Summary
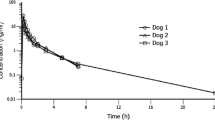
The concentration — time profiles of ethmozine, a newly introduced anti-arrhythmic drug, in the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) and plasma of six rabbits (New Zealand white rabbits of both sexes, 4.0–5.0 Kg) were studied after intravenous bolus administration. CSF samples at various intervals were obtained while the animal was lightly anaesthetized with intravenous thiopentone (40 mg Kg−1 ) and blood samples at other intervals were taken while the animal was conscious. Blood samples (1 ml) were collected from the implanted cannula of the ear artery while CSF samples (0.3 ml) were obtained from the cisterna magna. The plasma concentrations of ethmozine in six rabbits declined rapidly after intravenous injection for up to 30 min. then slowly over 12 h. Using non-compartmental analysis, the mean ( ± S.E.M.) elimination half-life, mean residence time, plasma clearance and volume of distribution at steady state were 13.9±9.2h, 19.9±13.4 h, 2.3 Lh−1 and 26.8±7.9 L respectively. The mean CSF-plasma concentration ratios for ethmozine at 0,5, 1.0, 2.0, 4.0, 8.0 and 12.0 h were 0.17, 0.14, 0.16, 0.16, 0.23 and 0.22 respectively. The results suggest that ethmozine is able to penetrate into the CSF from the general circulation and this may be related to its adverse effects on the central nervous system.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Danilo P., Langan W.B., Rosen M.R., (1977): Effects of the phenothiazine analog EN-313, on ventricular arrththmias in the dog. Eur J Pharmacol 45: 127–139.
Morganroth J., Pearlman A.S., Dunkman W.B. (1979): Ethmozine: A new antiarrththmic agent developed in the USSR, efficacy and tolerance. Am Heart J 98: 621–628.
Chazov E.I., Shugushev K.K., Rosenshtraukh L.V. (1984): Ethmozine I. Effects of intravenuos drug administration on paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia in the ventricular preexcitation syndrome. Am Heart J 108: 475–482.
Chazov E.I., Rosenshtraukh L.V., Shugushev K.K. (1984): Ethmozine II. Effects of intravenous drug administration on atrioventricular nodal reentrant tachycardia. Am Heart J 108: 483.
Pratt C.M., Yepsen S.C., Taylor A.A. (1983): Ethmozine suppression of single and repetitine ventricular premature depolarizations during therapy: Documentation of efficacy and long term safety. Am Heart J 106: 85–91.
Pratt C.M., Wierman A., Seals A.A. (1986): Efficacy and safety of moricizine in patients with ventricular tachycardia: results of a placebo — controlled prospective long — term clinical trial. Circulation 73: 718–726.
Yang J.M., Jiang W.D., Zhu J.R., Chen Y., Li Z.S., Chen Q.C., Wang Y.P. (1986): The determination of plasma concentration of ethmozine by HPLC and a pharmacokinetic study on ethmozine in normal subjects. Chin J Clin Pharmacol 2: 74–82.
Jiang W.D., Zhu J.R., Yang J.M., (1986): On the kinetics and dynamics of ethmozine in healthy subjects. Chin J Physiol Sei 2: 209–218.
Michelson E.L. and Dreifur L.S. (1988): Newer anti-arrhythmic drugs, Ethmozine. Med Clin North Am 72: 286–288.
Chan K., Wong C.L. and Wai M.K. (1986): Anti-tuberculous drug penetration into cerebrospinal fluid in a rabbit model. Asia Pacific J Pharmacol 1: 41–45.
Yang J.M., Chan K., Wai M.K.J, and Jiang W.D (1989): The physicochemical properties, distribution characteristics and CSF penetration of moricizine. Neuroscience Lett Suppl. 35: S61.
Martensson E., Nyberg G and Axelsson R. (1980): Thioridazine and thioridazine metabolites in cerebrospinal fluid in psychiatric patients. In: Usdin E., Eckert H and Forrest I S, Eds. Phenothazines and structurally related drugs: Basic and clinical studies. New York: Elsevier North Holland Inc. 173–176.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chan, K., Yang, J.M., Wai, M.K. et al. Disposition of ethmozine in cerebrospinal fluid and plasma of rabbits. Eur. J. Drug Metab. Pharmacokinet. 14, 279–282 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03190111
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03190111