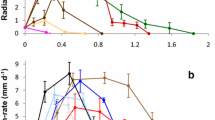
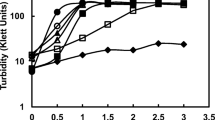
Abstract
The pathways for biosynthesis of pyrimidines, L-arginine and the polyamines are intimately interrelated in many microorganisms. We discovered in this study that growth of wild-typeEscherichia coli in low-water-activity minimal media is inhibited by the addition of uracil. Uracil sensitivity was observed irrespective of whether the dissolved solute(s) contributing to decreased water activity was ionic (e.g. NaCl, K2SO4), nonionic and impermeable (e.g. sucrose), nonionic and freely permeable (e.g. glycerol), or any mixture of these types. A mutant resistant to such growth inhibition was isolated and was shown to harbour a bradytrophic mutation inargA, the gene encoding the first step in the L-arginine biosynthetic pathway. Mutations inargR, whose product is the aporepressor of the same pathway, or exogenous supplementation with L-arginine or L-citrulline, also conferred resistance to uracil inhibition in low-water-activity media. A similar uracil-sensitivity phenotype, which was reversible byargA, argR, or L-arginine addition, was exhibited even in media with a more moderate reduction in water activity in two different situations: for aspeC mutant (which is defective in the enzyme ornithine decarboxylase required for biosynthesis of the polyamines) and for the wild-type strain in media additionally supplemented with L-ornithine. On the basis of these observations, we propose a model in which high cytoplasmic levels of the intermediary metabolite L-ornithine are inhibitory to growth ofE. coli in media of low water activity. Our results also provide the first evidence for the existence of a third component of physiological water stress, which is elicited by both impermeable and permeable dissolved solutes (the other two known components are ionic stress, which is elicited only by ionic solutes, and osmotic stress, which is elicited only by impermeable solutes either ionic or nonionic). We propose the term anhydrotic stress to refer to this novel component of water stress.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bae J. -H. and Miller K. J. 1992 Identification of two proline transport systems inStaphylococcus aureus and their possible roles in osmoregulation.Appl. Environ. Microbiol 58, 471–475.
Bae J. -H., Anderson S. H. and Miller K. J. 1993 Identification of a high-affinity glycine betaine transport system inStaphylococcus aureus.Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 59, 2734–2736.
Berlyn M. K. B., Low K. B., Rudd K. E. and Singer M. 1996 Linkage map ofEscherichia coli K-12, edition 9. InEscherichia coli and Salmonella: cellular and molecular biology, 2nd edn. (ed. F. C. Neidhardt, R. Curtiss III, J. L. Ingraham, E. C. C. Lin, K. B. Low, B. Magasanik, W. S. Reznikoff, M. Riley, M. Schaechter and H.E. Umbarger), pp. 1715–1902. ASM Press, Washington, DC.
Boyle S. M., Markham G. D., Hafner E. W., Wright J. M., Tabor H. and Tabor C. W. 1984 Expression of the cloned genes encoding the putrescine biosynthetic enzymes and methionine adenosyl-transferase ofEscherichia coli (speA, speB, speC and metK).Gene 30, 129–136.
Bradford M. M. 1976 A rapid and sensitive method for the quantification of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding.Anal. Biochem. 72, 248–254.
Bray G. A. 1990 A simple efficient liquid scintillator for counting aqueous solutions in a liquid scintillation counter.Anal. Biochem. 1, 279–285.
Capp M. W., Cayley D. S., Zhang W., Guttman H. J., Melcher S. E., Saecker R. M., Anderson C. F. and Record M. T. Jr. 1996 Compensating effects of opposing changes in putrescine (2+) and K+ concentrations onlac repressor-lac operator binding:in vitro thermodynamic analysis andin vivo relevance.J. Mol. Biol 258, 25–36.
Cataldi A. A. and Algranati I. D. 1989 Polyamines and regulation of ornithine biosynthesis inEscherichia coli.J. Bacteriol. 171, 1998–2002.
Celis T. F. R. 1977 Properties of anEscherichia coli K-12 mutant defective in the transport of arginine and ornithine.J. Bacterial. 130, 1234–1243.
