Abstract
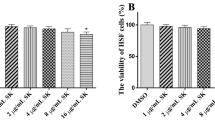
Resveratrol, a phenolic antioxidant found in grapes, has been known to mediate various biological activities on the human body. In the present study, we tested the antifungal activity of resveratrol against human pathogenic fungi before carrying out further studies to elucidate the antifungal mechanism(s) of resveratrol. Resveratrol displayed potent antifungal activity against human pathogenic fungi at concentration levels of 10–20 μg/mL Furthermore, time-kill curve exhibited fungicidal effect of resveratrol on C. albicans, but the compound had no hemolytic activity against human erythrocytes. The destruction of C. albicans cells by resveratrol was confirmed by scanning electron microscopy. These results suggest that resveratrol could be employed as a therapeutic agent to treat fungal infections of humans.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams, M. L. and Kwon, G. S., Relative aggregation state and hemolytic activity of amphotericin B encapsulated by poly(ethylene oxide)-block-poly(N-hexyl-L-aspartamide)-acyl conjugate micelles: effects of acyl chain length.J. Controlled Release, 87, 23–32 (2003).
Clement, M. V., Hirpara, J. L., Chawdhury, S. H., and Pervaiz, S., Chemopreventive agent resveratrol, a natural product derived from grapes, triggers CD95 signaling-dependent apoptosis in human tumor cells.Blood, 92, 996–1002 (1998).
Daroch, F., Hoeneisen, M., Gonzalez, C. L., Kawaguchi, F., Salgado, F., Solar, H., and Garcia, A.,In vitro antibacterial activity of Chilean red wines againstHelicobacter pylori.Microbios, 104, 79–85 (2001).
ElAttar, T. M. and Virji, A. S., Modulating effect of resveratrol and quercetin on oral cancer cell growth and proliferation.Anticancer Drugs, 10, 187–193 (1999).
Filip, V., Plockova, M., Smidrkal, J., Spickova, Z., Melzoch, K., and Schmidt, S., Resveratrol and its antioxidant and antimicrobial effectiveness.Food Chem., 83, 585–593 (2003).
Gronbaek, M., Deis, A., Sorensen, T. I., Becker, U., Schnohr, P., and Jensen, G., Mortalilty associated with moderate intakes of wine, beer, or spirits.Br. Med. J., 310, 1165–1169 (1995).
Hoos, G. and Blaich, R., Influence of resveratrol on germination of conidia and mycelial growth ofBotrytis cinerea andPhomopsis riticola.J. Phytopathol., 129, 102–110 (1990).
Hsieh, T. and Wu, J. M., Differential effects on growth, cell cycle arrest, and induction of apoptosis by resveratrol in human prostate cancer cell lines.Exp. Cell Res., 249, 109–115 (1999).
Jahn, B., Martin, E., Stueben, A., and Bhakdi, S., Susceptibility testing ofCandida albicans andAspergillus species by a simple microtiter menadione-augmented 3-(4,5-dimethyl-2-thiazolyl)-2,5-diphenyl-2H-tetrazolium bromide assay.J. Clin. Microbial., 33, 661–667 (1995).
Jang, M., Cai, L., Udeani, G. O., Slowing, K. V., Thomas, C. F., Beecher, C. W. W., Fong, H. H. S., Farnsworth, N. R., Kinghorn, A. D., Mehta, R. G., Moon, R. C., and Pezzuto. J. M., Cancer chemopreventive activity of resveratrol, a natural product derived from grapes.Science, 275, 218–220 (1997).
Klepser, M. E., Ernst, E. J., Lewis, R. E., Ernst, M. E., and Pfaller, M. A., Influence of Test Conditions on Antifungal Time-Kill Curve Results: Proposal for Standardized Methods.Antimicrob. Agents Chemother, 42, 1207–1212 (1998).
Lee, D. G., Kim, D. -H., Park, Y., Kim, H. K., Kim, H. N., Shin, Y. K., Choi, C. H., and Hahm, K. -S., Fungicidal effect of antimicrobial peptide, PMAP-23, isolated from porcine myeloid againstCandida albicans. Biochem.Biophys. Res. Commun., 282, 570–574 (2001).
Lee, D. G., Park, Y., Kim, H. N., Kim, H. K., Kim, P. I., Choi, B. H., and Hahm, K. -S., Antifungal Mechanism of an Antimicrobial Peptide, HP(2-20), Derived from N-Terminus ofHelicobacter pylori Ribosomal Protein L1 againstCandida albicans.Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 293, 231–238 (2002).
Pace-Asciak, C. R., Hahn, S., Diamandis, E. P., Soleas, G., and Goldberg, D. M., The red wine phenolics trans-resveratrol and quercetin block human platelet aggregation and eicosanoid synthesis: Implications for protection against coronary heart disease.Clin. Chim. Acta, 235, 207–219 (1995).
Rotondo, S., Rajtar, G., Manarini, S., Celardo, A., Rotillo, D., de Gaetano, Evangelista, V., and Cerletti, C., Effect of transresveratrol, a natural polyphenolic component on human polymorphonuclear leukocyte function.Br. J. Pharmacol., 123(8), 1691–1699(1998).
Tegos, G., Stermitz, F. R., Lomovskaya, O., and Lewis, K., Multidrug Pump Inhibitors Uncover Remarkable Activity of Plant Antimicrobials.Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 46, 3133–3141 (2002).
Yoon, S. -H, Kim, Y. -S., Ghim, S. -Y, Song, B. -H., and Bae, Y. -S., Inhibition of protein kinase CK activity by resveratrol, a natural compound in red wine and grapes.Life Sci., 71, 2145–2152 (2002).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jung, H.J., Hwang, I.A., Sung, W.S. et al. Fungicidal Effect of Resveratrol on Human Infectious Fungi. Arch Pharm Res 28, 557–560 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02977758
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02977758