Summary
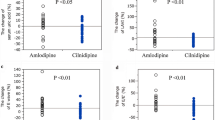
The renal, metabolic and antihypertensive effects of enalapril (E) and slow-release verapamil (V) were compared in a 2-month double-blind crossover trial in 22 patients with newly discovered essential hypertension. The glomerular filtration rate and renal vascular resistance were unaltered; renal blood flow was slightly decreased by V. Serum Ca2+ increased and Na+ excretion declined after V. Serum lipids, glucose, and erythrocyte electrolytes were unchanged. Blood pressure (BP) was lower with E after half the maximum dosage compared with V, but similar BP reductions were obtained after 2 months with the maximum dosage.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fagher, B., Henningsen, N., Hulthén, L. et al. Antihypertensive and renal effects of enalapril and slow-release verapamil in essential hypertension. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 39 (Suppl 1), S41–S43 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03216275
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03216275