Crabeel M., Charlier D., Cunin R., Boyen A., Glansdorff N. and Pierard A. 1975 Accumulation of arginine precursors inEscherichia coli: effects on growth, enzyme repression, and application to the forward selection of arginine auxotrophs.J. Bacteriol 123, 898–904.
Csonka L. N. 1989 Physiological and genetic responses of bacteria to osmotic stress.Microbiol. Rev. 53, 121–147.
Csonka L. N. and Epstein W. 1996 Osmoregulation. InEscherichia coli and Salmonella: cellular and molecular biology, 2nd edn. (ed. F. C. Neidhardt, R. Curtiss III, J. L. Ingraham, E. C. C. Lin, K. B. Low, B. Magasanik, W. S. Reznikoff, M. Riley, M. Schaechter and H. E. Umbarger), pp. 1210–1223. ASM Press, Washington, DC.
Cunin P., Glansdorff N., Pierard A. and Stalon V. 1986 Biosynthesis and metabolism of arginine in bacteria.Microbiol. Rev. 50, 314–352.
Cunningham-Rundles S. and Maas W. K. 1975 Isolation, characterization, and mapping ofEscherichia coli mutants blocked in the synthesis of ornithine decarboxylase.J. Bacteriol. 124, 791–799.
Epstein W. and Schultz S. G. 1965 Cation transport inEscherichia coli. V. Regulation of cation content.J. Gen. Physiol 49, 221–234.
Fernandes T., Iyer V. and Apte S. K. 1993 Differential effects of salt and osmotic stress on growth and nitrogen fixation inAnabaena sp. strain L-31.Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 59, 899–904.
Gaxiola R., de Larrinoa I.E., Villalba J.M. and Serrano R. 1992 A novel and conserved salt-induced protein is an important determinant of salt tolerance in yeast.EMBO J. 11, 3157–3164.
Glansdorff N. 1996 Biosynthesis of arginine and polyamines. InEscherichia coli and Salmonella: cellular and molecular biology, 2nd edn. (ed. F. C. Neidhardt, R. Curtiss III, J. L. Ingraham, E. C. C. Lin, K. B. Low, B. Magasanik, W. S. Reznikoff, M. Riley, M. Schaechter and H. E. Umbarger), pp. 408–433. ASM Press, Washington, DC.
Gorini L. and Kalman S. M. 1963 Control by uracil of carbamyl phosphate synthesis inEscherichia coli.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 69, 355–360.
Gouesbet G., Jebbar M., Bonnassie S., Hugouvieux-Cotte-Pattat N., Himdi-Kabbab S. and Blanco C. 1995Erwinia chrysanthemi at high osmolarity: influence of osmoprotectants on growth and pectate lyase production.Microbiology 141, 1407–1412.
Gowrishankar J. 1985 Identification of osmoresponsive genes inEscherichia coli: evidence for participation of potassium and proline transport systems in osmoregulation.J. Bacteriol. 164, 434–445.
Gowrishankar J. and Pittard J. 1982 Construction from Mu dl (lac Apr) lysogens of lambda bacteriophage bearing promoter-lac fusions: isolation of λppheA-lac.J. Bacteriol. 150, 1122–1129.
Greenway H. and Munns R. 1980 Mechanisms of salt tolerance in nonhalophytes.Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol. 31, 149–190.
Guilloton M. and Karst F. 1987 Cyanate specifically inhibits arginine biosynthesis inEscherichia coli K-12: a case of byproduct inhibition?J. Gen. Microbiol. 133, 655–665.
Gutierrez C., Barondess J., Manoil C. and Beckwith J. 1987 The use of transposonTnphoA to detect genes for cell envelope proteins subject to a common regulatory stimulus: analysis of osmotically regulated genes inEscherichia coli.J. Mol. Biol. 195, 289–297.
Haas D., Kurer V. and Leisinger T. 1972 N-Acetylglutamate synthetase ofPseudomonas aeruginosa. An assayin vitro and feedback inhibition by arginine.Eur. J. Biochem. 31, 290–295.
Hafner E. W., Tabor C. W. and Tabor H. 1977 Isolation of ametK mutant with a temperature-sensitive S-adenosylmethionine synthetase.J. Bacteriol 132, 832–840.
