Abstract
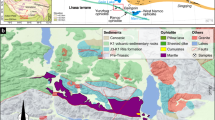
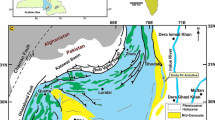
The Upper Jurassic evaporite-carbonate sequence (Sabatayn Formation and its equivalent Madbi Formation or Transition Beds) and its constituent systems tracts have been recognized at the western side of Wadi Al-Jawf-Marib intracratonic rift basin and its adjacent shelf areas. The Sabatayn Formation was subdivided, from the base to the top, into the Shabwa Salt Member, the Layadim Shale Member, the Ayad Gypsum Member and its equivalent M’qah Sandstone Member. The evaporite depositional systems of the lowstand facies (or systems) tract LST began in Middle Kimmeridgian times after the complete drawdown of the shelf area and basin isolation. The effect of ephemeral flooding events of the marine water and/or surface run-off water on the basinal salt pans resulted in the deposition of four or more parasequences (shallowing upward salinas of the Shabwa Salt Member).
When the rift was reconnected to the open ocean in Late Kimmeridgian times, the basinal LST and the formerly exposed carbonate sequence of the shelf area were flooded and an onlapping retrogradational transgressive facies tract (TST) represented by the lagoonal-sabkha Layadim Shale and the Ayad Gypsum members and their equivalent shoals, shallow subtidal to intertidal Madbi Formation were established. The continued relative sea-level rise followed by relative sea-level falls due to orogenic movement during Portlandian times resulted in the deposition of aggradational to progradational offlapping strata of early and late highstand facies tract (HST representing part of the Naifa Formation). On the shelf area, the early HST consists of a subtidal ammonitic limestone which changes westwards into a shallow subtidal-intertidal sandy rippled mudstone containing fossil fish remains and varicolored cross bedded sandy mudstone containing plant remains, while the late HST consists of supratidal to sabkha gypsiferous shale and sandstone with gypsum lenses. However, on the shelf slope, a brecciated ammonitic limestone interbedded with calcareous mudstone containing pelagic fauna represent the forced regressive wedge-systems tracts (FRWST).
Similar content being viewed by others
References
BEYDOUN, Z.R., 1966, Eastern Aden Protectorate and part of Dhufar, in Geology of the Arabian Peninsula:United States Geological survey Professional Paper, v. 560-H, p. 1–48.
BEYDOUN, Z.R., 1988, The Middle East. Regional geology and petroleum resources: Scientific Press LTD, Beaconfield, Bucks, United Kingdom, 340 p.
EL-ANBAAWY, M.I., 1984, Contribution to lithostratigraphic subdivision of the Amran sequence in the Yemen Arab Republic (Y.A.R.):Faculty of Science Bulletin, Sana a, University, v. 4, p. 65–84.
FRIEDMAN, G.M., SANDERS, J.E., and KOPASKA-MERKEL, D.C., 1992. Principles of sedimentary deposits: Stratigraphy and Sedimentology. Macmillan Publishing Company, New York, 649 p.
GEUKENS, F.P., 1966, Geology of the Arabian Peninsula (Yemen):United States Geological survey Professional Paper, v. 560-B, p. 1–23.
HALLAM, A., 1978, Eustatic cycles in the Jurassic:Paleogeography, Paleoclimatology, Paleoecology, v. 23, p. 1–32.
HALLAM, A. and BRADSHAW, M.J., 1979, Bituminous shales and oolitic ironstones as indicators of transgressions and regressions:Journal of the Geological Society of London, v. 136, p. 157–164.
HUDSON, R.G.S., 1954, Jurassic stromatoporoids from southern Arabia:Paris, Mus. nat d’Historie nat. Notes et Mem., sur le Moyen-orient, v. 5, p. 207–221, pls. 6–8.
HUNT, D. and TUCKER, M.E., 1993, Sequence stratigraphy of carbonate shelves with an example from the mid-Cretaceous (Urgonian) of southeast France:In Posamentier, H.W., Summerhayes, C.P., Haq, B.U. and Alen, G.P., eds., Sequence Stratigraphy and Facies Association:Special Publication, International Association of Sedimentologists, v. 18, p. 307–341.
LAMARE, P., BASSE, E., MAURICE, L., and TEILHARD DE CHARDIN, P., 1930. Etudes geologique en Ethiopie, Somalie, et Arabie meridionale:Societee Geologique de France, New Series, v. 6, p. 1–83.
POWERS, R.W., RAMIREZ, L.F., REDMOND, C.D., and ELBERG, J.E.L., 1966, Sedimentary geology of Saudi Arabia, Geology of the Arabian Peninsula:United States Geological Survey Professional Paper, v. 560-D, p. 1–141.
SAINT-MARC, P., 1978. Arabian Peninsula,in Moullade, M. and Nairn A.E.M., eds., The Phanerozoic Geology of the world II. The Mesozoic, (A). Elsevier Scientific Publishing Company, Amsterdam, p. 435–462.
TUCKER, M.E., 1991, Sequence stratigraphy of carbonate-evaporite basins, models and application to the Upper Permian (Zechstein) of northeast England and adjoining North Sea:Journal of the Geological Society of London, v. 148, p. 1019–1036.
VAN WAGONER, J.C., POSAMENTIER, H.W., MITCHUM, R.M., VIAL P.R., SARG, J.F., LOUTIT, T.S., and HARDENBOL, J., 1988, An overview of the fundamentals of sequence stratigraphy and key definitions,in Wilgus, C.K. et al., eds., Sea-level changes, an integrated approach:Special Publication, Society of Economic, Paleontologists and Mineralogists, v. 42, p. 39–45.
VAIL, P.R., MITCHUM, R.M., and THOMPSON, S., 1977, Seismic stratigraphy and global changes of sea level, part four, global cycles of relative changes of sea level:American Association of Petroleum Geologists Memoir 26, p. 83–98.
YOUSSEF, E.A.A. and EL-ANBAAWY, M.I., 1989, Petrography and diagenesis of Jurassic oncolitic limestone in the Amran Group, Yemen Arab Republic:Arab Gulf Journal of Scientific Research: A7, v. 1, p. 51–67.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Youssef, E.S.A.A. Sequence stratigraphy of the upper jurassic evaporite-carbonate: Sequence at the western area of Wadi Al-Jawf-Marib basin, Yemen. Carbonates Evaporites 13, 168–173 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03176590
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03176590