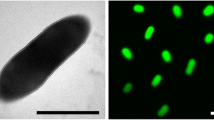
Abstract
A fragment of DNA (pBTBX) from the genome ofSinorhizobium fredii USDA257 was sequenced by shotgun strategy to identify the potential genes which enabled theRhizobium species NGR234 to fix nitrogen on soybean,Glycine max (L.) Merr cv. Peking. The total length of the cosmid is 32,824 base pairs with a GC content of 61%. A 29 open reading frames (ORF) were identified representing 71.8% (23,574 bp) of the cosmid. Out of these ORF, 96.5% (22,749 bp) were identical and similar to reported and hypothetical genes and proteins. The remaining 3.5% (825 bp) had no apparent similarity to any genes in the data base. Gene and gene products found on the DNA fragment include those involved in the synthesis of FeMo component of nitrogenase, regulation of nitrogen fixation, transport of amino acids and sugars, chemotaxis and transcriptional regulation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ames, P. and Bergman, K. 1981. Competitive advantage provided by bacterial motility in the formation of nodules byRhizobium meliloti.Journal of Bacteriology 148: 728–729.
Balatti, P.A. and Pueppke, S.G. 1992. Identification of North American soybean lines that form nitrogen-fixing nodules withRhizobium fredii USDA257.Canadian Journal of Plant Science 72: 49–55.
Borofsky, M. 1995. GeneMark, version 2.3. Georgia Institute of Technology, School of Biology, Atlanta, GA, USA
Brock, T.D., Smith, D.W., and Madigan, M.T. 1984.Biology of Microorganisms. Fourth edition. Prentice-Hall Int., Inc. pp. 108–113.
Caetano-Anollés, G., Wall, L.G., Micheli, AT.D., Macchi, E.M., Bauer, W.D., and Favelukes, G. 1988. Role of motility and chemotaxis in efficiency of nodulation byRhizobium meliloti.Plant Physiology 86: 1228–1235.
Cloutier, J., Laberge, S., and Antoun, H. 1997. Sequence and mutational analysis of the 6.7-kb region containingnodAFEG genes ofRhizobium species strain N33: Evidence of DNA rearrangements.Molecular Plant Microbe Interaction 10: 401–406.
Cooper, J.E. 2007. Early interactions between legumes and rhizobia: disclosing complexity in a molecular dialogue.Journal of Applied Microbiology 103: 1355–1365.
Debellé, F., Moulin, L., Mangin, B., Dénarié, J., and Boivin, C. 2001. Nod genes and Nod signals and the evolution of theRhizobium-legume symbiosis.Acta Biochimica Polonicá 48: 359–365.
Fellay, R., Rochepeau, P., Rélic, B., and Broughton, W.J. 1995b. Signals to and emanating fromRhizobium largely control symbiotic specificity. Histopathological, Biochemical, Genetic and Molecular Bases. Vol. 1:Prokaryotes. Singh, U.S. Singh, R.P., and Khomoto, K., eds. Pergamon Elsevier Science Ltd., Oxford. pp. 199–220.
Finnie, C., Hartley, N.M., Findlay, K.C., and Downie, J.A. 1997. TheRhizobium leguminosarum prsDE genes are required for secretion of several proteins, some of which influence nodulation, symbiotic nitrogen fixation and exopolysaccharide modification.Molecular Microbiology 25: 135–146.
Fischer, H.M. 1994. Genetic regulation of nitrogen fixation in rhizobia.Microbiology Review 58: 352–386.
Freiberg, C., Fellay, R., Bairoch, A., Broughton, W.J., Rosenthal, A., and Perret, X. 1997. Molecular basis of symbiosis betweenRhizobium and legumes.Nature 387: 394–401.
Freiberg, C., Perret, X., Broughton, W.J., and Rosenthal, A. 1996. Sequencing the 500kb GC-rich symbiotic replicon ofRhizobium species NGR234 using dye terminators and thermostable “Sequenase”: a beginning.Genome Research 6: 590–600.
Hanahan, D. 1983. Studies on transformation ofEscherichia coli with plasmids.Journal of Molecular Biology 166: 557–580.
Hanin, M., Jabbouri, S., Broughton, W.J., Fellay, R., and Quesada-Vincens, D. 1998. Molecular aspects of host-specific nodulation. In:Plant-Microbe Interactions. G.X. and Keen, N.T., eds. American Phytopathology Society, St. Paul, MN, USA. pp. 1–29.
Henikoff, S., Haughn, G.W., Calvo, J.M., and Wallace, J.C. 1988. A large family of bacterial activator proteins.Proceedings of the National Academy of Science, USA 85: 6602–6606.
