Abstract
This paper describes the importance of fumonisins for human beings and animals and shows data for the occurence in food. Corn-based food samples (n = 299) purchased in the area of munich were analyzed for fumonisin content using an enzyme immunoassay.
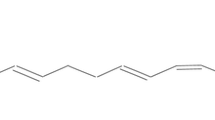
Fumonisins are mycotoxins produced byFusarium species, especially byFusarium moniliforme andFusarium proliferatum. Occurrence of fumonisins in corn and in cornbased foods and feeds has been reported from almost all over the world. In several animal species different diseases are traced back to fumonisin toxicosis. Fumonisin levels of 5–10 ppm inhorse feed induce “Equine Leucoencephalomalacia” and hepatic lesions. Hepatotoxic (10 150 ppm fumonisin in feed) and pneumotoxic (>150 ppm fumonisin in feed) effects have been reported for swine. Cattle and poultry appear to be less susceptible to fumonisins. Fumonisin B1 Revels of 50 ppm in the diet of rats cause hepatotoxic and nephrotoxic effects, long time exposure results in hepatic cancer. A possible role of fumonisins in the etiology of human esophageal cancer is under discussion, although no direct causal evidence is known so far. The mode of action of the fumonisins is probably based on inhibition of sphingolipidbiosynthesis caused by the blockade of the enzyme sphyngosine (sphinganine)-N-acyltrans-ferase.
Similar content being viewed by others
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schlichtherle, C. Fumonisins — Importance and occurence of a new group of mycotoxins. Mycotox Res 13, 49 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02945062
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02945062