Abstract
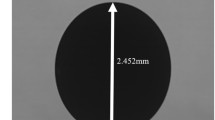
The surface tension and the viscosity of a series of industrial alloys have been measured by the oscillating drop technique with an electromagnetic levitation device under reduced gravity conditions in several parabolic flights. It was demonstrated that the 20 seconds of reduced gravity available in a parabola were sufficient for melting, heating into the liquid phase, and cooling to solidification of typically 7 mm diameter metallic specimen. The surface tension and the viscosity were obtained from the frequency and the damping time constant of the oscillation which were evaluated from the temperature signal of a highresolution pyrometer. Alloys processed included steels, Ni-based superalloys, and Ti-alloys which were supplied by industrial partners to the project. Three to four parabolas were sufficient to obtain the surface tension and the viscosity over a large range in temperature.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dantzig, J. A.: Solidification Modeling: Status and Outlook, JOM, vol. 52, no. 12, p. 18 (2000).
Saunders, N., in: Superalloys 1996. Kissenger, R. D. et al. (Eds.), TMS, Warrendale, Pennsylvania, p. 101 (1996).
Egry, I., Lohöfer, G., Jacobs, G.: Surface Tension of Liquid Metals: Results from Measurements on Ground and in Space, Phys. Rev. Letters, vol. 75, p. 4043 (1995).
Wunderlich, R. K., Fecht, H.-J.: Thermophysical Properties of Bulk Metallic Glass Forming Alloys in the Stable and Undercooled Liquid — A Microgravity Investigation, J. Mat. Trans. JIM, vol. 42, no. 4, p. 565 (2001).
Egry, I., Jacobs, G., Schwartz, E., Szekely, J.: Surface Tension Measurements of Metallic Melts under Micro-Gravity, Int. J. Thermophys., vol. 17, p. 1181 (1996).
Rösner-Kuhn, M., Hofmeister, W. H., Kuppermann, G., Morton, C. W., Bayuzick, R. J., Frohberg, M. G., in: Solidification 1999. Hofmeister, W. H., Rogers, J. R., Marsh, S., Singh, N. B., Vorhees, P. W. (Eds.), TMS, Warrendale, Pennsylvania, p. 33 (1999).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aune, R., Battezzati, L., Brooks, R. et al. Surface tension and viscosity of industrial alloys from parabolic flight experiments — Results of theThermoLab project. Microgravity sci. Technol. 16, 11–14 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02945937
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02945937