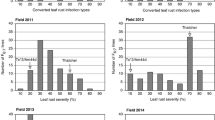
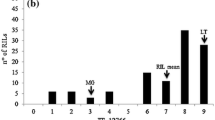
Abstract
Quantitative resistance ofSalix toMelampsora larici-epitea leaf rust was studied in 2Salix mapping populations. One population was a backcross between aS. schwerinii ×S. viminalis hybrid andS. viminalis, and the other was an F2 population betweenS. viminalis andS. dasyclados. A leaf disc bioassay was used to study the components of quantitative resistance (latent period, uredinia number, and uredinia size) to 3 isolates of the leaf rust. The analysis of quantitative trait loci (QTLs) revealed 9 genomic regions in the backcross population and 7 genomic regions in the F2 population that were important for rust resistance, with QTLs explaining 8–26% of the phenotypic variation. An important genomic region was identified for the backcross population in linkage group 2, where QTLs were identified for all resistance components for 2 of the rust isolates. Four of the QTLs had overlapping mapping intervals, demonstrating a common genetic background for latent period, uredinia diameter, and uredinia number. QTLs specific to some rust isolates and to some resistance components were also found, indicating a combination of common and specific mechanisms involved in the various resistance components. Breeding implications in relation to these findings are discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Åhman I, Larsson S, 1999. Resistensförädling iSalix för energiproduktion. Växtskyddsnotiser 2: 17–19.
Åhman I, Bertholdsson N-O, 2001. Biomass willow cultivars and local variation in attacks by herbivores and rust. Asp Appl Biol 65: 205–214.
Basten CJ, Weir BS, Zeng Z-B, 2001. QTL Cartographer, Version 1.15. Department of Statistics, North Carolina State University, Raleigh, NC.
Beavis WD, 1994. The power and deceit of QTL experiments: lessons from comparative studies. Proceedings of the 49th Annual Corn And Sorghum Industry Research Conference, Chicago, IL: 250–266.
Dowkiw A, Husson C, Frey P, Pinon J, Bastien C, 2003. Partialresistance toMelampsora larici-populina leaf rust in hybrid poplars: Genetic variability in inoculated excised leaf disk bioassay and relationship with complete resistance. Phytopathology 93: 421–427.
Dowkiw A, Bastien C, 2004. Characterization of two major genetic factors controlling quantitative resistance toMelampsora larici-populina leaf rust in hybrid poplars: strain specificity, field expression, combined effects, and relationship with a defeated qualitative resistance gene. Phytopathology 94: 1358–1367.
Dowkiw A, Bastien C, 2007. Presence of defeated qualitative resistance genes frequently has a major impact on quantitative resistance toMelampsora larici-populina leaf rust inP. interamericana hybrid poplars. Tree Genetics and Genomes 3: 261–274.
Grattapaglia D, Sederoff R, 1994. Genetic linkage maps ofEucalyptus grandis andEucalyptus urophylla using a pseudo-testcross: mapping strategy and RAPD markers. Genetics 137: 1121–1137.
Jorge V, Dowkiw A, Faivre-Rampant P, Bastien C, 2005. Genetic architecture of qualitative and quantitativeMelampsora larici-populina leaf rust resistance in hybrid poplar: genetic mapping and QTL detection. New Phytol 167: 113–127.
Larsson S, 1998. Genetic improvement of willow for the short-rotation coppice. Biomass and Bioenergy 15: 23–26.
Lascoux M, Ramstedth M, Åström B, Gullberg U 1996. Components of resistance of leaf rust (Melampsora laricii-epitea Kleb./Melampsora ribesii-viminalis Kleb.) inSalix viminalis L. Theor Appl Genet 93: 1310–1318.
Lefèvre F, Pichot C, Pinon J, 1994. Intra- and interspecific inheritance of some components of the resistance to leaf rust (Melampsora larici-epitea Kleb.) in poplars. Theor Appl Genet 88: 501–507.
Lefèvre F, Goué-Mourier MC, Faivre-Rampant P, Villar M, 1998. A single gene cluster controls incompatibility and partial resistance to variousMelampsora larici-populina races in hybrid poplars. Phytopathology 88: 156–163.
