Abstract
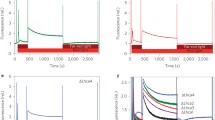
The ε subunit of the chloroplast ATP synthase and the truncated ε mutants which lack some amino acid residues from the N-terminus or C-terminus were overexpressed inE. coli. When the ε subunit or the truncated ε proteins was added to the spinach chloroplast suspension, both the intensity of the fast phase of millisecond delayed light emission (ms-DLE) and the cyclic and noncyclic photophosphorylation activity of chloroplast were enhanced. With an increase in the number of residues deleted from the N-terminus, the enhancement effect of the N-terminal truncated proteins decreased gradually. For the C-terminal truncated proteins, the enhancement effect increased gradually with an increase in the number of residues deleted from the C-terminus. Besides, the ATP synthesis activity of ε-deficient membrane reconstituted with the ε subunit or the truncatedε proteins was compared. The ATP synthesis activity of reconstituted membrane with the N-terminal truncated proteins decreased gradually as the number of residues deleted from the N-terminus increased. For the C-terminal truncated proteins, the ATP synthesis activity of reconstituted membrane increased gradually with an increase in the number of residues deleted from the C-terminus, but was still lower than that of the wild type ε protein. These results suggested that: (a) the N-terminal domain of the ε subunit of the chloroplast ATP synthase could affect the ATP synthesis activity of ATP synthase by regulating the efficiency of blocking proton leakage of ε subunit; and (b) the C-terminal domain of the ε subunit of the chloroplast ATP synthase had a subtle function in modulating the ATP synthesis ability of ATP synthase.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Engelbrechft, S., Junge, W., ATP synthase: A tentative structural model, FEBS Letters, 1997, 414: 485–491.
Richter, M. L., Patrie, W. J., McCarty, R. E., Preparation of the ε subunit and ε subunit-deficient chloroplast coupling factor 1 in reconstitutively active forms, J. Biol. Chem., 1984, 259: 7371–7373.
Johnson, E. A., McCarty, R. E., The carboxyl terminus of ε subunit of the chloroplast ATP synthase is exposed during illumination, Biochemistry, 2002, 41: 2446–2451.
Jounouchi, M., Takeyama, M., Noumi, T. et al., Role of the amino terminal region of the ε subunit ofEscherichia coli H+-ATPase, Arch. Biochem. Biophys., 1992, 292: 87–94.
Kuki, M., Mouni, T., Maeda, M. et al., Functional domains of ε subunit ofEscherichia coli H+-ATPase, J. Biol. Chem., 1988, 263: 17437–17442.
Cruz, J. A., Harfe, B., Radkowski, C. A. et al., Molecular dissection of the ε subunit of the chloroplast ATP synthase of spinach, Plant Physiol., 1995, 109: 1379–1388.
Cruz, J. A., Christopher, A., Radkowski, A. et al., Functional consequences of the deletions of the N terminus of the ε subunit of the chloroplast ATP synthase, Plant Physiol., 1997, 113: 1185–1192.
Shi, X. B., Wei, J. M., Shen, Y. G., Effects of sequential deletions of residues from the N-terminus or C-terminus on the functions of ε subunit of the chloroplast ATP synthase, Biochemistry, 2001, 40: 10825–10831.
Malkin, S., Delayed luminescence, Photosynthesis I, Encyclopedia of Plant Physiology (eds. Trebst, A., Avron, M.), Heidelberg/New York: Springp-Verlag, 1997, 473–491.
Xu, C. H., Shen, Y. G., Relationship between the changes of the fast phase of millisecond delayed light emission and the proton released by the oxidation of water, Sci. Sin., Ser. B, 1983, 9: 802–810.
Shi, J., Wei, J. M., Shen, Y. G., The properties of expressed product of chloroplast atpE gene, Acta Phytophysiologica Sinica, 1996, 22(3): 225–230.
Shi, J., Wei, J. M., Li, D. Y. et al., Effects of ε subunit of chloroplast ATP synthase on the fast phase of millisecond delayed fluorescence in spinach chloroplast, Acta Phytophysiologica Sinica, 1998, 24(2): 119–123.
Wei, J. M., Shen, Y. G., Li, D. Y., Study about hydrogen atom participating in photophosphorylation, Sci. Bull. Sin., 1987, 2: 144–147.
Arnon, D. I., Copper enzymes in isolated chloroplasts, Polyphenol oxidase inBeta vulgaris, Plant Physiol., 1949, 24: 1–15.
Wei, J. M., Shen, Y. G., Li, D. Y., Stimulatory effects of polymixin B on photophosphorylation, Acta Phytophysiologica Sinica, 1990, 16: 251–256.
Nelson, N., Eytan, E., Approach to the membrane sector of the chloroplast coupling device, Cation Flux Across Biomembranes (eds. Mukahata, Y., Packer, L.), New York: Academic Press, 1979, 409–415.
Wei, J. M., Bruce, H., Jagendorf, A. T., Azide inhibition of chloroplast ATPase is prevented by a high proton motive force, Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 1988, 934: 72–79.
Nowak, K. F., Tabidze, V., McCarty, R. E., The C-terminal domain of the ε subunit of the chloroplast ATP synthase is not required for ATP synthesis, Biochemistry, 2002, 41: 15130–15134.
Hisabori, T., Nakanishi, H. U., Konno, H. et al., Molecular evolution of the modulation of chloroplast ATP synthase: Origin of the conformational change dependent regulation, FEBS Letters, 2003, 545: 71–75.
Tsunoda, S. P., Rodgers, A. J. W., Aggeler, R. et al., Large conformational changes of the ε subunit in the bacterial F1F0 ATP synthase provide a ratchet action to regulate this rotary motor enzyme, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci., 2001, 98(12): 6560–6564.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Zeng, X., Shi, X. & Shen, Y. Effects of truncated mutants of the ε subunit of chloroplast ATP synthase on the fast phase of millisecond delayed light emission of chloroplast and its ATP synthesis ability. Chin.Sci.Bull. 49, 258–262 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03182809
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03182809