Abstract
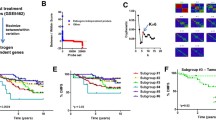
Estrogen plays an important role in growth and progression of human breast cancer. To understand the mechanism of estrogen signaling is very important to clarify the breast cancer biology and fight breast cancer. One promising method of study is a DNA microarray, specifically a down-sized, specific, custommade cDNA microarray, which was used for 200 estrogen-responsive genes in the present study. We performed three different studies using our custom microarray. First, clustering analysis of the gene expression profile among the breast cancer specimens before and after aromatase inhibitor treatment could separate patients into two groups showing different estrogen responses. Second, analysis of tamoxifen-effects on the gene expression profile of a tamoxifen-resistant MCF-7 subline, clone 9, showed that most estrogen responsive genes in MCF-7 cells did not contribute to tamoxifen resistance in these cells. Third, a study of the function of estrogen receptor (ER) \ and ER\cx co-expressing with ERα, suggested that ER\cx would be a stronger modulator of ERα than ER\. These data indicate that a custom microarray is a useful tool for assessing the estrogen signaling pathway. Furthermore, DNA microarray could be a very efficacious application for predicting response to breast cancer treatments.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ER:
-
Estrogen receptor
References
West M, Blanchette C, Dressman H,et al: Predicting the clinical status of human breast cancer by using gene expression profiles.Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98: 11462–11467, 2001.
Sørlie T, Perou CM, Tibshirani R,et al: Gene expres-sion patterns of breast carcinomas distinguish tumor subclasses with clinical implications.Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98: 10869–10874, 2001.
Gruvberger S, Ringnér M, Chen Y,et al: Estrogen receptor status in breast cancer is associated with remarkably distinct gene expression patterns.Cancer Research 61: 5979–5984, 2001.
van’t Veer LJ, Dai H, van de Vijver MJ,et al: Gene expression profiling predicts clinical outcome of breast cancer.Nature 415: 530–536, 2002.
Inoue A, Yoshida N, Omoto Y,et al: Development of cDNA microarray for expression profiling of estrogen-responsive genes.J Mol Endocrinol 29: 175–192, 2002.
Early Breast Cancer Trialists’ Collaborative Group: Tamoxifen for early breast cancer: an overview of the randomised trials.Lancet 351: 1451–1467, 1998.
Kuiper GGJM, Enmark E, Pelto-Huikko M,et al: Cloning of a novel estrogen receptor expressed in rat prostate and ovary.Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93: 5925–5930, 1996.
Omoto Y, Inoue S, Ogawa S,et al: Clinical value of the wild-type estrogen receptor \ expression in breast cancer.Cancer Lett 163: 207–212, 2001.
Omoto Y, Kobayashi S, Inoue S,et al: Evaluation of oestrogen receptor \ wild type and variant protein expression and relationship with clinicopathological factors in breast cancers.Eur J Cancer 38: 380–386, 2002.
Ogawa S, Inoue S, Watanabe T,et al: Molecular cloning and characterization of human estrogen receptor \cx: a potential inhibitor of estrogen action in human.Nucleic Acids Res 26: 3505–3512, 1998.
Moore JT, McKee DD, Slentz-Kesler K,et al: Cloning and characterization of human estrogen receptor \ isoforms.Biochem Biophys Res Commun 247: 75–78, 1998.
Saji S, Omoto Y, Shimizu C,et al: Expression of Estrogen Receptor (ER) \cx protein in ERα-positive breast cancer; specific correlation with Progesterone receptor.Cancer Res 62: 4849–4853, 2002.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Reprint requests to Shin-ichi Hayashi, Division of Endocrinology, Saitama Cancer Center Research Institute, 81 8 Komuro, Ina, Saitama 362-0806, Japan.
About this article
Cite this article
Omoto, Y., Hayashi, Si. A study of estrogen signaling using DNA microarray in human breast cancer. Breast Cancer 9, 308–311 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02967609
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02967609