Abstract
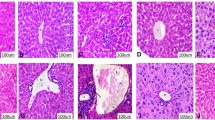
Inhibitory effects of food additives on toxicity induced by aflatoxin B1 was conducted in 3-day-old ducklings. Aflatoxin B1 at a dose of 5 μg/day per animal for 14 days induced severe liver damage which included necrosis, fatty changes, and biliary hyperplasia. These changes were found to be inhibited by the daily administration of turmeric (50mg), curcumin (10 mg), and ellagic acid (10 mg) in the diet. Addition of BHA-butylated hydroxy anisole (10 mg), BHT-butylated hydroxy toluene (10 mg), garlic (500 mg), and asafoetida (50 mg) inhibited necrosis and degeneration of the tissue, while biliary hyperplasia persisted. Biochemical and haematological parameters were not significantly altered under the conditions studied.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Robinson P (1967) Infantile cirrhosis of the liver in India with special reference to probable aflatoxin etiology. Clin Pediatr 6: 57–62
Becroft DMO, Webster DR (1972) Aflatoxin and Rye’s syndrome. Br Med J 114–117
Essigman JM, Croy RG, Bennet RA, and Wogan GN (1982) Metabolic activation of Aflatoxin B1: Pattern of DNA adduct formation, removal and excretion in relation to carcinogenesis. Drug Metabol Rev 13: 581–602
Swenson DH, Miller EC, and Miller JA (1974) Aflatoxin B1 2, 3 — epoxide: evidence for its formation in rat liver in vivo and by human liver microsomes in vitro. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 60: 1036–1043
Mandai S, Ahuya A, Shivapurkar NM, Cheng S-J, Groopman JD, and Stoner GD (1987) Inhibition of aflatoxin B1 mutagenesis in Salmonella typhimurium and DNA damage in cultured rat and human tracheobronchial tissues by ellagic acid. Carcinogenesis 8: 1651–1656
Francis AR, Shetty TK, and Bhattacharya RK (1989) Modifying role of dietary factors on the mutagenicity of Aflatoxin B1; in vitro effect of plant flavanoids. Mutat Res 222: 393–401
Unnikrishnan MC and Kuttan R (1990) Tumour reducing and anti-carcinogenic activity of selected spices. Cancer Letters 51: 85–89
Determination of haemoglobin by cyanmethaemoglobin method (1980)In: Practical Clinical Biochemistry, 5th edn; Varley H, Gowenlock AH, and Bell M (eds): William Heinemann Medical Books, Ltd, London 1, 979
Bergmeyer HU and Bernt E (1980) Colorimetric method for aspartate and alanine amino transferases.In: Practical Clinical Biochemistry, 5th edn; Varley H, Gowenlock AH, and Bell M (eds). William Heinemann Medical Books, Ltd, London 1, 741–742
King EJ and Amstrong AR (1980) Method of King and Armstrong.In: Practical Clinical Biochemistry, 5th edn, Varley H, Gowenlock AH, and Bell M (eds). William Heinemann Medical Books, Ltd, London 1, 897–899
Bishayee A, Balasubramanian AS (1971) Lipid peroxide in rat brain. J Neurochem 18:909–920
Bhattacharya RK, Firozi PF, and Aboobacker VS (1984) Factors modulating the formation of DNA adduct by Aflatoxin B1 in vitro. Carcinogen 5: 1359–1362
Soudamini KK and Kuttan R (1988) Cytotoxic and tumour reducing properties of curcumin. Indian J Pharmacol 20: 95–101
Firozi PF, Aboobaker VS, and Bhattacharya RK (1986) Modulation by dertain factors of metabolic activation of aflatoxin B1 as detected in vitro in a simple fluorimetric assay. Chem Biol Interact 58: 173–184
Williams GM, Tanaka T, and Maccura Y (1986) Dose — related inhibition of aflatoxin B1 induced hepatocarcinogenesis by the phenolic antioxidants, butylated hydroxy anisole, and butylated hydroxy toluene. Carcinogen 7: 1043–1050
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Soni, K.B., Rajan, A. & Kuttan, R. Inhibition of aflatoxin-induced liver damage in ducklings by food additives. Mycotox Res 9, 22–26 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03192228
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03192228