Summary
Intraperitoneal injection of rats with 2 mg/kg ring labelled14C AFB1 (spec. act. 110 mCi/mM/nmole) showed a higher level of radioactivity in the urine of test animals on diets containing 600 mg/kg vit. E 24 h after pretreatment. Analysis of the urine by chloroform extraction, thin layer chromatography and liquid scintillation counting of the various fractions showed less aflatoxin M1 (AFM1) and less unmetabolized AFB1 in test samples than in controls.
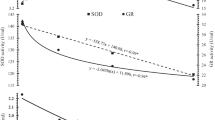
Incubation of ring labelled14C AFB1 with hepatic 10,000 g supernatant fractions, however, showed increased metabolism of AFB1 by fractions from test animals as compared with the controls. Rate of disappearance of14C AFB1 and the consequent formation of AFM1 was greater in the test fractions than in the controls (4). At 30 days all test animals showed higher levels of serum vitamin E than the controls. Hepatic aniline hydroxylase and ethyl morphine N-demethylase activities of the liver fractions and blood glutathione reductase activity were greater in the tests. P-nitroanisole-O-demethylase activity was reduced while hepatic and serum reduced glutathione levels remained basically unaltered.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AFB1 :
-
Aflatoxin B1
- AFM1 :
-
Aflatoxin M1
- AFP1 :
-
Aflatoxin P1
- T.L.C.:
-
thin layer chromatography
- GSH:
-
glutathione (reduced)
References
Packer L. and Walten J. (1977): Antioxidants vs. ageing. Chemtech.,7(5), 276–281.
Black E.R. (1979): Potentiation of acute paraquat toxi city by vitamin E deficiency. Lung,156(3), 195–204.
Burk R.F. and Lane J.M. (1979): Ethane production and liver necrosis in rats after administration of drugs and other chemicals. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol.,50 (3), 467–478.
Welsh S.O. (1979): The protective effect of vitamin E and N-N-diphenyl p-phenyl diamine against methyl mercury toxicity in rat. J. Nutr.,709(10), 1673–1681.
Wang Y., Madanat F.F., Kimball J.C., Gleiser C.A., Ali M.K., Kaufman W.M. and Van eys J.C. (1980): Effect of vitamin E against adriamycin-induced toxicity in rabbits. Cancer Res.,40, 1022–1027.
Cook M.G. and McNamara P. (1980): Effect of dietary vitamin E on dimethylhydrazine-induced colonic tumours in mice. Cancer Res.,40, 1329–1331.
Dashman T. and Kamm J.J. (1979): Effects of high doses of vitamin E on dimethylnitrosamine hepatotoxicity and drug metabolism in the rat. Biochem. Pharmacol.,28, 1485–1490.
Carpenter M.P. (1972): Vitamin E and microsomal drug hydroxylations. Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci.,203, 81–92.
Newberne P.M. (1965): Carcinogegecity of aflatoxin-contaminated peanut meals. In: G.N. Wogan (ed.). Mycotoxins in Foodstuffs: pp. 187–208, Cambridge, Mass, MIT Press.
Peers F.G. and Linsell C.A. (1973): Dietary aflatoxins and liver cancer. A population based study in Kenya. Brit. J. Cancer,27, 473–484.
Peers F.G., Gilman G.A. and Linsell C.A. (1976): Dietary aflatoxins and human liver cancer. A study in Swaziland. Int. J. Cancer,17, 167–176.
Shank R.C. (1977): Metabolic activation of mycotoxins by animals and humans: An overview. J. toxicol. Environ. Hlth.,2, 1229–1244.
Swensen D.H., Miller E.C. and Miller J.A. (1974): Anatoxin B1 2, 3-epoxide: Evidence for its formation in rat liver in vivo and by human liver microsomes in vitro. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun.,60(3), 1036–1043.
Shenkman J.B., Remmer H. and Estabrook R.W. (1967): Spectral studies of drug interaction with hepatic microsomal cytochrome. Mol. Pharmacol.,3, 113–123.
Holtzman J.C., Gram T.E., Gigon P.C. and Gillette J.R. (1968): The distribution of the components of the mixed function oxidases between rough and smooth endoplasamic reticulum of liver cells. Biochem. J.,110, 407.
Nash T. (1953): The colorimetric estimation of formaldehyde by means of the Hantzech reaction. Biochem. J.,55, 416–421.
Netter K.J. and Seidel G. (1964): An adaptively stimulated o-denethylating system in rat liver microsomes and its kinetic properties. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther.,146, 61–66.
Dawson J.P., Thayer W.W. and Desforges J.F. (1958): Acute haemolytic anemia in the new born infant due to cases with investigations into the mechanism of the disease. Blood: J. of Haematol.,13, 113.
Gornal A.G., Bardawill C.J. and David M.M. (1949): Determination of serum proteins by means of the biuret reaction. J. Biol. Chem.,177, 751.
Jollow D.J., Mitchell J.R., Zampaglione R. and Gillette J.R. (1974): Bromobenzene induced liver necrosis: Protective role of glutathione and evidence for 3, 4-bromobenzene oxide as the hepatic metabolite. Pharmacology,11, 151–169.
Ellman G.L. (1959). Tissue sulfhydryl groups. Arch. Biochem. Biophys.,82, 70–77.
Kayden H.J., Chow C.K. and Bjornson L.K. (1973): Spectrophotometric method for determination of tocopherol in red blood cells. J. of Lipid Res.,14, 533–540.
Wong Z.A. and Hsieh D.P.N. (1980): The comparative metabolism and toxikinetics of aflatoxin B1 in the monkey, rat and mouse. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol.,55, 115–125.
Roebuck B.D. and Wogan G.N. (1977): Species comparison of in-vitro metabolism of aflatoxin Bt. Cancer Res.,37, 1649–1656.
Miller J.A. and Miller E.C. (1977): The concept of reactive electrophitic metabolites in chemical carcinogenesis: Recent results with aromatic amines safrole and aflatoxin B1 In “Biological reactive intermediates formation, toxicity and inactivation. Ed. Jollow D.J., Kocsis J.J., Snyder R. and Vainio J.J. (New York and London, Plenum Press), pp. 6–24.
Giasuddin A.S.M., Caygill C.P.J., Diplock A.T. and Jeffery E.H. (1975): The dépendance on vitamin E and selenium of drug demethylation in rat liver microsomal fractions. Biochem. J.,146, 339–350.
Giovanni C.C. (1978): Phenacetin abuse: A Review. Toxicology,10(4), 322.
Emerole G.O., Neskovic N. and Dixon R.L. (1979): The detoxication of aflatoxin B( with glutathione in the rat. Xenobiotica,9, 737–743.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Emerole, G.O., Thabrew, M.I. & Kwanashie, H.O. Effect of dietary vitamin E (α-tocopherol) on aflatoxin B metabolism. European Journal of Drug Metabolism and Pharmacokinetics 9, 295–300 (1984). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03189679
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03189679