Abstract
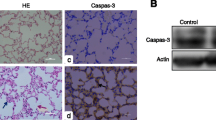
Previous epidemiological studies have shown association between coal burning and human lung cancer. To confirm relationship between coal burning and lung cancer formation and progression the expression of p53 and c-myc in 13 mouse lung cancer induced by coal burning smoke and 5 mouse lung tissue control was studied by DNA-RNA in situ hybridization (ISH). Nine of 13 specimens showed c-myc overexpression but it occurred only 1 of adjacent tissue. There was over pression of p53 mRNA in all 13 lung cancer and 5 adjacent tissue. None in the controls was expression of p53 and c-myc detected. When compared to controls, there was significant higher expression of c-myc gene (P=0.002) and p53 gene (P=0.0001).
The results confirm that overexpression of p53 and c-myc are common molecular events of lung cancer by coal burning smoke and provide further evidence that smoke from coal burning is a causative agent of lung cancer.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
SuZuki H, Takahashi T, Kuroishi T, et al. p53 mutation in non-small cell lung cancer in Japan: association between mutation and smoking. Cancer Res 1992; 52: 734.
Robert Booker Stein. p53 is mutated in a subset of advanced-stage prostate cancers. Cancer Res 1993; 53: 3369.
Antonio Marchetti, Fiamma Buttitta, Giorgio Merlo, et al. p53 alterations in non-small cell lung cancers correlate with metastatic involvement of hilar and mediastinal lymph nodes. Cancer Res 1993; 53: 2846.
Takashi Takahashi, David Carbone, Toshitada Takahashi, et al. Wild-type but not mutate p53 suppresses the growth of human lung cancer cells bearing multiple genetic lesions. Cancer Res 1992; 52: 2340.
Jim Batty, Antonio MH. The human c-myc oncogene: Structural consequence of translocation in to the IgH locus in Burkitt lymphoma. Cell 1983; 34: 779.
Odd Morkve. Quantitation of biological tumor markers (p53, c-myc ki — 69 and DNA Ploidy) by multiparemeter flow cytometry in non-small-cell lung cancer. Int J Cancer 1992; 52: 851.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This project partly supported by The National Natural Science Foundation of China (38970650)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lin, C., Dai, X., Sun, X. et al. Expression of P53 and c-myc in mouse lung cancer induced by coal burning. Chinese Journal of Cancer Research 8, 253–255 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02954742
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02954742