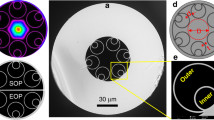
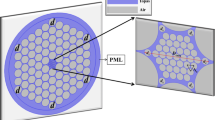
Abstract
The main modelling methods devoted to microstructured air-silica optical fibres (MOFS) are presented and discussed. Then, the specific propagation properties ofMOFS are studied in detail. Characteristics measured on fibres manufactured in our laboratory or reported in the literature are analysed. A large number of potential and demonstrated applications are presented and the obtained performances are discussed. A particular attention is given to hollow-core photonic bandgap fibres and their applications.
Résumé
Les principales méthodes de modélisation appliquées aux fibres microstructurées airsilice (FMAS) sont présentées et discutées. Puis les propriétés de propagation spécifiques desFMAS sont détaillées. Les caractéristiques mesurées sur les fibres fabriquées au laboratoire ou rapportées dans la littérature sont analysées. Un grand nombre d’applications potentielles ou démontrées sont présentées et les performances obtenues sont discutées. Une attention particulière est accordée aux fibres à cœur creux à bande interdite photonique et à leurs applications.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yeh (P.), Yariv (A.), Marom (E.), Theory of Bragg fiber,Journal of Optical Society of America,68, no 9, pp. 1196–1201, (1978).
Bréchet (F.), Roy (P.), Marcou (J.), Pagnoux (D.), Single-mode propagation into depressed-core photonicbandgap fibre designed for zero-dispersion propagation at short wavelengths,Electronics Letters,36, no 6, pp. 514–515, (2000).
Marcou (J.),Roy (P.), Monomode photonic bandgap fibres for dispersion shifting towards short wavelengths, proceedings ofEuropean Conference on Optical Communications, Nice, 26–30 september 1999.
Bréchet (F.), Leproux (P.), Roy (P.), Marcou (J.), Pagnoux (D.), Analysis of bandpass filtering behaviour of singlemode depressed-core-index photonic -bandgap fibre,Electronics Letters,36, no 10, pp. 870–872, (2000).
Hart (S.D.), Maskaly (G.R.), Temelkuran (B.), Prideaux (P.H.), Joannopoulos (J.D.), Fink (Y), External reflection from omnidirectional dielectric mirror fibers,Science,296, pp. 510–513, (2002).
Birks (T.A.), Roberts (P.J.), Russell (P. St. J.), Atkin (D.M.), Shepherd (T.J.), Full 2-D photonic bandgaps in silica/air structures,Electronics Letters,31, no 22, pp 1941–1943 (1995).
Roberts (P.J.),Birks (T.A.),Russell (P.St.J.),Shepherd (T.J.),Atkin (D.M.), Two-dimensional photonic band-gap structures as quasi-metals,Optics Letters,21, no 7, (1996).
Yablonovitch (E.), Photonic bandgap structures,Journal of Optical Society of AmericaB, 10, p 283, (1993)
Knight (J.C.), Birks (T.A.), Russell (P.St.J.), Atkin (D.M.), All-silica single-mode fiber with photonic crystal cladding,Optics Letters,21, no 19, pp. 1547–1549, (1996).
Birks (T.A.), Knight (J.C.), Russell (P.St.J.), Endlessly single-mode photonic crystal fiber,Optics Letters,22, no 13, pp. 961–963, (1997).
Russell (P.St.J.), Holey new fibres, tutorial TuL1,OFC 2001, Anaheim, 20 March 2001.
Birks (T.A.), Knight (J.C.), Mangan (B.J.) Russell (P.St.J.), photonic crystal fibres: an endless variety,IEICE trans. Electron.,E84-C, no 5, pp. 585–592, (2001).
Bréchet (F), Marcou (J), Pagnoux (D), Roy (P), Complete analysis of the propagation characteristics into photonic crystal fibers by the finite element method,Optical Fiber Technology,6, no 2, pp. 181–191, (2000).