Legionnet A, Muranty H, Lefèvre F, 1999. Genetic variation of the riparian tree speciesPopulus nigra. II. Variation in susceptibility to the foliar rustMelampsora larici-populina. Heredity 82: 318–327.
McCracken AR, Dawson M, 1994. Effect ofMelampsora rust on the growth and development ofSalix burjatica ‘Korso’ in Northern Ireland. European Journal of Forest Pathology 24: 32–39.
McCracken AR, Dawson M, 1998. Short rotation coppice willow in Northern Ireland since 1973: development of the use of mixtures in the control of foliar rust (Melampsora spp.). Eur J Forest Pathol 28: 241–250.
McCracken AR, Dawson M, 2003. Rust disease (Melampsora epitea) of willow (Salix spp.) grown as short rotation coppice (SRC) in inter- and intra-species mixtures. Ann Appl Biol 143: 381–393.
McDonald BA, Linde C, 2002. Pathogen population genetics, evolutionary potential and durable resistance. Annu Rev Phytopathol 40: 349–79.
Newcombe G, 1998. Association ofMmd1, a major gene for resistance toMelampsora medusae f. sp.deltoidae, with quantitative traits in poplar rust. Phytopathology 88: 114–121.
Pei MH, Royle DJ, Hunter T, 1996. Pathogen specialisation inMelampsora epitea var.epitea onSalix. Plant Pathol 45: 679–690.
Pei MH, Yuan ZW, Hunter T, Ruiz C, 2000. Heterogeneous nature of a ‘new’ pathotype ofMelampsora rust onSalix, revealed by AFLP. Eur J Plant Pathol 106: 771–779.
Pinon J, van Dam BC, Genetet I, de Kam M, 1987. Two pathogenic races ofMelampsora larici-populina in north-western Europe. Eur J Forest Pathol 17: 47–53.
Pinon J, Frey P, 2005. Interactions between poplar clones andMelampsora populations and their implications for breeding for durable resistance. In: Pei M, McCracken AR, eds. Rust Diseases on Willow and Poplar. Wallingford UK: CAB International: 139–154.
Rönnberg-Wästljung AC, Gunnerbeck E, 1985. Infektionsmönster och värdväxtskillnader vid Melampsora-angrepp i Salixodlingar. [Infection patterns and host differences inMelampsora attacks onSalix plantations]. Report 38. Dept. of Ecology and Environmental Sciences, Swedish University of Agricultural Sciences.
Rönnberg-Wästljung A, Thorsén J, 1988. Inter- and intraspecific variation and genotype site interaction inSalix alba L.,S. dasyclados Wimm. andS. viminalis L. Scand J Forest Res 3: 449–463.
Rönnberg-Wästljung AC, Gullberg U, 1999. Genetics of breeding characters with possible effects on biomass production inSalix viminalis (L.). Theor Appl Genet 98: 531–540.
Rönnberg-Wästljung AC, Tsarouhas V, Semerikov V, Lagercrantz U, 2003. A genetic linkage map of a tetraploidSalix viminalis andS. dasyclados hybrid based on AFLP markers. Forest Genet 10: 185–194.
Rönnberg-Wästljung AC, Åhman I, Glynn C, Widenfalk O, 2006. Quantitative trait loci for resistance to herbivores in willow: field experiments with varying soils and climates. Entomol Exp Appl 118: 163–174.
Samils B, Stepien V, Lagercrantz U, Lascoux M, Gullberg U, 2001. Genetic diversity in relation to sexual and asexual reproduction in populations ofMelampsora larici-epitea. Eur J Plant Pathol 107: 871–881.
Tsarouhas V, Gullberg U, Lagercrantz U, 2002. An AFLP and RFLP linkage map and quantitative trait loci (QTL) analysis of growth traits inSalix. Theor Appli Genet 105: 277–288.
Vos P, Hogers R, Bleeker M, Reijans M, van de Lee T, Hornes M, et al. 1995. AFLP: a new technique for DNA fingerprinting. Nucl Acids Res 23: 4407–4414.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rönnberg-Wästljung, AC., Samils, B., Tsarouhas, V. et al. Resistance toMelampsora larici-epitea leaf rust inSalix: analyses of quantitative trait loci. J Appl Genet 49, 321–331 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03195630
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03195630