Abstract
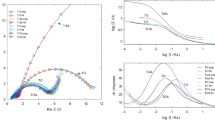
In order to investigate the effect of the equilibrium hydrogen pressure (plateau pressure) of metal hydride (MH) alloys on self-discharge behavior, V09Ti01 alloys having multi-plateau pressures (the low and high plateau pressure) have been used as working electrodes in a half cell. A thermal desorption experiment and open-circuit potential monitoring were conducted to observe the self-discharge behavior of the electrodes. From the thermal desorption spectra of fully charged and discharged V09Ti01 electrodes (to-0.7 V vs. Hg/ HgO), it was found that only the high plateau pressure region from V09Ti01 electrodes is electrochemically useful in battery application. However, the open-circuit potential change and thermal desorption spectra of V09Ti01 electrodes after various open-circuit storage periods prove that self-discharge behavior is caused by hydrogen desorption from the low plateau pressure region (10-8 atm) as well as the high plateau pressure region (0.1 atm). Therefore, it is suggested that the self-discharge behavior of V09Ti01 electrodes cannot be suppressed effectively by reduction of the plateau pressure of alloys through alloy modification.In addition, the pressure-composition-isotherms (P-C-T) of the low pressure region can be estimated by using the open-circuit potential corresponding to this region in Nernst’s equation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. J. G. Willems and K. H. J. Buschow,J. Less-Common Met. 129, 13 (1987).
J. J. G. Willems,Philips Tech. Rev. 43, 22 (1986).
Y. Q. Lei, Z. P. Li, P. Chen, J. Wu and Q. D. Wang,J. Less-Commen Met. 172–174, 1265 (1991).
T. Sakai, T. Hazama, H. Miyamura, N. Kuriyama, A. Kato and H. Ishikawa,J. Less-Commen Met. 172–174, 1175 (1991).
T. Sakai, H. Ishikawa, K. Oguro, C. Iwakura and H. Yoneyama,J. Electrochem. Soc. 134, 558 (1987).
Iwakura, Y. Kajiya, H. Yoneyama, T. Sakai, K. Oguro, H. and H. Ishikawa,J. Electrochem. Soc. 134, 1351 (1989).
Z. Mao, A. Visintin, S. Srinivasan, A. J. Appleby and H. S. Lim,J. Appl. Electrochem. 22, 409 (1992).
S. Venkatesan, B. Reichman and M.A. Fetencko, US Patent 4 728 586, 1988; S. Ovshinsky, P. Gifford, S. Venkatesan, M. A. Fetencko, D. Corrigan and S. Dhar,10th Int. Seminar on Primary and Secondary Battery Technology and Application, Deerfield Beach, FL (1993).
J. H. Lee, K. Y. Lee, S. M. Lee and J. Y. Lee,J. Alloys 221, 174(1995).
D. M. Kim, K. Y. Lee and J. Y. Lee,J. Alloys 231, 650(1995).
H. Wenzl,J. Less-Commen Met. 89, 489 (1983).
M. H. J. Van Rijswick,Proc. Int. Symp. on Hydrides for Energy Storage, p. 261, Ge: 10, Norway (1997).
S. R. Kim,Ph. D. Thesis, KAIST, Taejon, Korea (1993).
J. H. Lee, K. Y. Lee and J. Y. Lee,J. Alloys 232, 197(1996).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jung, JH., Lee, HH., Yu, JS. et al. Self-discharge mechanism of vanadium-titanium metal hydride electrodesfor Ni-MH rechargeable battery. Metals and Materials 3, 178–182 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03025959
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03025959