Knight (J.C.), Birks (T.A.), Cregan (R.F.), Russell (P.St.J.), Desandra (J.P.), Large mode area photonic crystal fibre,Electronics Letters,34, no 13, pp. 1347–1348, (1998).
Février (S.),Hilaire (S.),Marcou (J.),Pagnoux (D.),Peyrilloux (A.),Roy (P.), Modélisation simplifiée des fibres à cristal photonique par la méthode de l’indice moyenné en azimut,OPTIX 2001, Marseille, 26–28 novembre 2001.
Peyrilloux (A.), Février (S.), Marcou (J.), Berthelot (L.), Pagnoux (D.), Sansonetti (P.), Comparison between the finite element method, the localized function method and a novel equivalent averaged index method for modelling photonic crystal fibres,Journal of Optics A: Pure and applied optics,4, pp. 257–262, (2002).
Argyros (A.),Bassett (I.A.),Van Eijkelenborg (M.A.),Large (M.C.J.),Zagari (J.),Nicorovici (N.A.P.),Mcphedran (R.C.),Martijn De Sterke (C.), Ring structures in microstructured polymer optical fibres,Optics Express,9, no 13, (2001).
Silvestre (F.), Andrès (M.V.), Andrès (P.), Biorthonormal-basis method for the vector description of opticalfibre modes,Journal of Lightwave Technology,LT-16, pp. 923–928, (1998).
Ferrando (A.), Silvestre (F.), Miret (J.J.), Andrès (P.), Andrès (M.V.), Full-vector analysis of a realistic photonic crystal fiber,Optics Letters,24, no 5, pp. 276–278, (1999).
Broeng (J.), Barkou (S.E.), Sondegaard (T.), Bjarklev (A.), Analysis of air-guiding photonic bandgap fibers,Optics Letters,25, no 2, pp. 96–98, (2000).
Ferrando (A.), Silvestre (F.), Miret (J.J.), Monsoriu (J.A.), Andrès (M.V.), Russell (P.St.J.), Designing a photonic crystal fibre with flattened chromatic dispersion,Electronics Letters,35, no 4, pp. 325–327, (1999).
Monro (T.M.), Richardson (D.J.), Broderick (N.G.R.), Bennett (P.J.), Holy optical fibers: an efficient modal model,Journal of Lightwave Technology,17, no 6, pp. 1093–1102, (1999).
Monro (T.M.), Richardson (D.J.), Broderick (N.G.R.), Bennett (P.J.), Modeling large air fraction holey optical fibers,Journal of Lightwave Technology,18, no 1, pp. 50–56, (2000).
Monro (T.M.), Bennett (P.J.), Broderick (N.G.R.), Richardson (D.J.), Holey fibers with random cladding distribution,Optics Letters,25, no 4, pp. 206–208, (2000).
White (T.P.), Kuhlmey (B.), Mcphedran (R.C.), Maystre (D.), Renversez (G.), Martijn De Sterke (C.), Botten (L.C.), Multipole method for microstructured optical fibers I: formulation,Journal of Optical Society of AmericaB, 10, no 19, pp. 2322–2330, (2002).
Kuhlmey (B.), White (T.P.), Renversez (G.), Maystre (D.), Botten (L.C.), Martijn De Sterke (C.), Mcphedran (R.C.), Multipole method for microstructured optical fibers II: implementation and results,Journal of Optical Society of AmericaB, 10, no 19, pp. 2331–2340, (2002).
Kuhlmey (B.),Renversez (G.),Maystre (D.), chromatic dispersion and losses of microstructured optical fiber, Applied Opticsot, in press, (2003).
Maystre (D.), Vincent (P.), diffraction d’une onde électromagnétique plane par un objet cyclindrique non infiniment conducteur de section arbitraire,Optics Communications,5, no 5, pp. 327–330, (1972).
