Abstract
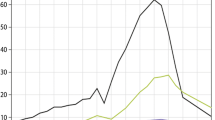
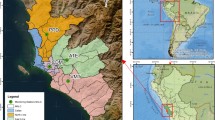
The Beijing City Air Pollution Observation Field Experiment (BECAPEX) is described with emphases on the “point-surface” research approach and composite analysis. The analysis results of measurements from four observation sites across the Beijing urban area from January to March indicate that the overall impact of urban emission sources in the heating season is significant, and the staggered impact of urban emission sources has different features at observation sites over different parts of Beijing in both heating and non-heating seasons. The pollutants NO x , SO2 and CO in the urban boundary layer have the in-phase variation features over a large area. O3 concentrations at different sites have the same variation trend but its change is reversed phases with above pollutants. The pollutants over the urban area in heating and non-heating seasons also have the synchronous variation trend. The comprehensive sounding of BECAPEX indicates that pollutants and aerosol vertical profiles are closely correlated to the vertical structure of the large-scale inversion layer in the urban boundary layer over the urban area. The localized 3D-structural features of local urban polluting processes associated with the peripheral areas are discussed with a “point-surface” comprehensive sounding technique.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
WMO, The Global Atmosphere Watch (GAW) Strategic Plan 2001–2007, 2001.
Apple, B. R., Berkeley visibility as related to atmospheric aerosol constituents, Atmospheric Environment, 1985, 19(9): 1525–1534.
James, F. S., William, C. M., The relative importance of soluble aerosols to spatial and seasonal trends of impaired visibility in the United States, Atmospheric Environment, 1994, 28(5): 851–862.
Malm, W. C., Gebhart, K. A., Examining The relationship between atmospheric aerosols and light extinction at Mount Rainier and North Cascades National Parks, Atmospherc Environment, 1994, 28(2): 347–360.
Dupont, E., Carissimo, B., Pelon, J. et al., Comparison between the atmospheric boundary layer in Paris and its rural Suburbs during the ECLAP experiment, Atmospheric Environment, 1999, 33(6): 979–994.
Ichinose, T., Hanaki, K., Shimodozono, K., Impact of atmospheric heat on Urban Climate in Tokyo, Atmospheric Environment, 1999, 33(24–25): 3897–3909.
Romero, H., Rivera, A., Zalazar, P. et al., Rapid urban growth, Land-use Changes and air pollution in Santiago, Chile, Atmospheric Environment, 1999, 33(24–25): 4039–4047.
Xu Xiangde, Tang Xu, Introduction to Urbanized Environment Meteorology (in Chinese), Beijing: China Meteorological Press, 2002.
Wang Xiaoyun, Pan Liqing, Lu Weilin et al., Relations between perpendicular distribution of air pollutants and weather condition in winter in beijing urban districts, Journal of Applied Meteorological Science, 2001, 12(3): 277–286.
Xie Shaodong, Zhang Yuanhang, Tang Xiaoyan, Current situation and trend of motor vehicle exhaust pollution in urban areas of China, Research of Environment Sciences (in Chinese), 2002, 13(14): 22–25.
Xu Xiangde, Dynamic issues of urban atmospheric pollution models. Journal of Applied Meteorological Science (in Chinese), 2002, 13(suppl.): 1–12.
Bian Lingen, Cheng Yanjie, Wang Xin et al., Observation study of wind and temperature profiles of urban boundary layer in beijing winter. Journal of Applied Meteorological Science, 2002, 13(suppl.): 13–25.
Zheng Xiangdong, Ding Guoan, Sun Minfeng et al., Prelimary analysis on boundary layer ozone vertical profiles observed in winter in Beijing urban region. Journal of Applied Meteorological Science. 2002, 13(suppl.): 100–108.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, X., Ding, G., Zhou, L. et al. Localized 3D-structural features of dynamic-chemical processes of urban air pollution in Beijing winter. Chin.Sci.Bull. 48, 819–825 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03187060
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03187060