Abstract
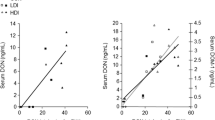
A feeding-trial was conducted to determine the effects of a deoxynivalenol (DON)-contaminated diet in growing pigs. DON was added as either the purified toxin or as naturally contaminated wheat. Growth performance, biochemical and hematological parameters and DON-transformation through intestinal bacteria were monitored throughout the study. Epithelial tissues along the gastro-intestinal tract were also examined for pathological changes and selected enzyme activities (oxoglutarat dehydrogenase, alanine-amino-transferase). There were no differences among the dietary treatments in all parameters measured except for feed intake and weight gain in the naturally contaminated diets fed ad libitum. Effectsin vivo could not be explained exclusively by cytotoxicity of DON foundin vitro. These observations may reflect the presence of other unidentified (toxic) compounds in the naturally contaminated grain or the influence of further factors. In future studies synergistic/additive interactions with substances promoting appetite should be taken into consideration.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature
Rotter BA, Prelusky DB, Pestka JJ (1996) Toxicology of Deoxynivalenol (Vomitoxin). J. Toxicol. Environm. H. 48(1): 1–34
Williams KC, Blaney BJ, Magee MH (1988) Responses of pigs fed wheat naturally infected with Fusarium graminearum and containing the mycotoxins 4-deoxynivalenol and zearalenone. Aust. J. Agric. Res. 39: 1095–1105
Bergsjoe B, Matre T, Nafstad I (1992) Effect of diets with graded levels of deoxynivalenol on performance in growing pigs. J. Vet. Med. A 39: 752–758
Trenholm HL, Foster BC, Charmley LL, Thompson BK, Hartin KE, Coppock RW, Albassam MA (1994) Effects of feeding diets containing Fusarium (naturally) contaminated wheat or pure deoxynivalenol (DON) in growing pigs. Can. J. Anim. Sci. 74: 361–369
Forsyth DM, Yoshizawa T, Mordka N, Tuite J (1977) Emetic and refusal activity of deoxynivalenol in swine. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 34: 547–552
Friend DW, Trenholm HL, Thompson BK, Fiser PS, Hartin KE (1986) Effect of feeding diets containing deoxynivalenol (vomitoxin)-contaminated wheat or corn on the feed consumption, weight gain, organ weight and sexual development of male and female pigs. Can. J. Anim. Sci. 66 (3): 765–775
Arnold DL, McGuire PF, Nera EA, Karpinski KF, Bickis MGM, Zawidzka ZZ, Fernie S, Versonder RF (1986) The toxicity of orally administered deoxynivalenol in rats and mice. Fd. Chem. Toxic. 24(9): 935–941
Dong W, Sell JE, Pestka JJ (1991) Quantitative assessment of mesangial immunoglobulin A (IgA) accumulation, elevated circulating IgA immune complexes, and hematuria during vomitoxin-induced IgA nephropathy. Fund. Appl. Toxicol. 17 (1): 197–207
Dillenburger T, Lauber U, Schollenberger M, Müller HM, Drochner W (2000) Wirkung von Deoxynivalenol beim wachsenden Schwein in Abhängigkeit von der Darreichungsform. Proceedings of 22. Mykotoxin-Workshop, 5.–7. June 2000, Bonn, Germany, Mycotox. Res. 16A(2): 170–173
Lauber U, Dillenburger T, Schollenberger M, Müller HM, Drochner W (2000) Transformation von Deoxynivalenol durch die Darmflora des Schweines — In-vitro Untersuchungen zur Adaptation in Abhängigkeit der Darreichungsform. Mycotox. Res. 16A (No. 2.): 166–169
Madaj M, Lundh T, Lindberg JE (1999) Effect of exposure to dietary Nivalenol on activity of enzymes involved in glutamine catabolism in the epithelium along the gastrointestinal tract of growing pigs. Arch. Anim. Nutr. 00: 1–10
Prelusky DB, Gerdes RG, Underhill KL, Rotter BA (1994) Effects of low-level dietary deoxynivalenol on haemtological and clinical parameters of the pig. Nat. Tox. 2: 97–104
Prelusky DB (1993) The effect of low-level Deoxynivalenol on neurotransmitter levels measured in pig cerebrospinal fluid. J. Environ. Sci. Health, B 28(6): 731–761
Smith TK, McMillan EG, Castillo JC (1997) Effect of feeding blends of fusarium mycotoxin-contaminated grains containing deoxynivalenol and fusaric acid on growth and feed consumption of immature swine. J. Anim. Sci. 75: 2184–2191
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dillenburger, T., Lauber, U., Klobasa, F. et al. Deoxynivalenol in pigs: An exclusive effect on the appetite?. Mycotox Res 17 (Suppl 1), 58–61 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03036713
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03036713