Aubourg (M.), Guillon (P.), A mixed finite element formulation for microwave devices problems; application to MIS structure,Journal of Electromagn. Waves Appl.,5, pp. 371–375, (1991).
Bréchet (F.), Marcou (J.), Pagnoux (D.), Roy (P.), Complete analysis of the propagation characteristics into photonic crystal fibers by the finite element method,Optical Fiber Technology,6, no 2, pp. 181–191, 2000.
Steel (M.J.), White (T.P.), Martijn De Sterke (C.), Mcphedran (R.C.), Botten (L.C.), Symmetry and degeneracy in microstructured optical fibers,Optics Letters,26, no 8, pp. 488–490, (2001).
Peyrilloux (A.),Chartier (T.),Hideur (A.),Berthelot (L.),Melin (G.),Gasca (L.),Pagnoux (D.),Roy (P.), Theoretical and experimental study of the birefringence of a photonic crystal fiber, to be published inJournal of Lightwave Technology.
Peyrilloux (A.),Pagnoux (D.),Sansonetti (P.), Modelling of photonic crystal fibres by means of the finite elements method, proceedings of the 2ndElectromagnetic Optics Symposium, Paris, 26–30 august 2001.
Feit (M.D.), Fleck (J.A.), computation of mode properties in optical fiber waveguides by a propagating beam method,Applied Optics,19, pp. 1154–1164, (1980).
Leproux (P.),Bréchet (F.),Doya (V.),Roy (P.),Pagnoux (D.),Marcou (J.),Mortessagne (F.), Méthodes de modélisation appliquées aux fibres à cristal photonique,19è Journées Nationales d’Optique Guidée, Limoges (F), 6–8 décembre 1999.
Fogli (F.),Saccomandi (L.),Bassi (P.),Bellanca (G.),Trillo (S.), Full vectorialbpm modeling in index-guiding photonic crystal fibers and couplers,Optics Express,10, no 1, (2002).
Renversez (G.), Study of microstructured optical fibers using the multipole method, private communication
Gander (M.J.), Mcbride (R.), Jones (J.C.D.), Mogilevtsev (D.), Birks (T.A.), Knight (J.C.), Russell (P.St.J.), Experimental measurement of group velocity dispersion in photonic crystal fibre,Electronics Letters,35, no 1, pp. 63–64, (1999).
Peyrilloux (A.),Berthelot (L.),Pagnoux (D.),Sansonetti (P.), Comparison between two methods used for modelling photonic crystal fibres,2nd Electromagnetic Optics Symposium, Paris, 26–30 August 2001.
White (T.P.), Mcphedran (R.C.), De Sterke (C.M.), Confinement losses in microstructured optical fibers,Optics Letters,26, no 21, pp. 1660–1662, (2001).
Bennett (P.J.), Monro (T.M.), Richardson (D.J.), Toward practical holey fiber technology: fabrication, splicing, modeling, and characterization,Optics Letters,24, no 17, pp. 1203–1205, (1999).
Tajima (K.),Nakajima (K.),Kurokawa (K.), Low-loss photonic crystal fibers, proceedings ofEuropean Conference on Optical Communications, paper 1.2, Copenhagen, 8–12 September 2002.
Farr (L.),Knight (J.C.),Mangan (B.J.),Roberts (P.J.), Low-loss photonic crystal fibre, proceedings ofEuropean Conference on Optical Communications, paper PD13., Copenhagen, 8–12 September 2002.
Hasegawa (T.), Sasaoka (E.), Onishi (M.), Nishimura (M.), Hole-assisted lightguide fiber for large anomalous dispersion and low optical loss,Optics Express,9, no 13, pp. 681–686, (2001).
Van Eijkelenborg (M.A.), Canning (J.), Ryan (T.), Lyytikainen (K.), Bending-induced colouring in a photonic crystal fibre,Optics Express,7, no 2, pp. 88–94, (2000).
