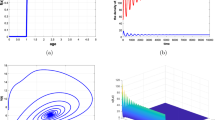
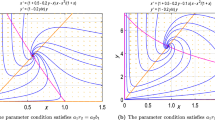
Abstract
A mathematical model dealing with a prey-predator system with disease in the prey is considered. The functional response of the predator is governed by a Hoilling type-II function. Mathematical analysis of the model regarding stability and persistence has been performed. The effect of delay and diffusion on the above system is studied. The role of diffusivity on stability and persistence criteria of the system has also been discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
R. M. Anderson and R. M. May,The population dynamics of macroparasites and their invertebrate hosts, Phil. Trans. Roy. Soc. LondonB291 (1981), 451–524.
R. M. Anderson and R. M. May,Directly transmitted infectious diseases: control by vaccination, Science,215 (1982), 1053–1060.
R. M. Anderson and R. M. May,The invasion and spread of infectious diseases within animal and plant communities, Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond.B314 (1986), 533–570.
R. Bhattacharyya, M. Bandyopadhyay and S. Banerjee,Stability and bifurcation in a diffusive prey-predator system: non-linear bifurcation analysis, J. Appl. Math. & Computing10 (2002), 17–26.
R. Bhattacharyya, B. Mukhopadhyay and M. Bandyopadhyay,Diffusion driven stability analysis of a prey-predator system with Holling type-IV functional response, System Analysis Modelling Simulation,43(8) (2003), 1085–1093.
G. Birkhoff and G. C. Rota,Ordinary Differential Equations, Ginn. and Co., 1982.
G. J. Bulter, H. I. Freedman and P. Waltman,Uniformly persistent system, Proc. Am. Math. Soc.96 (1986), 425–430.
J. Chattopadhyay, G. Ghosal and K. S. Chaudhuri,Nonselective harvesting of a preypredator community with infected prey, Korean J. Comput. & Appl. Math.6(3) (1999), 601–616.
K. Das and A. K. Sarkar,Effect of time delay in an autotroph-herbivore system with nutrient recycling, Korean J. Comput. & Appl. Math.5(3) (1998), 507–516.
A. P. Dobson,The population biology of parasite induced changes in host behaviour, Q. Rev. Biol.63 (1988), 139–165.
P. C. Fife,Mathematical Aspects of Reacting and Diffusing Systems, Lect. Notes in Biomathematics,28, Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, New York, 1979.
H. I. Freedman and P. Waltman,Persistence in models of three interacting predator-prey populations, Math. Biosci.68 (1984), 213–231.
H. I. Freedman and P. Waltman,Persistence in a model of three competitive populations, Math. Biosci.73 (1985), 89–101.
H. I. Freedman,A model of predator-prey dynamics as modified by the action of a parasite, Math. Biosci.99 (1990), 143–155.
T. C. Gard,Persistence in food chains general interactions, Math. Biosci.51 (1980), 165–174.
A. K. Ghosh, J. Chattopadhyay and P.K. Tapaswi, An SIRS epidemic model on a dispersive population, Korean J. Comput. & Appl. Math.,7(3) (2000), 693-
K. P Hadeler and H. I. Freedman,Predator-prey populations with parasite infection, J. Math. Biol.27 (1989), 609–631.
H. W. Hethcote,A thousand and one epidemic models, InFrontiers in Mathematical Biology, (Ed.) Levin, S.A., Lecture Notes in Biomathematics100, Springer, Berlin, 1994.
J. Hofbauer,General co-operation theorem for hypercycles, Monatsh. Math.91 (1981), 233–240.
J. C. Holmes and W. M. Bethel,Modification of intermediate host behaviour by parasite InBehavioral Aspects of Parasite Transmission, No.1 to the Zool. J. Linnean. Soc., (Eds.) Cunning, E. V. and Wright, C. A.51 (1972), 123–149.
V. Hutson and G. T. Vickers,A criterion for permanent co-existence of species with an application to a two prey one predator system, Math. Biosci.63 (1983), 253–269.
S. Kováis,Spatial inhomogenity due to Turing bifurcation in a system of Gierer-Meinhardt type, J. Appl. Math. & Computing11(1–2) (2003), 125–142.
W. O. Kermack and A. G. Mckendrick,Contributions to the mathematical theory of epidemics, Proc. Roy. Soc.A115 (1927), 700.
R. M. May,Population biology of microparasite infections InMathematical Ecology, (eds.) Hallam, T.G. and Levin, S. A., Biomathematics17, Springer, Berlin, 1986, 405–442.
D. Mukherjee,Uniform persistence in a generalised prey-predator system with parasitic infection, Biosystems,47 (1998), 149–155.
S. Muratori and S. Rinaldi,Low and high frequency oscillations in three-dimensional food chain system, SIAM. J. Appl. Math.52(6) (1992), 1688–1706.
A. Okubo,Diffusion and Ecological Problems: Mathematical Models, Biomathematics,10, Springer, Berlin, 1980.
A.M. Turing,The chemical basis of morphogenesis, Philos. R. Sec. Ser.B237 (1952), 37–72.
Y. Xiao and L. Chen,Modeling and analysis of a predator-prey model with disease in the prey, Math. Biosci.171 (2001), 59–82.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Banibrata Mukhopadhyay is continuing his research work for the Ph.D. degree in the University of Calcutta. His research interests are Dynamical modeling involving diffusion and delay differential equations with application to complex biological systems.
Rakhi Bhattacharyya has recently submitted her thesis for Ph. D. degree of the University of Calcutta. She has obtained her M. Sc. and M. Phil. degrees from the University of Calcutta. Her research interest focus on stability and bifurcation analysis of dynamical models with application to biological systems.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mukhopadhyay, B., Bhattacharyya, R. Dynamics of a delay-diffusion prey-predator model with disease in the prey. JAMC 17, 361–377 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02936062
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02936062