-situ embedded into the hydrogels were also investigated: the release mechanism of BSA based on the Peppas equation was followed Case II diffusion. Such biodegradable dual-sensitive hydrogel materials may have more advantages as a potentially interesting platform for smart drug delivery carriers and tissue engineering scaffolds.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. Shinji, O. Masayuki, and I. Isao,Macromolecules,40, 3394 (2007).
D. T. Pual, R. H. Jonathan, J. C. Colin, P. A. Steven, A. L. J. Richard, and J. R. Anthony,Macromolecules,40, 4393 (2007).
T. Tanaka, I. Nishio, S. T. Sun, and S. Ueno-Nishio,Science,218, 467 (1982).
S. P. Jin, M. Z. Liu, F. Zhang, S. L. Chen, and A. Z. Niu,Polymer,47, 1526 (2006).
M. Akira, Y. Ryo, and K. Kazunori,Biomacromolecules,5, 1038 (2004).
Y. H. Bae, T. Okano, R. Hsu, and S. W. Kim,Macromol. Chem. Rapid Commun.,8, 481 (1987).
K. S. Soppimath, L. H. Liu, W. Y. Seow, S. Q. Liu, R. Powell, P. Chan, and Y. Y. Yang,Adv. Funct. Mater.,17, 355 (2007).
W. S. Shim, J. S. Yoo, Y. H. Bae, and D. S. Lee,Biomacromolecules,6, 2930 (2005).
J. M. Suh, S. J. Bae, and B. Jeong,Adv. Mater.,17, 118 (2005).
M. R. Guilherme, R. Silva, E. M. Girotto, A. F. Rubira, and E. C. Muniz,Polymer,44, 4213 (2003).
L. D. Taylor and L. D. Cerankowski,J. Polym. Sci. Part A: Polym. Chem.,13, 2551 (1975).
H. Chen and Y. L. Hsieh,J. Polym. Sci. Part A: Polym. Chem.,42, 6331 (2004).
X. Z. Zhang, Y. Y. Yang, F. J. Wang, and T. S. Chung,Langmuir,18, 2013 (2002).
R. Silva and M. G. Oliveira,Polymer,48, 4114 (2007).
H. Tanii and K. Hashimoto,Archives of Toxicology,54, 203 (1983).
Y. Qiu and K. Park,Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev.,53, 321 (2001).
J. T. Zhang, S. W. Huang, S. X. Cheng, and R. X. Zhuo,J. Polym. Sci. Part A: Polym. Chem.,42, 1249 (2004).
X. J. Loh, S. H. Goh, and J. Li,Biomacromolecules,8, 585 (2007).
X. J. Loh, S. H. Goh, and J. Li,Biomaterials,28, 4113 (2007).
J. C. Ha, S. Y. Kim, and Y. M. Lee,J. Control. Rel.,62, 381 (1999).
P. Chandaroy, A. Sen, and S. W. Hui,J. Control. Rel.,76, 27 (2001).
J. H. Ha, S. H. Kim, S. Y. Han, Y. K. Sung, Y. M. Lee, I. K. Kang, and C. S. Cho,J. Control. Rel.,49, 253 (1997).
S. C. Woodward, P. S. Brewer, F. Moatamed, A. Schindler, and C. G. Pitt,J. Biomed. Mater. Res.,19, 437 (1985).
S. P. Zhao, L. M. Zhang, D. Ma, C. Yang, and L. Yan,J. Phys. Chem. B,110, 16503 (2006).
S. S. Kim, Y. M. Lee, and C. S. Cho,Polymer,36, 4497 (1995).
E. Kokufuta, B. Wang, R. Yoshida, A. R. Khokhlov, and M. Hirata,Macromolecules,31, 6878 (1998).
G. H. Chen and A. S. Hoffman,Nature,373, 49 (1995).
S. Beltran, J. P. Bakai, H. H. Hooper, H. W. Blanch, and M. Prausnitz,Macromolecules,24, 549 (1991).
P. L. Rigter and N. A. Peppas,J. Control. Rel.,5, 37 (1987).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, S., Cao, M., Wu, J. et al. Synthesis and characterization of biodegradable thermo- and pH-sensitive hydrogels based on pluronic F127/poly(ε-caprolactone) macromer and acrylic acid. Macromol. Res. 17, 1025–1031 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03218652
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03218652