Abstract
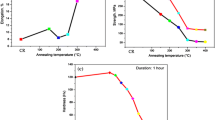
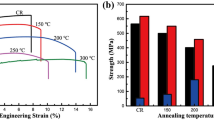
Effects of the annealing temperature on microstructures and mechanical properties of 5052 Al alloy that have received 88% reduction at cryogenic temperature were investigated for an annealing temperature range of 150–300°C, in comparison with those at room temperature. Equiaxed grains, approximately 200nm in diameter, were observed in 5052 Al alloy deformed 88% and annealed at 200°C for 1 h. When compared with the deformation at room temperature, the deformation at cryogenic temperature showed higher strengths and equivalent elongation after annealing at temperatures below 200°C. However, for annealing above 250°C, materials deformed at cryogenic temperature showed lower strength than those deformed at room temperature. This behavior might be attributable to the higher rate of recrystallization and growth in materials deformed at cryogenic temperature during annealing, due to the lager density of dislocations accumulated during the deformation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. Furukawa, Z. Horita, and T. G. Langdon,Met. Mater.-Int. 9, 141 (2003).
I. V. Alexandrov, A. A. Dubravina, A. R. Kilmametov, V. U. Kazykhanov, and R. Z. Valiev,Met. Mater.-Int. 9, 151 (2003).
N. Tsuji, Y. Ito, Y. Saito, and Y. Minamono,Scripta mater. 47, 893 (2002).
R. Valiev,Met. Mater.-Int. 7, 413 (2001).
I. Alexandrov,Met. Mater.-Int. 7, 565 (2001).
Y. Saito, H. Utsunomiya, and T. Sakai,Acta mater. 47, 579 (1999).
R. Z. Valiev, R. K. Islamgaliev, and I. V. Alexandrov,Prog. Mater. Sci. 45, 103 (2000).
Z. Y. Liu, L. X. Hu, and E. D. Wang,Mater. Sci. Eng. A. 255, 16 (1998).
M. Richert, Q. Liu, and N. Hansen,Mater. Sci. Eng. A. 260, 275 (1999).
Y. Wang, M. Chen, F. Zhou, and E. Ma,Nature 419, 912 (2002).
K. T. Park and D. H. Shin,Matall. Mater. Trans. A 33, 705 (2002).
J. S. Hayes, R. Keyte, and P. B. Prangnell,Mater. Sci. & Tech. 16, 1259 (2000).
D. G. Morris, and M. A. Munoz-Morris,Acta materialia,50, 4047 (2002).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, Y.B., Shin, D.H. & Nam, W.J. Effect of deformation temperature on the formation of ultrafine grains in the 5052 Al alloy. Met. Mater. Int. 10, 407–410 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03027340
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03027340