Abstract
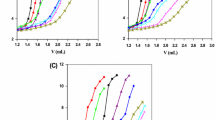
The effect of a wide array of positively charged compounds, comprising antibiotics, basic proteins, metal coordinates and drugs, on the activity of pancreatic ribonuclease has been studied. All the tested compounds inhibit the enzyme activity in a range of 30-70%, when used in optimal concentrations at pH 4.8. The fall in the enzyme activity in homogeneous mileu could be due to the inhibition of the enzyme by these polycations or to an altered state of the substrate on reacting with polycations. For this purpose, optimal conditions for complexation of RNA with these polycations were determined, and the rates of hydrolysis of the insolubilized RNA by RNase have been monitored in a heterogeneous system. The highest rate of hydrolysis is obtained in the case of protamine-RN A (11 %) and the lowest in the case of propamidine-RNA (3%). Rates of hydrolysis of insolubilized RNA show an exponential fall when the reaction is prolonged up to 2 h. Moreover, the level of inhibition obtained in all the cases was nearly the same, despite considerable variance in size and conformation of the compounds used. It is proposed that these compounds, on complexing with RNA, make the hydrolyzable bonds unavailable by forming a protective layer upon the RNA surface. Biological implications of these investigations are also discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Singh, C. (1970) Ind. J. Biochem. 7: 255.
Eisinger, J., Bell. Teleph. Co. (U.S.A.), personal communication.
Singh, C. (1971) Ind. J. Biochem. Biophys. 8: 71.
Singh, C., andMishra, J. (1978) Arzneim-Forsch 28: 1320.
Ehrenpreis, S. (1970)(itIn) Progress in Drug Research, Vol. 14,Ariens, E. J. et al. (eds.), Birkhauser Verlag, Basel, p. 59.
Hahn, F. E., Puck, T. T., Springer, G. F., Szybalski, W., andWallenfels, K. (1971) (itIn) Progress in Molecular and Subcellular Biology, Vol. 2,Hahn, F. E. (ed.), Springer-Verlag, Berlin.
Altman, P. L., andDittmer, D. S. (eds.) (1974) Biology Data Book, Vol. Ill, Fed. Am. Soc. Exp. Biol., Bethesda, Maryland.
Anfinsen, C. B., andWhite, F. H. (1961) In The Enzymes,Boyers, P. D., andLardy, H. (eds.), Academic, New York, p. 95.
Josefsson, L., andLagersted, S. (1962), In Methods of Biochemical Analysis, Vol. IX,Glick, D. (ed.), Interscience Publishers, New York, p. 39.
Altescu, E. J., (1964) Analy. Biochem. 8: 373; (1966) Enzymol. Biol. Clin. 6: 305.
Massart, L., Peeters, G., andLagrain, A. (1948) Arch. Int. Pharmacodyn. Ther. 76:72.
Sober, H. A., Schlossman, S. F., Yaron, A., andRuzhizky, G. W. (1965) Science (N.Y.) 50: 384.
Ariens, E. J. (1970) (itIn) Progress in Drug Research, Vol. 14,Areins, E. J. et al. (eds.), Birkhauser Verlag, Basel, p. 11.
Lees, C. W., andVon Hippel,P. H. (1968) Biochemistry 7: 2480.
Kurnick, N. B. (1962) (itIn) Methods of Biochemical Analysis, Vol. IX,Glick, D. (ed.), Interscience Publishers, New York.
Sela, M., andKatchalski, E. (1959) Adv. Prot. Chem. 14: 391.
Haurowitz, F. (1963) (itIn) Chemistry and Functions of Proteins, Academic, New York, p. 287.
Mandl, I., andNeuberg, C. (1956) (itIn) Advances in Enzymology, Vol. 17,Nord, F. F. (ed.), Interscience Publishers, New York.
Webb, J. L. (1966) (itIn) Enzyme and Metabolic Inhibitors, Vol. II, Academic, New York, p. 461.
Wiklander, L., (In) Ion Exchangers in Organic and Biochemistry,Calmon, C., andKressman, T. R. E. (eds.), Interscience Publishers, New York.
Suryanarayana, T., andBurma, D. P. (1975) Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 65:708.
Takashis, H., Laeson, T. J., andDownan, W. (1976) Biochemistry 15: 5205.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Singh, C., Anjaneyulu, K., Ramesh, V. et al. Studies on complexation of rna with polycationic compounds and use of complexed rna as a substrate for ribonuclease. Journal of Solid-Phase Biochemistry 5, 245–253 (1980). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03000660
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03000660