Broeng (J.), Barkou (S.E.), Bjarklev (A.), Sondergaard (T.), Knudsen (E), Review paper: Crystal Fibre Technology, DOPS-NYT2, pp. 22–28, (2000).
Marcou (J.),Pagnoux (D.),Bréchet (F.),Leproux (P.),Roy (P),Peyrilloux (A.), Theoretical and experimental study of light propagation into novel fibres designed for the management of the chromatic dispersion, proceedings ofPhotonics 2000, Calcutta, 18–20 december 2000.
Marcou (J.),Peyrilloux (A.),Bréchet (F.),Pagnoux (D.),Roy (P),Février (S.),Mélin (G.),Chartier (T.), Bragg fibers and microstructured air-silica fibres for the management of the chromatic dispersion: modelling and experimentation, proceedings ofPIERS 2000, invited paper, Boston, 5–7 july 2002.
Ferrando (A.), Silvestre (E.), Miret (J.J.), Andrès (P.), Nearly zero ultraflattened dispersion in photonic crystal fibers,Optics Letters,25, no 11, pp. 790–792, (2000).
Koch (F.),Chernikov (S.V.),Taylor (J.R.), Dispersion measurement in optical fibres over the entire spectal range from 1.1µm to 1.7µm,Optics Communications, no 175, pp. 209–213, (2000).
François (P.L.), Alard (F.), Monerie (M.), Chromatic dispersion measurement from Fourier transform of white-light interference pattern,Electronics Letters,23, pp. 357–358, (1987).
Diddams (S.), Diels (J.C.), Dispersion measurements with white-light interferometry,Journal of Optical Society of AmericaB, 13, no 6, pp. 1120–1129, (1996).
Reeves (W.H.),Knight (J.C.),Russell (P.St.J.),Roberts (P.J.), Demonstration of ultra-flattened dispersion in photonic crystal fibers,Optics Express,10, no 14, pp. 609–613.
Gander (M.J.), Mcbride (R.), Jones (J.D.C.), Mogilevtsev (D.), Birks (T.A.), Knight (J.C.), Russell (P.St.J.), Experimental measurement of group velocity dispersion in photonic crystal fibre,Electronics Letters,35, no 1, pp. 63–64, (1999).
Russell (P.St.J.), Holey new fibres,Optical Fiber Conference, tutorial TuL, Anaheim, 20 mars 2001.
Knight (J.C.), Arriaga (J.), Birks (T.A.), Ortigosa-Blanch (A.), Wadsworth (W.J.), Russell (P.St.J.), Anomalous dispersion in photonic crystal fibres,IEEE Photonics Technology Letters,12, pp. 870–809, (2000).
Andersen (P.A.),Paulsen (H.N.),Larsen (J.J.), A photonic crystal fibre with zero dispersion at 1064nm, proceedings ofEuropean Conference on Optical Communications, paper 3.4.6., Copenhagen, 8–12 September 2002.
Libori (S.B.),Knudsen (E.),Bjarklev (A.),Simonsen (H.R.), High-birefringent photonic crystal fiber,Optical Fiber Conference, paper TuM2, Anaheim, 19–22 mars 2001.
Cucinotta (A.), Selleri (S.), Vincetti (L.), Zoboli (M.), Perturbation analysis of dispersion properties in photonic crystal fibers through the finite element method,Journal of Lightwave Technology,20, no 8, pp. 1433–1442, (2002).
Chartier (T.), Hideur (A.), Ozkul (C.), Sanchez (F.), Stephan (G.), Measurement of the elliptical birefringence of single-mode optical fibers,Applied optics,40, no 30, pp. 5343–5353, (2001).
Wegmuller (M.),Von Der Weid (J.P.),Oberson (P.),Gisin (N.), High resolution fiber distributed measurements with coherent OFDR, proceedings ofEuropean Conference on Optical Communications, paper 11.3.4, pp. 109–110, Amsterdam, 1–3 October 2001.