Horvath, B., Kondorosi, E., John, M., Schmidt, J., Torok, I., Gyorgypal, Z., Barabas, I., Wieneke, U., Schell, J., and Kondorosi, A. 1986. Organization, structure and symbiotic function ofRhizobium meliloti nodulation genes determining host specificity for alfalfa.Cell 46: 335–343.
Keyser, H.H., Bohlool, B.B., Hu, T.S., and Weber, D.F. 1982. Fast-growing rhizobia isolated from root nodules of soybean.Science 215: 1631–1632.
Kröl, J. and Skorupska, A. 1997. Identification of genes inRhizobium leguminosarum bv.trifolii whose products are homologous to a family of ATP-binding proteins.Microbiology UK 143: 1389–1394.
Lewin, A., Rosenberg, C., Meyer, Z.A.H., Wong, C.H., Nelson, L., Manen, J-F., Stanley, J., Dowling, D.N., Dénaire, J., and Broughton, W.J. 1987. Multiple host-specificity loci of the broad host-rangeRhizobium species NGR234 selected using the widely compatible legumeVigna unguiculata.Plant Molecular Biology 8: 447–459.
Paulsen, I.T., Beness, A.M., and Saier, M.H. Jr. 1997. Computer-based analyses of the protein constituents of transport systems catalyzing export of complex carbohydrates in bacteria.Microbiology 143: 2685–2699.
Perret, X., Staehelin, C., and Broughton, W.J. 2000. Molecular basis of symbiotic promiscuity.Molecular Biology Review 64: 180–201.
Pueppke, S.G. and Broughton, W.J. 1999.Rhizobium sp. strain NGR234 andR. fredii USDA257 share exceptionally broad, nested host ranges.Molecular Plant Microbe Interaction 12: 293–318.
Rélic, B., Perret, X., Estrada-Garcia, M.T., Kopcinska, J., Golinowski, W., Krishnan, H.B., Pueppke, S.G., and Broughton, W.J. 1994. Nod factors ofRhizobium are a key to the legume door.Molecular Microbiology 13: 171–178.
Roelvinic, P. and van den Bos, R.C. 1989. Regulation of nitrogen fixation in diazotrophs: the regulatorynifA gene and its characteristics.Acta Botanica Neerlandica 38: 233–252.
Sambrook, J., Fritsch, E.F., and Maniatis, T.A. 1989.Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual. 2nd ed. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, Cold Spring Harbor, New York. pp. 136–147.
Shaw, L.J., Morris, P., and Hooker, J.E. 2006. Perception and modification of plant flavonoid signals by rhizosphere microorganisms.Environmental Microbiology 8: 1867–1880.
Steinkellner, S., Lendzemo, V., Langer, I., Schweiger, P., Khaosaad, T., Toussaint, J.P., and Vierheilig, H. 2007. Flavonoids and strigolactones in root exudates as signals in symbiotic and pathogenic plant-fungus interactions.Molecules 12: 1290–1306.
Stephanie, S., Pao, I., Paulsen, T., and Saier, M.H. Jr. 1998. Major facilitator superfamily.Molecular Biological Review 62: 1–34.
Sternberg, N., Sauer, B., Hoess, R., and Abremski, K. 1986. Bacteriophage P1cre gene and its regulatory region evidence for multiple promoters and for regulation by DNA methylation.Journal of Molecular Biology 187: 197–212.
Tong, S., Porco, A., Isturiz, T., and Conway, T. 1996. Cloning and molecular genetic characterization of theEscherichia coli gntR,gntK andgntU genes of Gntl, the main system for gluconate metabolism.Journal of Bacteriology 178: 3260–3269.
Trinick, M.J. 1980. Relationships amongst the fast-growingRhizobium ofLablab purpureus, Leucaena łeucocephala, Mimosa species,Acacia farnesiana andSesbaenia grandiflora and their affinities with otherRhizobium groups.Journal of Applied Bacteriology 49: 39–53.
Wilson, R.L. and Stauffer, G.V. 1994. DNA sequence and characterization of GcvA, a LysR family regulatory protein for theEscherichia coli glycine cleavage enzyme system.Journal of Bacteriology 176: 2862–2868.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Boboye, B., Nyakatura, G., Rosenthal, A. et al. Sequence analysis of a DNA fragment fromSinorhizobium fredii USDA257 which extends the nitrogen fixation host range ofRhizobium species NGR234 to soybean,Glycine max (L.) Merr cultivar Peking. Symbiosis 48, 110–119 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03179990
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03179990