Summary
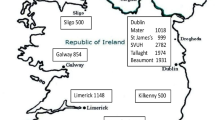
This paper analyses data on 2,226 cases of Hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection detected during the years 1970 to 1987. Of those where information on risk-group was available (1,301), infection among intravenous drug-abusers accounted for the largest proportion (49%). Most became infected during and since an outbreak of hepatitis B and Delta hepatitis which originated in this group in 1980. A comparison of the data before and after the start of the outbreak among drug-abusers shows a marked increase in the number of HBV infections in nondrug users, including haemophiliacs, homosexuals and health-care staff, and a dramatic decrease in hepatitis B following blood transfusion. A larger group (165 cases), many of whom are long-term healthy hepatitis B surface antigen carriers, were patients in institutions for the mentally handicapped (IMH). Most were detected recently during pre-vaccination sampling programmes. Others affected included visitors to and from high-incidence areas, tattooed persons, dialysis patients, persons born to infected mothers, and members of the security forces dealing with drug-abusers.
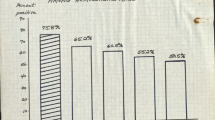
In all, 8.4% of the hepatitis B cases detected were found to be carriers and 67% of these remained carriers in 1987. The mean duration of carriage was 3.25 years. Intravenous drug-abusers and IMH patients constituted the two largest groups of carriers.
The running-three-yearly mean incidence of new cases of hepatitis B has levelled off below the peak of 1981. Although the number of cases among drug-abusers has apparently decreased, the number of cases among non drugabusing groups has increased by 50%. The use of recently introduced vaccines in some risk groups should help to reverse this upward trend.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Shattock, A. G. Hepatitis associated antigen in the Republic of Ireland: a preliminary report. Irish J. Med. Sci. 1974: 143, 162–167.
Shattock, A. G., Kelly, M. G., Fielding, J., Arthurs, Y. Epidemic Hepatitis B with Delta-antigenaemia among Dublin drug-abusers. Irish J. Med. Sci. 1982: 151, 334–338.
Shatock, A. G., Irwin, F. M., Morgan, B. M., Hillary, I. B., Kelly, M. G., Fielding, J. F., Kelly, D. A., Weir, D. G. Increased severity and morbidity of acute hepatitis in drug-abusers with simultaneously acquired hepatitis B and hepatitis D virus infections. Brit. Med. J. 1985: 290, 1377–1380.
Kelly, D. A., Carroll, D., Shattock, A. C, O’Connor, E., Weir, D. G, A secondary outbreak of hepatitis B among contacts of drug-abusers in Dublin, Irish Med. J. 1983: 76, 205–208.
Smith, A, M., Tedder, R. S. Development of an enzyme-immunoassay (ELISA) for hepatitis Be antigen and antibody. j. Viroi. Methods. 1981: 3, 1–11.
Fitzgerald, G. R., Grimes, H., Reynolds.M.. Hitchcock, H., McCarthy, C. F. Hepatitis associated antigen positive hepatitis in a tuberculosis unit. Gut 1975: 16, 421–428.
McGregor, M. A. Hepatitis B in a hospital for the mentally subnormal in south Wales. J. Ment. Def. Res. 1988: 32, 75–77.
Krugman, S., Giles, J. P., Hammond, J Infectious hepatitis: Evidencefortwo district clinical, epidemiological and immunological types of infection. JAMA 1967: 200, 365.
Jackson, J. Occupationally acquired viral hepatitis in Irish pathology laboratories. Converse, Bulletin of the Academy of Medical Laboratory Science. 1987: 4–5.
Feldman, R. E., Schiff, E. R. Hepatitis in dental professionals. JAMA 1975: 232, 1228–1230.
Shattock, A. G., Gorry, H. F. Hepatitis B antigen (HBAg) in the Republic of Ireland: distribution of ad and ay subtypes. Irish J. Med. Sci. 1974: 143, 4, 214–219.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shattock, A.G., Jones, L., O’Mahony, M. et al. Changes in incidence of hepatitis B in Ireland from 1970–1987. I.J.M.S. 158, 210–214 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02943614
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02943614