Niemi (T.),Ludvigsen (H.),Scholder (F.),Legré (M.),Wegmuller (M.),Gisin (N.),Jensen (J.R.),Petersson (A.),Skovgaard (P.M.W.), Polarization properties of single-moded, large-mode area photonic crystal fibers, proceedings ofEuropean Conference on Optical Communications, paper 1.9, Copenhagen, 8–12 September 2002.
Ortigosa-Blanch (A.), Knight (J.C.), Wadsworth (W.J.), Arriaga (J.), Mangan (B.J.), Birks (T.A.), Russell (P.St.J.), Highly birefringent photonic crystal fibers,Optics Letters,25, no 18, pp. 1325–1327, (2000).
Mortensen (N.A.), Effective area of photonic crystal fibers,Optics Express,10, no 7, pp. 341–348, (2002).
Knight (J.C.), Birks (T.A.), Cregan (R.F.), Russell (P.St.J.), De Sandro (J.P.), Large mode area photonic crystal fibre,Electronics Letters,34, no 13, pp. 1347–1348, (1998).
Ranka (J.K.), Windeler (R. S.), Stentz (A.J.), Visible continuum generation in air-silica microstructure optical fibers with anomalous dispersion at 800nm,Optics Letters,25, no 1, pp. 25–27, (2000).
Fevrier (S.),Albert (A.),Louradour (F.),Roy (P.),Pagnoux (D.),Barthélémy (A.), Fibres optiques non-linéaires microstructurées pour source lumineuse blanche d’impulsions femtosecondes, proceedings ofCOLOQ 2001, Rennes, 5–7 september 2001.
Monro (T.M.),Finazzi (V.),Belardi (W.),Kiang (K.M.),Lee (J.H.),Richardson (D.J.), Highly nonlinear holey optical fibres: design, manufacture and device applications, proceedings ofEuropean Conference on Optical Communications, paper 1.5, Copenhagen, 8–12 september 2002.
Birks (T.A.), Roberts (P.J.), Russell (P.St.J.), Atkin (D.M.), Shepherd (T.J.), Full 2-D photonic bandgaps in silica/air structures,Electronics Letters,31, no 22, pp. 1941–1943, (1995).
Barkou (S.E.), Broeng (J.), Bjarklev (A.), Silica-air photonic crystal fiber design that permits waveguiding by true photonic bandgap effect, Optics Letters,24, no 1, pp. 46–48, (1999).
Knight (J.C.), Broeng (J.), Birks (T.A.), Russell (P.St.J.), Photonic band gap guidance in optical fibers,Science,282, pp. 1476–1478, (1998).
Cregan (R.F.), Mangan (B.J.), Knight (J.C.), Birks (T.A.), Russell (P.St.J.), Roberts (P.J.), Allan (D.C.), Single mode photonic band gap guidance of light in air,Science,285, pp. 1537–1539, (1999).
West (J.A.),Fajardo (J.C.),Gallagher (M.T.),Koch (K.W.),Borrelli (N.F.),Allan (D.C.), Demonstration ofir-optimized air-core photonic band-gap fiber, proceedings ofEuropean Conference on Optical Communications, pp. 41–42, Munich, 3–7 September 2000.
West (J.A.),Venkataraman (N.),Smith (C.M.),Gallagher (M.T.), Photonic crystal fibres, proceedings ofEuropean Conference on Optical Communications, paper Th A22, Amsterdam, 30 sept.–4 oct. 2001.
Venkataraman (N.),Gallagher (M.T.),Smith (C.M.),Müller (D.),West (J.A.),Koch (K.W.),Faiardo (J.C.), Low loss (13dB/km) air core photonic band-gap fibre, proceedings ofEuropean Conference on Optical Communications, paperpd1.1, Copenhagen, 8–12 september 2002.
Selleri (S.),Cucinotta (A.),Poli (F.),Vincetti (L.),Zoboli (M.), Amplification properties of erbium doped photonic crystal fibers, proceedings ofEuropean Conference on Optical Communications, holey fibres symposium, paper 1.8, Copenhagen, 8–12 september 2002.
