Abstract
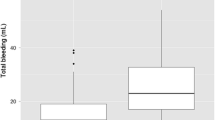
Surgery to the nasal septum and to the turbinates constitutes a significant part of the workload of an otolaryngologist. The patient invariably experiences short-term nasal obstruction following such surgery and different medications are commonly used to relieve this and to promote a sense of airway patency. However the efficacy of topical and systemic medication, given in the post-operative period is hot well documented. A prospective randomized trial was therefore undertaken to compare the efficacy of a topically applied vasoconstrictor and an anticholinergic agent in reducing the sensation of airway obstruction in the first week following simple nasal airway surgery. 0.5% Ephedrine hydrochloride nasal drops, Pseudoephedrine tablets and a combination of the two were compared to a control group who received no treatment. Eighty patients were randomised into four groups and nasal patency assessed by patients using a visual analogue sacle (VAS). When compared to the control group both medications were effective in relieving nasal congestion but a combination of topical and systemic therapy, given together, was superior to either agent used alone. The results achieved were independent of the seniority of the surgeon undertaking the operation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Low, W.K., Willat, D.J. (1992) Submucuos resection for deviated nasal septum: a critical appraisal.Singapore Medical Journal 33(6): 617–619.
Maran, A.G.D. (1986) Septoplasty. InRob and Smith’s Operative Surgery. 4th Edition. (Dudley, H., Carter, D., eds), Butterworths, London, pp 61–65.
Spraggs, P.D.R., Macnamara, M., Joseph, T. (1995) A Prospective randomised study to assess the efficacy of post-operative nasal medication after endonasal surgery.The Journal of Laryngology and Otology 109:618–621.
Stammberger, H., Hawke, M. (1993) Post-operative care. InEssentials of Functional Endoscopic Sinus Surgery, (Hurley, D., Taeyaerts, K.F. eds) Mosby-Year Book, U.S.A. pp 186–187.
Williams, R.A. (1986) Submucous resection of the septum. InRob and Smith’s Operative Surgery, 4th Edition (Dudley, H., Carter, D., eds), Butterworths, London, p 58.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kalan, A., Kenyon, G.S. & Pelekoudas, N. A prospective randomised study to assess the efficacy of differenct medications for relief of post-operative nasal obstruction. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 53, 210–212 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03028556
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03028556