Abstract
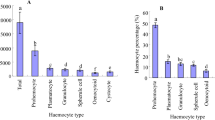
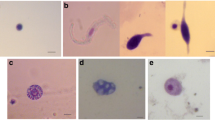
Effect of plumbagin, a phytochemical, on the haemocytes ofDysdercus koenigii was studied after topical application. Scanning electron microscopical studies showed deformity in surface morphology in almost all the 5 types of haemocytes categorized in the bug, especially that of granular haemocytes and plasmatocytes, which are devoid of their filopods in the treated insects. The fat droplets of adipohaemocytes shrink while oenocytoid is affected to a lesser degree. Plasma membrane of all the cells becomes fragile leading to a gradual loss of cytoplasm and ultimately only a few interconnected cytoplasmic strands are left. Ultrathin sections revealed a highly vacuolized condition and disintegrating organelles which pass out of the cells due to ruptures of very thin plasma membrane. Total and differential haemocyte counts performed after 24 and 48h of treatment showed a drastic reduction of all the types i.e. the prohaemocytes disappear from blood, the number of granular haemocytes and plasmatocytes declines while oenocytoids and adipohaemocytes comprise the major part of counts. Because of the damages caused to haemocytes and the suppression of filopodial elongations of plasmatocytes and granular haemocytes (the types that are active in defense mechanism), it can be inferred that cellular defense reactions ofDysdercus koenigii are reduced after plumbagin treatment.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chadha M S, Lathika K M, Joshi N K and Banerji A 1986 Biological effects of plumbagin on the red cotton bug,Dysdercus koenigii; Proc. 6th Int. Congr. Pesticide Chemistry IUPAC August 10–15th, Ottawa, Canada
Chain B M and Anderson R S 1983 Inflammation in insects: The release of a plasmatocyte depletion factor following interaction between bacteria and haemocytes;J. Insect Physiol. 29 1–4
Feir D 1979 Cellular and humoral responses to toxic substances; inInsect hemocytes, Development, forms, functions and techniques, (ed.) A P Gupta (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press) pp 415–421
Francois J 1975 L’encapsulation hemocytaire experimentale chez le lépismeThermobia domestica;J. Insect Physiol. 21 1535–1546
Joshi N K, Lathika K M, Banerji A and Chadha M S 1988 Effects of plumbagin on growth and development of red cotton bug,Dysdercus cingulatus Fab.;Proc. Indian Natl. Sci. Acad. B54 43–46
Kubo I, Uchiada M and Klocke J A 1983 An insect ecdysis inhibitor from the African medicinal plant;Plumbago capensis (Plumbaginaceae), a naturally occurring chitin synthetase inhibitor,Agric. Biol. Chem. 47 911–913
Ratcliffe N A and Rowley A F 1979 Role of hemocytes in defense against biological agents; inInsect hemocytes, Development, forms, functions, and techniques, (ed.) A P Gupta (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press) pp 331–414
Ratcliffe N A and Walters J B 1983 Studies on thein vivo cellular reactions of insects: Clearance of pathogenic and non-pathogenic bacteria inGalleria mellonella larvae;J. Insect Physiol. 29 407–415
Saxena B P, Sharma P R and Tikku K 1988 Scanning electron microscopical studies of the haemocytes ofSpodoptera litura Fabr.;Cytologia 53 385–391
Saxena B P and Srivastava J B 1972 Studies on plant extracts with juvenile hormone activity. Effects ofIris ensata Thumb. (Iridaceae) onDysdercus koenigii F. (Pyrrhocoridae);Experientia 28 112–113
Shapiro M 1979 Changes in hemocyte populations; inInsect hemocytes, Development, forms, functions, and techniques, (ed.) A P Gupta (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press) pp 475–523
Sharma P R, Tikku K and Saxena B P 1986 An electron microscopic study of normal haemocytes ofPoecilocerus pictus (Fab.) and their response to injected yeast cells;Insect Sci. Applic. 7 85–91
Wago H and Ichikawa Y 1979 Changes in the phagocytic rate during the larval development and manner of hemocytic reactions to foreign cells inBombyx mori;Appl. Entomol. Zool. 14 397–403
Wago H 1980 Humoral factors promoting the adhesive properties of the granular cells and plasmatocytes of the silkworm,Bombyx mori, and their possible role in the initial cellular reactions to foreignness;Cell. Immunol. 54 155–169
Wago H 1983 The important significance of filopodial elongation of phagocytic granular cells of the silkworm,Bombyx mori, in recognition of foreignness;Dev. Comp. Immunol. 7 445–453
Wago H and Kitano H 1985 Morphological and functional characterization of the larval hemocytes of the cabbage white butterfly,Pieris rapae crucivora;Appl. Entomoi Zool. 20 1–7
Walters J B and Ratcliffe N A 1983 Studies on the in vivo cellular reactions of insects: Fate of pathogenic and non-pathogenic bacteria inGalleria mellonella nodules;J. Insect Physiol. 29 417–424
Zaidi Z S and Khan M A 1977 Effect of aldrin and dipterex on the haemocytes of red cotton bugDysdercus cingulatus Fabr. (Hemiptera: Pyrrhocoridae);Botyu-Kagaku 42 141–148
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Saxena, B.P., Tikku, K. Effect of plumbagin on haemocytes ofDysdercus koenigii F.. Proc Ani Sci 99, 119–124 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03186380
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03186380