Sondergaard (T.), Photonic crystal distributed feedback fiber lasers with Bragg gratings,Journal of Lightwave Technology,18, no 4, pp. 589–597, (2000).
Furosawa (K.), Malinowski (A.), Price (J.H.V.), Monro (T.), Sahu (J.K.), Nilsson (J.), Richardson (D.J.), Cladding pumped Ytterbium-doped laser with holey inner and outer cladding,Optics Express,9, no 13, pp. 714–720, (2001).
Cregan (R.F.), Knight (J.C.), Russell (P.St.J.), Roberts (P.J.), Distribution of spontaneous emission from an Er3+-doped photonic crystal fiber,Journal of Lightwave Technology,17, no 11, pp. 2138–2141, (1999).
Wadsworth (W.J.), Knight (J.C.), Reeves (W.H.), Russell (P.St.J.), Arriaga (J.), Yb3+-doped photonic crystal fibre laser,Electronics Letters,36, no 17, pp. 1452–1454, (2000).
Glas (P.), Fisher (D.), Cladding pumped large-mode-area Nd-doped holey fiber laser,Optics Express,10, no 6, pp. 286–290, (2002).
Wadsworth (W.J.), Percival (R.M.), Bouwmans (G.), Knight (J.C.), Russell (P.St.J.), High power air-clad photonic crystal fibre laser,Optics Express,11, no 1, pp. 48–53, (2003).
Leproux (P.), Février (S.), Doya (V.), Roy (P.), Pagnoux (D.), Modeling and optimization of double clad fiber amplifiers using chaotic propagation of the pump,Optical Fiber Technology,7, no 4, pp. 324–339, (2001).
Holswarth (R.), Zimmermann (M.), Udem (T.), Hansch (T.W.), Russbuldt (P.), Gäbel (K.), Poprawe (R.), Knight (J.C.), Wadsworth (W.J.), Russell (P.St.J.), White-light frequency comb generation with a diodepumped Cr:LiSAF laser,Optics Letters,26, no 17, pp. 1376–1378, (2001).
Provino (L.),Dudley (J.M.),Maillotte (H.),Grossard (N.),Windeler (R.S.),Eggleton (B.J.), Compact broadband continuum source based on microchip laser pumped microstructured fibre,Electronics Letters,37, no 9, (2001).
Fedotov (A.B.), Naunov (A.N.), Zheltikov (A.M.), Bugar (I.), Chorvat (D.) Jr.,Chorvat (D.), Tarasevitch (A.P.), Von Der Linde (D.), Frequency-tunable supercontinuum generation in photonic-crystal fibers by femtosecond pulses of an optical parametric amplifier,Journal of the Optical Society of AmericaB, 19, no 9, pp. 2156–2164, (2002).
Holswarth (R.), Udem (T.), Hänsch (T.W.), Knight (J.C.), Wadsworth (W.J.), Russell (P.St.J.), Optical frequency synthesizer for precision spectroscopy,Physical Review Letters,85, pp. 2264–2266, (2000).
Sharping (J.E.), Fiorentino (M.), Kumar (P.), Windeler (R.S.), All-optical switching based on cross phase modulation in microstructure fiber,IEEE Photonics Technology Letters,14, pp. 77–79, (2002).
Lee (J.H.),Zulfadzli (Y.),Belardi (W.),Monro (T.M.),Thomsen (B.),Richardson (D.J.), HOley fiber based tunableWDM wavelength converter using cross-phase modulation and filtering. Proceedings ofEuropean Conference on Optical Communications, paper 3.4.3, Copenhagen, 8–12 september 2002.
Liu (X.), Xu (C.), Knox (W.H.), Chandalia (J.K.), Eggleton (B.J.), Kosinski (S.G.), Windeler (R.S.), Soliton self-frequency shift in a short tapered air-silica microstructure fiber,Optics Letters,26, no 6, pp. 358–360, (2001).
