Abstract
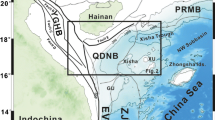
In the Ying-Qiong basins in the South China Sea developed a set of giant inner shelf slope and submarine gravity flow deposits in the Ying-Huang formations since the Late Miocene. These deposits can be classified into 9 sequences in which slope slump-debris flow, slope fan and particularly, the large-scale axial basin-floor incised valley fills have been recognized. They were distributed in a distinctive pattern attributed to tectonic control. The development of shelf slopes and abyssal plains in the basins was related to the last episode of rapid subsidence and a large amount of sediment inputs. Large-scale basin-floor incised valleys, formed during the late Miocene and Pliocene, indicate several major sea level falls that occurred in the South China Sea.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gong Zaisheng, Lisitian, Xie Taijun et al., Continental Margin Basin Analysis and Hydrocarbon Accumulation of the Northern South China Sea (in Chinese), Beijing: Science Press, 1997.
Percy, P. H., Chen, Zhiyong Chen, Qimin Zhang, Sequence strtigraphy and continental margin development of the northwestern shelf of the South China Sea, AAPG Bulletin, 1993, 77(5): 842.
Van Wagoner, J. C., Mittchum, R. M., Campion, K. M. et al., Siliciclastic sequence stratigraphy in well logs, cores and outcrops: concepts for high-resolution correlation of time and facies, AAPG Methods in Exploration Series (7), Tulsa, 1990.
Galloway, W. E., Siliciclastic slope and base-of-slope depositional systems: component facies, stratigraphic architecture, and classification, AAPG Bulletin, 1998, 82(4): 569.
Weimer, P., Varnai, P., Budhijanto, F. M. et al., Sequence stratigraphy of Pliocene and Pleistocene turbidite systms, northern Green Canyon and Ewing, Bank (offshore Louisiana), northern Gulf of Mexico, AAPG Bulletin, 1998, 82(5b): 918.
Lin Changsong, Li Sitian, Zhang Qiming et al., Lithospheric stretching, subsidence and thermal history modeling: application to Yinggehai, Qiongdongnan and Songliao basins in East China, Journal of China University of Geosciences, 1997, 8(1): 83.
Zhong Dalai, Ding Lin, Ring process of the Qinghai-Xizang (Tibet) Plateau and its mechanism, Science in China, Ser. D, 1996, 39(4): 369.
Lin Changsong, Zhang Yanmei, Li Sitian et al., Sequence stratigraphy modeling of sedimentary basin: application to Erlian and Yinggehai basins in East China, Joural of China University of Geosciences, 1996, 7(1): 132.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
About this article
Cite this article
Lin, C., Liu, J., Cai, S. et al. Depositional architecture and developing settings of large-scale incised valley and submarine gravity flow systems in the Yinggehai and Qiongdongnan basins, South China Sea. Chin. Sci. Bull. 46, 690–693 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03182838
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03182838