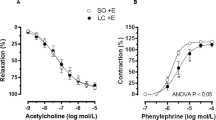
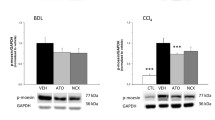
Abstract
Nitric oxide (NO) and prostaglandins have been proposed as vasodilator substances involved in peripheral vasodilatation characteristic of the liver cirrhosis. A link between NO and prostanoids has been suggested. The present study investigated the effect of simultaneous blockade of both, NO synthase (NOS) and cyclooxigenase (COX) in sham-operated (SO), or rats with bile-duct ligation (BDL) in the development of liver fibrosis. Animals were distributed in two groups SO (n=15) or BDL (n=15). Treatments (5 days) started three weeks after surgical procedure. Both, SO and BDL animals were treated with indomethacin (INDO) (5 mg/kg/day) alone, with NG-nitro-L-arginine-methyl-ester (NAME) (4 mg/kg/day) alone or with INDO and NAME combination at the same doses. At the end of follow-up body weight, packed cell volume, mean arterial blood pressure (MAP) and heart rate were measured. Liver tissue was processed for histological studies. In this study, BDL animals showed a decreased MAP. Treatment with L-NAME in BDL rats increased MAP. The chronic COX inhibition alone did not play an important role in the haemodynamic changes. The BDL produced a loss of hepatic structure, with ductular metaplasia that occupied the greater part of the hepatic parenchyma. Also, an important degree of fibrosis was observed. Both NO and PG synthesis inhibitors, alone or in combination, induced enhancing collagen fiber deposition in the hepatic parenchyma. These findings support the notion that the interaction between the NOS and COX pathways should be relevant in hepatic cirrhosis in which both NOS and COX are induced.
Resumen
En la vasodilatación periférica característica de la cirrosis hepática han sido involucrados diferentes vasodilatadores como son el óxido nítrico (NO) y las prostaglandinas, entre los cuales se ha sugerido que existe una estrecha relación. En este estudio se investiga el efecto del bloqueo simultáneo de la NO sintasa (NOS) y de la ciclooxigenasa (COX) en ratas con cirugía simulada (SO) o con ligadura del conducto biliar (LCB). Los animales se distribuyen en dos grupos SO (n=15) y LCB (n=15). Los tratamientos (5 días) comienzan tres semanas después de la cirugía. Tanto los animales SO como los LCB se tratan con indometacina (5 mg/kg/día), con NG-nitro-L-arginina-metiléster (NAME) (4 mg/kg/día), o con la combinación de ambos a la misma dosis. Al final del tratamiento se mide el peso corporal, el hematocrito, la presión arterial media (PAM) y la frecuencia cardiaca. Se realizan estudios histológicos en el tejido hepático. Los animales LCB muestran un descenso de la PAM. No se observan cambios hemodinámicos con el tratamiento con indometacina mientras que el NAME eleva la PAM. La LCB produce una pérdida de la estructura hepática, con metaplasia ductular que ocupa la mayor parte del parénquima hepático y un importante grado de fibrosis. Los animales tratados con NAME y/o indometacina muestran un empeoramiento del grado de fibrosis. Nuestros resultados indican que la interacción entre las vías de la NOS y la COX puede ser relevante en la cirrosis hepática, en la cual ambos sistemas están activados.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beck, P. L., McKnight, W., Kelly, J. K., Wallance, J. L. and Lee, S. (1993): Gastroenterology, 105: 1483–1489.
Beno, D., Espiral, R., Edelstein, B. and Davis, B. (1993): Hepatology, 17, 707–714.
Better, O. S. and Bomzon, A. (1988): In: “The kidney in liver disease” (M. Epstein, ed.). Williams and Wilkins, Baltimore. pp. 508–534.
Criado, M., Flores, O., Hidalgo, F., López-Novoa, J. M. and Sánchez-Rodríguez, A. (1999): Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol., 77, 111–117.
Criado, M., Flores, O., Ortiz, M. C., Hidalgo, F., Rodríguez-López, A. M., Eleno, N., Atucha, N. M., Sánchez-Rodríguez, A., García-Estañ, J. and López-Novoa, J. M. (1997): Hepatology, 26, 268–276.
Fabbri, A., Magalotti, D., Brizi, M., Bianchi, G., Zoli, M. and Marchesini, G. (1999): Dig. Dis. Sci., 44, 377–384.
Fort, J., Pilette, C., Oberti, F., Veal, N., Gallois, Y., Douay, O. and Calès, P. (1999): J. Hepatol., 30, 70–76.
Gall, J. A. and Bhathal, P. S. (1990): Liver, 10, 116–125.
Gall, J. A. and Bhathal, P. S. (1990): Liver, 10, 106–115.
Hou, M. C., Cahill, P. A., Zhang, S. M., Wang, Y. N., Hendrickson, R. J., Redmond, E. M. and Sitzmann, J. V. (1998): Hepatology, 27, 20–27.
Mayoral, P., Criado, M., Hidalgo, F., Flores, O., Arévalo, M., Eleno, N., Sánchez-Rodríguez, A., López-Novoa and Esteller, A. (1999): Clin. Sci., 96, 297–305.
Moncada, S., Palmer, R. M. J. and Higgs, E. A. (1991): Pharmacol. Rev., 43, 109–142.
Ogino, H. (1994): Acta Hepatol., 35, 216–223.
Ohnishi, A., Harada, M., Matsuo, A., Kawai, B., Kunihiro, N., Tada, Y., Chau, T., Koizumi, F. and Tanaka, T. (1998): Hepatology Res., 10, 131–141.
Ramírez, A. M., Atucha, N. M., Quesada, T., Pérez, M. C., López-Ayerra, B., Martínez, C., Sánchez, A. and García-Estañ, J. (1994): Nefrología, 14, 656–662.
Ruwart, M. J., Rush, B. D., Snyder, K. F., Peters, K. M., Appelman, H. D. and Henley, K. S. (1988): Hepatology, 8, 61–64.
Salazar, F. J., Pinilla, J. M., López, F., Romero, J. C. and Quesada, T. (1992): Hypertension, 20, 113–117.
Salvemeni, D., Misko, T. P., Masferrer, J. L., Seibert, K., Currie, M. G. and Needleman, P. (1993): Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 90, 7241–7244.
Sánchez-Rodríguez, A., Criado, M., Rodríguez-López, A. M., Esteller, A., Martín de Arriba, A. and López-Novoa, J. M. (1998): Clin. Sci., 94, 637–643.
Sautebin, L., Ialenti, A., Ianaro, A. and Di Rosa, M. (1995): Br. J. Pharmacol., 114, 323–328.
Wang, X. E., Watanabe, S., Oide, H., Hirose, M., Itatsu, T., Osada, T., Takazakura, Y., Yokoi, Y. and Sato, N. (1998): Am. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol., 13, S14-S18.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Criado, M., Flores, O., Vázquez, M.J. et al. Role of prostanoids and nitric oxide inhibition in rats with experimental hepatic fibrosis. J. Physiol. Biochem. 56, 181–188 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03179785
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03179785