Abstract
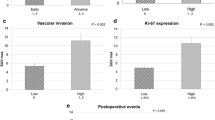
Objective: The aim of this study is to examine the correlation between tumor angiogenesis and response to preoperative radiotherapy evaluated using201T1 single photon emission computed tomography (Tl SPECT) in oral cavity squamous cell carcinoma (SCC).Methods: Tl SPECTs before and after preoperative radiotherapy were obtained from 11 patients diagnosed with SCC in oral cavity. Regions of interest were set around the tumor and scalp respectively, and the ratio of mean counts in the tumor to those in the scalp was calculated (T/N). Immunohistochemical staining for investigating microvessel density of pre-treatment biopsy specimen was performed using CD31 monoclonal antibody. We compared microvessel density with semi-quantitative parameters obtained using Tl SPECT (T/N at pre-an post-treatment, reduction ratio) and prognosis.Results: The subgroup with higher microvessel density showed a significantly higher reduction ratio than the one with lower microvessel density. Regarding prognosis, the subgroup with locoregional recurrent disease exhibited a significantly higher microvessel density than the one without recurrence.Conclusions: In SCC of the oral cavity, there was a significant correlation between microvessel density and response to preoperative radiotherapy. Namely, it was revealed that change of201Tl uptake after preoperative radiotherapy correlated with tumor angiogenesis of oral cavity SCC.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Shintani S, Kiyota A, Mihara M, Nakahara T, Ueyama Y, Matsumura T, et al. Association of preoperative radiation effect with tumor angiogenesis and vascular endothelial growth factor in oral squamous cell carcinoma.Jpn J Cancer Res 2000; 91: 1051–1057.
Teknos TN, Cox C, Barrios MA, Chepeha DB, Bradford CR, Fisher SG, et al. Tumor angiogenesis as a predictive marker for organ preservation in patients with advanced laryngeal carcinoma.Laryngoscope 2002; 112: 844–851.
Hironaka S, Hasebe T, Kamijo T, Ohtsu A, Boku N, Yoshida S, et al. Biopsy specimen microvessel density is useful prognostic marker in patients with T(2–4) M(0) esophageal cancer treated with chemoradiotherapy.Clin Cancer Res 2002; 8: 124–130.
Cooper RA, West CM, Wilks DP, Logue JP, Davidson SE, Roberts SA, et al. Tumor vascularity is a significant prognostic factor for cervix carcinoma treated with radiotherapy: independence from tumour radiosensitivity.Br J Cancer 1999; 81: 354–358.
Kamijo T, Yokose T, Hasebe T, Yonou H, Sasaki S, Hayashi R, et al. Potential role of microvessel density in predicting radiosensitivity of Tl and T2 stage laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma treated with radiotherapy.Clin Cancer Res 2000; 6: 3159–3165.
Gasparini G, Weidner N, Maluta S, Pozza F, Boracchi P, Mezzetti M, et al. Intratumoral microvessel density and p53 protein: correlation with metastasis in head-and-neck squamous-cell carcinoma.Int J Cancer 1993; 55: 739–744.
Ito Y, Kamijo T, Yokose T, Kawashima M, Ogino T, Ikeda H, et al. Microvessel density predicts the radiosensitivity of metastatic head and neck squamous cell carcinoma in cervical lymph nodes.Int J Oncl 2001; 19: 1127–1132.
Zatterstrom UK, Brun E, Willen R, Kjellin E, Wennerberg J. Tumor angiogenesis and prognosis in squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck.Head Neck 1995; 17: 312–318.
Brun J, Zatterstrom UK, Kjellen E, Wahlberg P, Willen R, Brun A, et al. Prognostic value of histopathological response to radiotherapy and microvessel density in oral squamous cell carcinoma.Acta Oncol 2001; 40: 491–496.
Moustafa HM, Omar WM, Ezzat I, Ziada GA, el-Ghonimy EG.201Tl single photon emission tomography in the evaluation of residual and recurrent astrocytoma.Nucl Med Commun 1994; 15: 140–114.
Lorberboym M, Mandell LR, Mosesson RE, Germano I, Lou W, DaCosta M, et al. The role of thallium-201 uptake and retention in intracranial tumors after radiotherapy.J Nucl Med 1997; 38: 223–226.
Lorberboym M, Baram J, Feibel M, Hercbergs A, Lieberman L. A prospective evaluation of thallium-201 single photon emission computerized tomography for brain tumor burden.Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 1995; 32: 249–254.
