Abstract
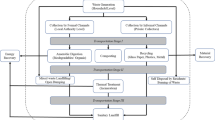
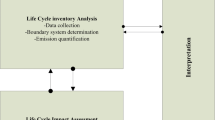
This paper discusses the application of an LCt model for solid waste management systems in Malaysia. The model was used to analyze the environmental and economic impacts of municipal waste management systems in Malaysia. In the first part of the study, the LCI model was adapted to analyze waste management systems of four selected cities: Kuala Lumpur and Penang to represent urban areas; Seremban to represent moderately urban areas and Muar to represent rural areas. The results have shown that Kuala Lumpur and Penang had greater Global Warming Potential (GWP) and the costs spent on the solid waste management were also higher as compared to that in suburban areas. In the second part of the study, a detailed evaluation was carried out by analyzing the implication of introducing incineration and composting into the solid waste management system, and the results were compared with the current system, i.e. 100 % landfilled. The relative GWP was lower for incineration, but the cost was extremely high. The results also showed that the final solid waste to be disposed to landfills and the impact due to water emissions could be reduced significantly when incineration and composting were introduced.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tamamushi, K.;White, P. (1998): Applying Life Cycle Assessment To Waste Management in Asia. In: Proceedings of the Third International Conference on Ecobalance. Japan, 25–27 November 1998, pp. 501–504
ENSIC (1994): A References Handbook for Trainers in Promotion of Solid Waste Recycling and Reuse in the Developing Countries of Asia. Kenya
Hassan, M.N.;Kamil, Y.;Azmin, S.;Rakmi, A.R. (1998): Issue and Problems of Solid Waste Management in Malaysia. In: National Review of Environmental Quality Management in Malaysia: Towards the Next Two Decades. Nordin. H. Lizuryaty, A. A., Ibrahim, K. (Eds.) pp.179–225
Tanaka, M.;Osaka, M.;Fujil, T.;Saito, A.;Sugiyama, R.;Kurihara, K. (1998): A Study on Comparison of Municipal Solid Waste Management Alternatives Based on Life Cycle Inventory. In: Proceedings of the Third International Conference on Ecobalance. Japan, 25–27 November 1998, pp. 497–500
White, P.;Franke, M.;Hindle, P. (1995): Integrated Solid Waste Management: An Life Cycle Inventory. Blackie Academic and Professional. Glasgow
IPCC (1992): Climate Change. In the IPCC Scientific Assessment. (Eds.) Houghton, J.T.
Coulon, R.;Camobrece, V.;Barlar, M.A.;Ham, R.T.;Repa, E.;Felker, M. (1998): Life Cycle Inventory of A Modern Municipal Solid Waste Landfill. In: Proceedings of the Third International Conference on Ecobalance. Japan, 25-27 November 1998, pp. 505–508
Morita, Y.;Tokuda, M. (1998): Life Cycle Assessment of Waste Management: A Study of City of Sendai. In: Proceedings of the Third International Conference on Ecobalance. Japan, 25– 27 November 1998, pp. 513–516
Tan, K.K.;Low, K.S.;Pillay, S.;Tan, H. (1986): A Computer Simulation Model of Solid Waste Management System. In: Management and Utilization of Solid Wastes. Yong, F.F. and Tan, K.K. (Eds.) pp. 59–83
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hassan, M.N., Awang, M., Lee Chong, T. et al. The application of an life cycle inventory (LCI) model for solid waste disposal systems in malaysia. Int. J. LCA 4, 188–190 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02979493
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02979493