Abstract
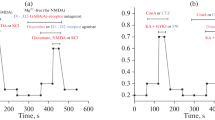
The β-amyloid peptide (Aβ) is centrally related to the pathogenesis of Alzheimer's disease (AD). Previous studies have suggested that the neurotoxicity of Aβ may be related to the over activation of glutamatergic transmission and excitotoxicity, and that blockade of glutamate receptors prevents Aβ-induced cell death. Here, we show that melatonin, a pineal hormone, protects chick retinal neurons in culture against the neurotoxicity of Aβ and glutamate. Right-angle light scattering and thioflavin T fluorescence measurements, as well as light microscopy analysis, indicated that, under our experimental conditions, melatonin had no effect on the aggregation of Aβ. Interestingly, the neuroprotective action of melatonin against the toxicity of Aβ was significantly decreased in the presence of picrotoxin, an antagonist of GABAA-like receptors. By itself, picrotoxin had no effect. These results suggest that the neuroprotective effects of melatonin against Aβ neurotoxicity could be at least in part related to a decrease in the excitatory tonus, mediated by activation of GABA receptors and the resulting hyperpolarization of the neurons. Thus, selective pharmacological manipulation of neuronal excitatory/inhibitory tonus could be a potentially interesting new approach in the treatment of AD.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Blanchard BJ, G Konopka, M Russell and VM Ingram (1997) Mechanism and prevention of neurotoxicity caused by beta-amyloid peptides: relation to Alzheimer's disease.Brain Res. 776, 40–50.
Espinar A, A Garcia-Oliva, EM Isorna, A Quesada, FA Prada and JM Guerrero (2000) Neuroprotection by melatonin from glutamate-induced excitotoxicity during development of the cerebellum in the chick embryo.J. Pineal Res. 28, 81–88.
Lipton SA and PA Rosemberg (1994) Excitatory amino acids as a final common pathway for neurologic disorders.New Engl. J. Med. 330, 613–622.
Louzada PRL, ACP Lima, FG de Mello and ST Ferreira (2001) Dual role of glutamatergic neurotransmission on amyloid Aβ1–42 aggregation and neurotoxicity in embryonic avian retina.Neurosci. Lett. 301, 59–63.
Mattson MP, B Cheng, D Davis, K Bryant, I Liberbug and RE Rydel (1992) β-amyloid peptides destabilize calcium homeostasis and render human cortical neurons vunerable to excitotoxicity.J. Neurosci. 12, 376–389.
Niles LP (1991) Melatonin interaction with the benzodiazepine-GABA receptor complex in the CNS in kinurenine and serotonine pathways: progress in trytophan research.Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 294, 267–277.
Pappolla MA, M Sos, RA Omar, RJ Bick, DL Hickson-Bick, RJ Reiter, S Efthimiopoulos and NK Robakis (1997) Melatonin prevents death of neuroblastoma cells exposed to the Alzheimer amyloid peptide.J. Neurosci. 17, 1683–1690.
Pappolla MA, P Bozner, C Soto, H Shao, NK Robakis, M Zagorski, B Frangioni and J Ghiso (1998) Inhibition of Alzheimer β-fibrilogenesis by melatonin.J. Biol. Chem. 273, 7185–7188.
Pappola MA, MJ Simovich, T Bryant-Thomas, Y-J Chyan, B Poeggler, M Dubocovich, R Bick, G Perry, F Cruz-Sanchez and SA Smith (2002) The neuroprotective effects of melatonin against the Alzheimer β-protein are not mediated by melatonin membrane receptors.J. Pineal Res. 32, 135–142.
Tan DX, LC Manchester, RJ Reiter, W Qi, SJ Kim and GH El-Sokkary (1998) Melatonin protects hippocampal neuronsin vivo against kainic acid-induced damage in mice.J. Neurosci. Res. 54, 382–389.
Tenn CC and LP Niles (1995) Central-type benzodiazepine receptors mediate the antidopaminergic effect of clonazepam and melatonin in 6-hydroxydopamine lesioned rats: involvement of a GABAergic mechanism.J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 274, 84–89.
Tenn CC and LP Niles (1997) Mechanisms underlying the antidopaminergic effect of clonazepam and melatonin in striatum.Neuropharmacology 36, 1659–1663.
Westlind-Danielsson AW and G Arnerup (2001) Spontaneousin vitro formation of supramolecular β-amyloid structures, “β-amy balls”, by β-amyloid 1–40 peptide.Biochemistry 40, 14376–14743.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lima, A.C.P., Louzada, P.R., De Mello, F.G. et al. Neuroprotection against Aβ and glutamate toxicity by melatonin: Are GABA receptors involved?. neurotox res 5, 323–327 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03033152
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03033152