Yamaji S. Usefulness of 20lTl SPECT in the evaluation of treatment effect for primary lung cancer.KAKU1GAKU (Jpn J Nucl Med) 1995; 32: 1333–1340. (in Japanese)
Shimizu M, Seto H, Kageyama M, Wu YW, Morijiri M, Watanabe N, et al. Assessment of treatment response in irradiated lung cancer by sequential thallium-201 SPECT: comparison with tumor volume change and survival time.Radiat Med 1996; 14: 7–12.
Suga K, Kume N, Nishigauchi K, Ogasawara N, Hara A, Miura G, et al.201Tl SPECT as an indicator for early prediction of therapeutic effects in patients with non-small cell lung cancer.Ann Nucl Med 1998; 12: 355–362.
Yoshimura N, Fukumoto M, Akagi N, Yoshida S. Diagnosis of lung cancer using functional image of201Tl SPECT with parameter of201Tl retention—evaluation of it applicability to post irradiated lung cancer.KAKU IGAKU (Jpn J Nucl Med) 1996; 33: 383–390. (in Japanese)
Kostakoglu L, Panicek DM, Divgi CR, Botet J, Healey J, Larson SM, et al. Correlation of the finding of thallium-201 chloride scans with those of other imaging modalities and histology following therapy in patients with bone and soft tissue sarcomas.Eur J Nucl Med 1995; 22: 1232–1237.
Togawa T, Yui N, Kinoshita F, Yanagisawa M, Hatano K, Sekiya Y, et al. Thallium-201 single-photon emission tomography in the treatment follow-up of nasopharyngeal carcinoma.Eur J Nucl Med 1997; 24: 305–311.
Kostakoglu L, Uysal U, Ozyar E, Elahi N, Hayra M, Uzal D, et al. Pre- and post-therapy thallium-201 and technetium-99m sestamibi SPECT in nasopharyngeal carcinoma.J Nucl Med 1996; 37: 1956–1962.
Kostakoglu L, Uysal U, Ozyar E, Hayran M, Uzal D, Demirkazik FB, et al. Monitoring response to therapy with thallium-201 and technetium-99m-sestamibi SPECT in nasopharyngeal carcinoma.J Nucl Med 1997; 38: 1009–1014.
Omura K, Suzuki H, Takeuchi Y, Harada H, Hatano K, Togawa T, et al. Prospective concurrent CBDCA chemotherapy and accelerated hyperfractionated radiotherapy for squamous cell carcinoma of the maxillary region.Head Neck Cancer 2001; 27: 663–669. (in Japanese)
Nagamachi S, Jinnouchi S, Flores LG 2nd, Nakahara H, Ono S, Ohnishi T, et al. The use of201Tl SPECT to predict the response to radiotherapy in patients with head and neck cancer.Nucl Med Commun 1996; 17: 935–942.
Kaplan WD, Takvorian T, Morris JH, Rumbaugh CL, Connolly BT, Atkins HL. Thallium-201 brain tumor imaging: comparative study with pathologic correlation.J Nucl Med 1987; 28: 47–52.
Nakahara T, Togawa T, Nagata M, Kikuchi K, Hatano K, Yui N, et al. Comparison of barium swallow, CT and thallium-201SPECT in evaluating response of patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma to preoperative chemoradiotherapy.Ann Nucl Med 2003; 17: 583–591.
Suzuki A, Togawa T, Kuyama J, Nakahara T, Takenouchi T, Kazuo Hatano, et al. Semi-quantitative assessment of oral cavity squamous cell carcinoma using201T1 SPECT for evaluating effectiveness of preoperative radiotherapy.Ann Nucl Med 2004; 18: 433–441.
Nakagawara J, Fukuoka S, Takahashi S, Takahashi M, Satoh K, Suematsu K, et al. Assessment of vascularity and permeability in brain tumor using SPECT and99mTc-DTPA-human serum albumin in relation to201Tl SPECT.KAKU IGAKU (Jpn J Nucl Med) 1994; 31: 117–124. (in Japanese)
Ohnishi H, Koizumi K, Uchiyama G, Yamaguchi M, Okada J, Ogata H, et al. Evaluation of malignancy and viability of brain tumors by201Tl SPECT: the correlation between201T1 SPECT and pathology, clinical progress and the intensity of enhancement on CT images.Nippon Igaku Hoshasen Gakkai Zasshi 1994; 54: 1388–1398. (in Japanese)
Taki S, Kakuda K, Kakuma K, Kobayashi K, Ohashi M, Ito S, et al.201Tl SPET in the differential diagnosis of brain tumours.Nucl Med Commun 1999; 20: 637–645.
