Abstract
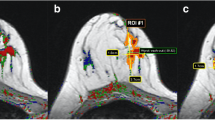
For the diagnosis of breast cancer using magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), one of the most important parameters is the analysis of contrast enhancement. A threedimensional MR sequence is applied before and five times after bolus injection of paramagnetic contrast medium (Gd-DTPA). The dynamics of absorption are described by a time/intensity enhancement curve, which reports the mean intensity of the MR signal in a small region of interest (ROI) for about 8 minutes after contrast injection. The aim of our study was to use an artificial neural network to automatically classify the enhancement curves as “benign” or “malignant.” We used a classic feed-forward back-propagation neural network, with three layers: five input nodes, two hidden nodes, and one output node. The network has been trained with 26 pathologic curves (10 invasive carcinoma [K], two carcinoma-in-situ [DCIS], and 14 benign lesion [B]). The trained network has been tested with 58 curves (36 K, one DCIS, 21 B). The network was able to correctly identify the test curves with a sensitivity of 76% and a specificity of 90%. For comparison, the same set of curves was analyzed separately by two radiologists (a breast MR expert and a resident radiologist). The first correctly interpreted the curves with a sensitivity of 76% and a specificity of 90%, while the second scored 59% for sensitivity and 90% for specificity. These results demonstrate that a trained neural network recognizes the pathologic curves at least as well as an expert radiologist. This algorithm can help the radiologist attain rapid and affordable screening of a large number of ROIs. A complete automatic computer-aided diagnosis support system should find a number of potentially interesting ROIs and automatically analyze the enhancement curves for each ROI by neural networks, reporting to the radiologist only the potentially pathologic ROIs for a more accurate, manual, repeated evaluation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Heywang-Kobrunner SH, Beck R: Contrast Enhanced MRI of the Breast (ed 2). Berlin, Germany, Springer-Verlag, 1996
Kühl CK, Mielcareck P, Klaschik S, et al: Dynamic breast MR imaging: Are signal intensity time course data useful for differential diagnosis of enhancing lesions? Radiology 211:5–7, 1999
Abdolmaleki P, Buadu LD, Murayama S, et al: Neural network analysis of breast cancer from MRI findings. Radiat Med 15:283–293, 1997
Fischer H, Henning J: Neural network-based analysis of MR time series. Magn Reson Med 41:124–131, 1999
Rumelhart DE, Hinton GE, Williams RJ: Learning internal representations by back-propagation errors. Nature 332: 533–536, 1986
Apolloni B, Ronchini G: Dynamic sizing of multilayer perceptions. Biol Cybernet 71:49–63, 1994
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vergnaghi, D., Monti, A., Setti, E. et al. A use of a neural network to evaluate contrast enhancement curves in breast magnetic resonance images. Journal of Digital Imaging 14 (Suppl 1), 58–59 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03190297
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03190297