Abstract
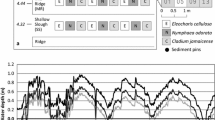
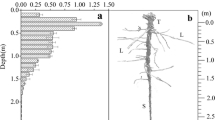
Spartina alterniflora was propagated in buckets of modified salt marsh soil with near-natural cyclic flood/drain regimes to determine effects of soil drainage on the vertical distribution of subsurface tissues. There was a significant correlation between aerial biomass and drainage during the first year but not during the second. No statistically significant correlation was found between soil drainage depth and subsurface tissue distribution either at the end of the first growing season or the second. Well-drained soils led to more uniform vertical distribution, but in general, soil drainage depth had no consistent effect either on distribution of subsurface plant biomass or on aerial: subsurface tissue ratios.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature cited
Boesch, D.F. and R.E. Turner. 1984. Dependence of fishery species on salt marshes: the role of food and refuge. Estuaries 7:460–468.
Bourn, W.S. and C. Cottam. 1950. Some biological effects of tidewater marshes. U.S. Deptartment of Interior, Washington, DC, USA. Report # 19.
Broome, S.W., E.D. Seneca, and W.W. Woodhouse, Jr. 1986. Longterm growth and development of transplants of the salt-marsh grassSpartina alterniflora. Estuaries 9:63–74.
De Laune, R.D., C.J. Smith, and W.H. Patrick, Jr. 1983. Relationship of marsh elevation, redox potential and sulfide toSpartina alterniflora productivity. Journal of the Soil Science Society of America 47:930–935.
De Laune, R.D., C.J. Smith, and M.D. Tolley. 1984. The effect of sediment redox potential on nitrogen uptake, anaerobic root respiration and growth ofSpartina altermiflora Loisel. Aquatic Botany 18:223–230.
Gallagher, J.L. 1974. Sampling macro-organic matter profiles in salt marsh plant root zones. Proceedings of the Soil Science Society of America 38:154–155.
Gallagher, J.L. and F.G. Plumley. 1979. Underground biomass profiles and productivity in Atlantic coast marshes. American Journal of Botany 66:156–161.
Good, R.E., N.F. Good, and B.R. Frasco. 1982. A review of primary production and decomposition dynamics of the below ground component. p. 139–158.In V.S. Kennedy (ed.) Estuarine Comparisons. Academic Press, New York, NY, USA.
Gross, M.F., M.A. Hardisky, P.L. Wolf, and V. Klemas. 1991. Relationship between aboveground and belowground biomass ofSpartina alterniflora (Smooth Cordgrass). Estuaries 14:186–191.
Howes, B.L., R.W. Howarth, J.M. Teal, and I. Valiela. 1981. Oxidation-reduction potentials in a salt marsh: spatial patterns and interactions with primary-production. Limnology and Oceanography 26:350–360.
Moy, L.D. and L.A. Levin. 1991. AreSpartina marshes a replaceable resource? A functional approach to evaluation of marsh creation efforts. Estuaries 14:1–16.
Odum, E.P. and A.A. De la Cruz. 1967. Particulate organic detritus in a Georgia salt marsh-estuarine ecosystem. p. 383–388.In G.A. Lauff (ed.) Estuaries. American Association for the Advancement of Science, Washington, DC, USA. Publication #83.
Posey, M.H., T.D. Alphin, and C.M. Powell. 1997. Plant and infaunal communities associated with a created marsh. Estuaries 20: 42–47.
Teal, J.M. 1962. Energy flow in the salt marsh ecosystem of Georgia. Ecology 43:614–624.
Teal, J.M. and J.W. Kanwisher. 1965. Gas transport in the marsh grassSpartina alterniflora. Journal of Experimental Botany 17: 355–361.
Warren, R.S. and W.A. Niering. 1993. Vegetation change on a northest tidal marsh: interaction of sea-level rise and marsh accretion. Ecology 74:96–103.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Padgett, D.E., Rogerson, C.B. & Hackney, C.T. Effects of soil drainage on vertical distribution of subsurface tissues in the salt marsh macrophyteSpartina alterniflora Lois. Wetlands 18, 35–41 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03161440
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03161440