Ueda T, Kaji Y, Wakisaka S, Watanabe K, Hoshi H, Jinnouchi S, et al. Time sequential single photon emission computed tomography studies in brain tumour using thallium-201.Eur J Nucl Med 1993; 20: 138–145.
Spector JG, Sessions DG, Haughey BH, Cha KS, Simpso J, Mofty EI, et al. Delayed regional metastases, distant metastases and second primary malignancies in squamous cell carcinoma of the larynx and hypopharynx.Laryngoscope 2001; 111: 1079–1087.
Dewhrist MW. Concepts of oxygen transport at the microcirculatory evel.Semin Radiat Oncol 1998; 8: 143–150.
Sehweil AM, McKillop JH, Milroy R, Wilson R, Abdel-Dayen HM, Omar YT. Mechanism of201Tl uptake in tumours.EurJ Nucl Med 1989; 15: 376–379.
Takekawa H, Itoh K, Abe S, Ogura S, Isobe H, Furudate M, et al. Thallium-201 uptake histopathological differentiation and Na-K ATPase in lung adenocarcinoma.J Nucl Med 1996; 37: 955–958.
Ishibashi M, Fujii T, Yamana H, Fujimoto K, Rikimaru T, Hayashi A, et al. Relationship between cancer cell proliferation and thallium-201 uptake in lung cancer.Ann Nucl Med 2000; 14: 255–261.
Slizofski WJ, Krishna L, Kasetos CD, Black P, Miyamoto C, Brown SJ, et al. Thallium imaging for brain tumors with results measured by semiquantitative index and correlated with histopathology.Cancer 1994; 74: 3190–3197.
Kallen K, Heiling M, Andersson AM, Brun A, Holtas S, Ryding E, et al. Evaluation of malignancy in ring enhancing brain lesions on CT by thallium-201 SPECT.J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 1997; 63: 569–574.
Higa T, Maetani S, Kobayashi Y, Nabeshima S.201Tl SPECT compared with histopathological grade in the prognostic assessment of cerebral gliomas.Clin Nucl Med 2001; 26: 119–124.
Yoshii Y, Moritake T, Yamamoto T, Takano S, Tsuboi K, Hyodo A, et al. Correlation of histopathological factor of brain tumor and high thallium-201 uptake in single photon emission computed tomography.Noshuyo Byori 1996; 13: 61–65.
Itoh J, Yasumura K, Takeshita T, Ishikawa H, Kobayash H, Ogawa K, et al. Three-dimensional imaging of tumor angiogenesis.Anal Quant Cyto Histol 2000; 22: 85–90.
Gleich LL, Biddinger PW, Paveli ZP, Gluckman JL. Tumor angiogenesis in Tl oral cavity squamous cell carcinoma: role in predicting tumor aggressiveness.Head Neck 1996; 18: 343–346.
Gleich LL, Biddinger PW, Duperier FD, Gluckman JL. Tumor angiogenesis as a prognostic indicator in T2-T4 oral cavity squamous cell carcinoma: a clinical-pathologic correlation.Head Neck 1997; 19: 276–280.
Weidner N, Semple JP, Welch WR, Folkman J. Tumor angiogenesis and metastasis—correlation in invasive breast carcinoma.N Engl J Med 1991; 324: 1–8.
Secomb TW, Hsu R, Dewhirst MW, Klitzman B, Gross JF. Analysis of oxygen transport to tumor tissue by microvascular networks.Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 1993; 25: 481–489.
Kamijo T, Yokose T, Hasebe T, Yonou H, Hayashi R, Ebihara S, et al. Image analysis of microvessel surface area predicts radiosensitivity in early-stage laryngeal carcinoma treated with radiotherapy.Clin Cancer Res 2001; 7: 2809–2814.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Suzuki, A., Togawa, T., Kuyama, J. et al. Correlation between angiogenesis and reduction ratio measured using201Tl chloride single photon emission computed tomography in patients with oral cavity squamous cell carcinoma. Ann Nucl Med 18, 599–607 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02984582
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02984582