Abstract
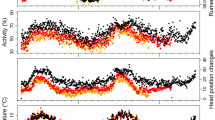
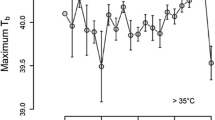
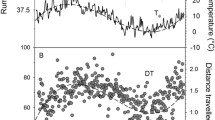
Microtine species are known to have an ultradian pattern of activity. Earlier study suggested that period of activity oscillations decreased after magnification of the average energy expenditure. Moreover, the lack of daily variation in nonshivering thermogenesis capacity suggests that the level of metabolic rate (MR) depends mainly on animal activity. Thus, (1) one could expect that ultradian oscillations of MR and activity were similarly dependent on the average level of energy expenditure. Moreover, I expected that animals at lower ambient temperature (Ta) should minimize their energy expenditure and the time of exposure to low Ta outside the nest. Thus (2) their mean activity near a feeder does not increase together with average level of energy expenditure. I tested these hypotheses using root voles Microtus oeconomus Pallas, 1776 acclimated to Ta of 20°C (12L∶12D). The MR and activity both inside (An) and outside the nest (Af), were measured continuously at Ta of 10 and 20°C. Average oxygen consumption differed between Tas. The period of MR and Af rhythm was shorter at lower Ta, but the period of An did not differ significantly. The level of energy expenditure did not affect mean Af. Close correlation between MR and Af length period suggests that oscillations of MR during the day are affected by activity related to feeding, rather than low cost An.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Curran-Everett D. 2000. Multiple comparisons: philosophies and illustrations. American Journal of Physiology 279: R1-R8.
Daan S. 1981. Adaptive daily strategies in behavior. [In: Handbook of behavioural neurobiology 4, Biological rhythms. J. Aschoff, ed]. Plenum Press, New York: 275–298.
Daan S. and Aschoff J. 1981. Short-term rhythm in activity. [In: Handbook of behavioural neurobiology 4, Biological rhythms. J. Aschoff, ed]. Plenum Press, New York: 491–498.
Daan S. and Slopsema S. 1978. Short-term rhythms in foraging behaviour of the common vole,Microtus arvalis. Journal of Comparative Physiology A 127: 215–227.
Gębczyńska Z. 1970. Bioenergetics of root vole population. Acta Theriologica 15: 33–66.
Gębczyński A. K. and Taylor J. R. E. 2004. Daily variation of body temperature, locomotor activity and maximum nonshivering thermogenesis in two species of small rodents. Journal of Thermal Biology 29: 123–131.
Gerkema M. P. and van der Leest F. 1991. Ongoing ultradian activity rhythm in the common vole, Microtus arvalis, during deprivation of food, water and rest. Journal of Comparative Physiology A 168: 591–597.
Gerkema M. P. and Daan S. 1985. Ultradian rhythms in behavior: the case of the common vole (Microtus arvalis). Experimental Brain Research, Supplement 12: 11–31.
Gerkema M. P., Groos G. A. and Daan S. 1990. Differential elimination of circadian and ultradian rhythmicity by hypothalamic lesion in the common vole,Microtus arvalis. Journal of Biological Rhythms 5:81–955.
Grodziński W. 1962. Influence of food upon the diurnal activity of small rodents. Proceedings of Symposium Theriologicum, Praha: 134–139.
Halle S. 1995a. Diel pattern of locomotor activity in populations of root voles,Microtus oeconomus. Journal of Biological Rhythms 10: 211–224.
Halle S. 1995b. Effect of extrinsic factors on activity of root voles,Microtus oeconomus. Journal of Mammalogy 76: 88–99.
Halle S. 2000. Voles — small graminivores with polyphasic patterns. Ecological Studies 141: 191–215.
Halle S. and Stenseth N. C. 1994. Microtine ultradian rhythm of activity: an evaluation of different hypotheses on the triggering mechanism. Mammal Review 24: 17–39.
Hansson L. 1971. Small rodent food, feeding and population dynamics. Oikos 22: 183–198.
Hatfield D. M. 1940. Activity and food consumption inMicrotus andPeromyscus. Journal of Mammalogy 21: 29–36.
Hill R. W. 1972. Determination of oxygen consumption by use of paramagnetic oxygen analyzer. Journal of Applied Physiology 33: 261–263.
Hoogenboom I., Daan S., Dallinga J. H. and Schoenmakers M. 1984. Seasonal change in the daily timing of behaviour of the common vole,Microtus arvalis. Oecologia 44: 403–409.
Karulin B. E., Litwin B. Yu., Nikitina N. A., Chlap L. A. and Ochotskij Yu. B. 1976. A study of activity, mobility and diurnal range inMicrotus oeconomus on the Yamal peninsula by means of marking with radioactive cobalt. Zoolgicheskii Zhurnal 55: 1052–1059. [In Russian with English summary]
Lehmann U. 1976. Short-term and circadian rhythms in the behaviour in the vole,Microtus agrestis (L.). Oecologia 32: 185–199.
Lehmann U. and Sommersberg C. W. 1980. Activity patterns of the common vole,Microtus arvalis — automatic recordings of behaviour in an enclosure. Oecologia 47: 61–75.
Madison D. M. 1981. Time patterning of nest visitation by lactating meadow voles. Journal of Mammalogy 62: 389–391.
McNab B. K. 1992. The comparative energetics of rigid endothermy: the arvicolidae. Journal of Zoology, London 227: 585–606.
Meerlo P., Bolle L., Viser G. H., Masman D. and Daan S. 1997. Basal metabolic rate in relation to body composition and daily energy expenditure in the field vole,Microtus agrestis. Physiological Zoology 70: 362–369.
Ruf T. 1999. The Lomb-Scargle periodogram in biological rhythm research: analysis of incomplete and unequally spaced time-series. Biological Rhythm Research 30: 178–201.
Schibler U., Ripperger J. and Brown S. A. 2003. Peripheral circadian oscillators in mammals: time and food. Journal of Biological Rhythms 18: 250–260.
Stephan F. K. 1992. Resetting of the feeding-entrainable circadian clock in the rat. Physiology and Behavior 52: 985–995.
Stephan F. K. 2002. The “other” circadian system: food as a zeitgeber. Journal of Biological Rhythms 17: 284–292.
Tavernier R., Largen A. and Bult-Ito A. 2004. Circadian organization of a subarctic rodent, the northern red-backed vole (Clethrionomys rutilus). Journal of Biological Rhythms 19: 238–247.
Van der Zee E. A., Jansen K. and Gerkema M. P. 2000. The suprachiasmatic nucleus in organotypic slice cultures of the common vole (Microtus arvalis). Comparison of development with rat and hamster and the effect of age. Journal of Biological Rhythms 15: 37–47.
Wang D.-H. and Wang Z.-W. 2000. Metabolism and thermoregulation in root voles (Microtus oeconomus) from the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Zeitschrift für Säugetierkunde 65: 15–20.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Associate Editor was Magdalena Niedziałkowska.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gębczyński, A.K. Patterns of ultradian rhythms of activity and metabolic rate in relation to average daily energy expenditure in root voles. Acta Theriol 51, 345–352 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03195181
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03195181