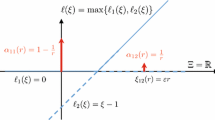
Abstract
We present a new methodology for the calibration of the Hull-White model to US market prices with consistent curves. It falls into the general class of nonlinear multicriteria optimization problems and we show how this algorithm is able to build a set of dicrete Pareto points of the implied trade-off curve. We also evaluate its fitting capabilities against non-consistent traditional methods with very promising results.
Resumen
El objetivo de este trabajo es la presentación de una nueva metodología para la calibración del modelo de Hull-White mediante el empleo de curvas consistentes, y tomando como datos empíricos los precios del mercado norteamericano. La base de nuestra propuesta está basada en el empleo de una clase de problemas de optimización multicriterio no lineales. Comparamos además, la capacidad de ajuste del algoritmo frente a los métodos tradicionales, basados en el uso de curvas no consistentes, obteniendo unos resultados que avalan la eficiencia de la metodología propuesta.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Angelini, F. and Herzel, S., (2002). Consistent Initial Curves for Interest Rate Models, Journal of Derivatives, 9(4), 8–18.
Angelini, F. and Herzel, S., (2005). Consistent Calibration of HJM Models to Cap Implied Volatilities, Journal of Future Markets, 25, 1093–1120.
BIS. Zero-coupon yield curves: Technical documentation, BIS Papers, 25. Bank for International Settlements, Basle, October 2005.
Björk, T., (2001). A Geometric View of Interest Rate Theory, in: Jouini, E., Cvitanic, J. and Musiela, M., Option Pricing, Interest Rates and Risk Management, Cambridge University Press.
Björk, T., (2003). On the Geometry of Interest Rate Models, in: Carmona, R. A., Cinlar, E., Ekeland, I., Jouini, E., Scheinkman, J. A. and Touzi, N., Paris-Princeton Lectures on Mathematical Finance 2003, Lecture Notes in Mathematics, 1847, Springer-Verlag.
Björk, T., (2004). Arbitrage Theory in Continuous Time, Second Edition, Oxford.
Björk, T. and Christensen, B. J., (1999). Interest Rate Dynamics and Consistent Forward Rate Curves, Math. Finance, 9, 323–348.
Björk, T. and Landen, C., (2002). On the construction of finite dimensional realizations for nonlinear forward rate models, Finance Stoch., 6(3), 303–331.
Black, F., (1976). The Pricing of Commodity Contracts, Journal of Financial Economics3, 167–179.
Black, F. and Karasinski, P., (1991). Bond and Option Pricing when Short Rates are Lognormal, Financial Analysts Journal, 4, 52–59. 127–155.
Buraschi, A. and Corielli, F., (2005). Risk Management Implications of Time-Inconsistency: Model Updating and Recalibration of No-Arbitrage Models. Journal of Banking and Finance, 29, 2883–2907.
Das, I. and Dennis, J. E., (1998). Normal-Boundary Intersection: A New Method for Generating the Pareto Surface in Nonlinear Multicriteria Optimization Problems, SIAM J. Optim., 8(3), 631–657.
De Rossi, G., (2004). Kalman Filtering of Consistent Forward Rate Curves: a Tool to Estimate and Model Dynamically the Term Structure, Journal of Empirical Finance, 11, 277–308.
Eschenauer, H., Koski, J. and Osyczka, A., (1990). Multicriteria Design Optimization, Springer.
Filipovic, D., (1999). A Note on the Nelson and Siegel Family. Math. Finance, 9(4), 349–359.
Heath, D. C., Jarrow, R. and Morton, A., (1992). Bond Pricing and the Term Structure of Interest Rates: A New Methodology for Contingent Claims Valuation, Econometrica, 60(1), 77–105.
Ho, T. S. Y. and Lee, S. B., (1986). Term Structure Movements and the Pricing of Interest Rate Contingent Claims. Journal of Financial and Quantitative Analysis41, 1011–1029.
Hull, J. and White, A., (1990). Pricing Interest Rate Derivatives Securities. The Review of Financial Studies, 3(4), 573–592.
Kloeden, P. E. and Platen, E., (1999). Numerical solution of stochastic differential equations, Springer-Verlag.
Musiela, M., (1993) Stochastic PDEs and term structure models. Working Paper, J. Intern. Finance, IGR-AFFI, La Baule.
Nelson, C. R. and Siegel, A. F., (1987). Parsimonious Modelling of Yield Curves. Journal of Business, 60(4), 473–489.
Vasicek, O., (1977). An Equilibrium Characterization of the Term Structure. Journal of Financial Economics, 5, 177–188.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Falcó, A., Navarro, L. & Nave, J. The Hull-White model and multiobjective calibration with consistent curves: empirical evidence. Rev. R. Acad. Cien. Serie A. Mat. 103, 235–249 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03191944
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03191944