Abstract
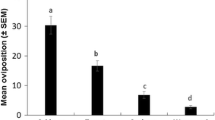
The ovipositional response ofHelicoverpa armigera (Hübner) to different cotton varieties and species was studied under caged conditions. Maximum oviposition (51.6 eggs/female) was recorded on LH 900, a variety ofGossypium hirsutum, and minimum oviposition (3.0 eggs/female) on G 27, a variety ofG. arboreum. Oviposition, in general, was low (3 to 6.5 eggs/female) onarboreum cottons as compared withhirsutum. Of the number of factors found to affect the oviposition ofH. armigera, the trichome length on the upper surface of the leaf, rather than the density, was positively correlated (r = 0.687*). Among different months in the cropping season, oviposition was maximum (552.7) during April. Oviposition was higher on leaves than on other plant parts.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Duhoon, S.S. and Singh, M. (1980) Resistance to spotted bollwormEarias spp. in cotton,Gossypium arboreum Linn.Indian J. Entomol. 42: 116–121.
Goyal, S.P. and Rathore, V.S. (1988) Patterns of insect-plant relationship determining susceptibility of different hosts toHeliothis armigera (Hüb.).Indian J. Entomol. 50:193–201.
Jayaswal, A.P. (1988) Recent outbreak of American bollworms,Heliothis armigera Hüb. on cotton in Andhra Pradesh and its management. Paper presented at Workshop onHeliothis Management (Tamil Nadu Agricultural University, Coimbatore, India).
Karmawati, E. (1988) Within plant distribution ofHelicoverpa armigera Hüb. eggs on cotton at Asembagus, East Java.Ind. Crop Res. J. 1(1):26–31.
Lukefahr, M.J., Houghtaling, J.E. and Graham, H.M. (1971) Suppression ofHeliothis populations with glabrous cotton strains.J. Econ. Entomol. 64:486–488.
Lukefahr, M.J., Houghtaling, J.E. and Graham, H.M. (1975) Suppression ofHeliothis spp. with cottons containing combinations of resistant characters.J. Econ. Entomol. 68:743–746.
Norris, D.M. and Kogan, M. (1980) Biochemical and morphological bases of resistance.in: Maxwell, F.C. and Jennings, P.R. [Eds.] Breeding Plants Resistant to Insects. John Wiley and Sons, Inc., New York, NY. pp. 323–361.
Parsons, F.S. (1940) Distribution of eggs ofHeliothis armigera Hüb. on cotton.Bull. Entomol. Res. 31:147–177.
Ramnath, S., Chitra, K. and Uthamasamy, S. (1992) Behavioral response ofHelicoverpa armigera (Hüb.) to certain host plants.J. Insect Sci. 5:147–149.
Singh, J. and Sidhu, A.S. (1990) Present status ofHeliothis on cotton and strategies for its management in Punjab, Haryana and Rajasthan.Proc. First National Workshop on Heliothis Management: Current Status and Future Strategies. Directorate of Pulses, Kanpur, India.
Steel, R.G.D. and Torrie, J.H. (1980) Principles and Procedures of Statistics: A Biometrical Approach. McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, NY.
Sundramurthy, V.T. (1993) Integrated insect management strategies for cotton insects to increase the production in 2000 A.D. Paper presented at the Seminar on Important Commercial Cotton Varieties (Ahmedabad, New Delhi, India).
Wilson, R.L. and Wilson, F.D. (1977) Effects of cottons differing in pubescence and other characters on pink bollworm in Arizona.J. Econ. Entomol. 70:196–198.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Butter, N.S., Singh, S. Ovipositional response ofHelicoverpa armigera to different cotton genotypes. Phytoparasitica 24, 97–102 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02981403
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02981403