Sharping (J.E.), Fiorentino (M.), Kumar (P.), Windeler (R.S.), Optical-parametric oscillator based on four-wave mixing in microstructure fiber,Optics Letters,27, no 19, pp. 1675–1677, (2002).
Lee (J.H.), Yusoff (Z.), Belardi (W.), Ibsen (M.), Monro (T.M.), Richardson (D.J.), Investigation of brillouin effects in small-core holey fiber: lasing and scattering,Optics Letters,27, no 11, pp. 927–929, (2002)
Benabid (F.), Knight (J.C.), Antonopoulos (G.), Russell (P.St.J.), Stimulated raman scattering in hydrogen-filled hollow-core photonic crystal fiber,Science,298, pp. 399–402, (2002).
Eggleton (B.J.), Westbrook (P.S.), Windeler (R.S.), Spälter (S.), Strasser (T.A.), Grating resonances in air-silica microstructured optical fibers,Optics Letters,24, no 21, pp. 1460–1462, (1999).
Kakarantzas (G.), Birks (T.A.), Russell (P.St.J.), Structural long-period gratings in photonic crystal fibers,Optics Letters,27, no 12, pp. 1013–1015, (2002).
Humbert (G.), Malki (A.), Février (S.), Roy (P.), Pagnoux (D.), Electric arc-induced long period gratings in Ge-free air-silica microstructure fibres,Electronics Letters,39, no 4, pp. 349–350, (2003).
Chandalia (J.K.), Eggleton (B.J.), Windeler (R.S.), Kosinski (S.G.), Liu (X.), Xu (C.), Adiabatic coupling in tapered air-silica microstructured optical fiber,IEEE Photonics Technology Letters,13, pp. 55–54, (2001).
Eggleton (B.J.), Kerbage (C.), Westbrook (P.S.), Windeler (R.S.), Hale (A.), Microstructured optical devices,Optics Express,9, no 13, pp. 698–713, (2001).
Kerbage (C.), Hale (A.), Yablon (A.), Windeler (R.S.), Eggleton (B.J.), Integrated all-fiber variable attenuator based on hybrid microstructure fibers,Applied Physics Letters,79, pp. 3191–3193, (2001).
Kerbage (C.), Eggleton (B.J.), Numerical analysis and experimental design of tunable birefringence in microstructured optical fiber,Optics Express,10, no 5, pp. 246–255, (2002).
Mangan (B.J.), Knight (J.C.), Birks (T.A.), Russell (P.St.J.), Greenaway (A.H.), Experimental study of dual-core photonic crystal fibre,Electronics Letters,36, no 16, pp. 1358–1359, (2000).
Van Eijkelenborg (M.A.),Large (M.C.J.),Argyros (A.),Zagari (J.),Manos (S.),Issa (N.A.),Bassett (I.A.),Fleming (S.),Mcphedran (R.C.),Martijn De STerke (C.),Nicorovici (N.A.P.), Microstructured polymer optical fibres,Optics Express,9, no 7, (2001).
Monro (T.M.),West (Y.D.),Hewak (D.W.),Broderick (N.G.R.),Richardson (D.J.), Chalcogenide holey fibres,Electronics Letters,36, no 24, (2000).
Benabid (F.), Knight (J.C.), Russell (P.St.J.), Particle levitation and guidance in hollow-core photonic crystal fiber,Optics Express,10, no 21, pp. 1195–1203, (2002).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pagnoux, D., Peyrilloux, A., Roy, P. et al. Microstructured air-silica fibres: Recent developments in modelling, manufacturing and experiment. Ann. Télécommun. 58, 1238–1274 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03001731
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03001731
Key words
- Optical fiber
- Compound structure
- Photonic crystal
- Periodic structure
- Modeling
- Optical fiber cladding
- Manufacturing
- Optical properties
- Transmission characteristic
- Optical component