Harris C. L. 1981 Cysteine and growth inhibition ofEscherichia coli: threonine deaminase as the target enzyme.J. Bacteriol. 145, 1031–1035.
Hershkovitz N., Oren A., Post A. and Cohen Y. 1991 Induction of water-stress proteins in cyanobacteria exposed to matric- or osmotic-water stress.FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 83, 169–172.
Houssin C., Eynard N., Shechter E. and Ghazi A. 1991 Effect of osmotic pressure on membrane energy-linked functions inEscherichia coli.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1056, 76–84.
Hunter J. S. V., Greene R. C. and Su C.-H. 1975 Genetic characterization of themetK locus inEscherichia coli K-12.J. Bacteriol 122, 1144–1152.
Jensen K. F. 1993The Escherichia coli K-12 “wild-types” W3110 and MG1655 have anrph frameshift mutation that leads to pyrimidine starvation due to lowpyrE expression levels.J. Bacteriol. 175, 3401–3407.
Karpel R., Alon T., Glaser G., Schuldiner S. and Padan E. 1991 Expression of a sodium proton antiporter (NhaA) inEscherichia coli is induced by Na+ and Li+ ions.J. Biol Chem. 266, 21753–21759.
Kapyaho K. and Janne J. 1982 Regulation of putrescine metabolism in Ehrlich ascites carcinoma cells exposed to hypotonic medium.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 714, 93–100.
Kelker N. and Eckhardt T. 1977 Regulation ofargA operon expression inEscherichia coli K-12: cell-free synthesis ofβ- galactosidase underargA control.J. Bacteriol. 132, 67–72.
Kunst F. and Rapoport G. 1995 Salt stress is an environmental signal affecting degradative enzyme synthesis inBacillus subtilis.J. Bacteriol 111, 2403–2407.
Laimins L. A., Rhoads D. B. and Epstein W. 1981 Osmotic control ofkdp operon expression inEscherichia coli.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 78, 464–468.
Leikin S., Parsegian V. A., Rau D. C. and Rand R. P. 1993 Hydration forces.Annu. Rev. Phys. Chem. 44, 369–395.
Leisinger T. and Haas D. 1975N-Acetylglutamate synthase ofEscherichia coli: regulation of synthesis and activity by arginine.J. Biol. Chem. 250, 1690–1693.
Le Rudulier D. and Bouillard L. 1983 Glycine betaine, an osmotic effector inKlebsiella pneumoniae and other members of the Enterobacteriaceae.Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 46, 152–159.
Le Rudulier D., Yang S. S. and Csonka L. N. 1982 Nitrogen fixation inKlebsiella pneumoniae during osmotic stress: effects of exogenous proline or a proline overproducing plasmid.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 719, 273–283.
Le Rudulier D., Strom A. R., Dandekar A. M., Smith L. T. and Valentine R. C. 1984 Molecular biology of osmoregulation.Science 224, 1064–1068.
Mager J. 1955 Influence of osmotic pressure on the polyamine requirement ofNeisseria perflava andPasteurella tularensis for growth in defined media.Nature 176, 933–934.
Miller J. H. 1992A short course in bacterial genetics: a laboratory manual and handbook for Escherichia coli and related bacteria. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, New York.
Morris D. R. and Koffron K. L. 1969 Putrescine biosynthesis inEscherichia coli.J. Biol. Chem. 244, 6094–6099.
Munro G. F. and Bell C. A. 1973 Polyamine requirements of a conditional polyamine auxotroph ofEscherichia coli.J. Bacteriol 115, 469–475.
Munro G. F. and Sauerbier W. 1973 Osmotically induced excretion of putrescine by mutants ofEscherichia coli defective in potassium transport.J. Bacteriol. 116, 488–490.
Munro G. F., Hercules K., Morgan J. and Sauerbier W. 1972 Dependence of the putrescine content ofEscherichia coli on the osmotic strength of the medium.J. Biol. Chem. 247, 1272–1280.
Munro G. F., Miller R. A., Bell C. A. and Verderber E. L. 1975 Effects of external osmolarity on polyamine metabolism in HeLa cells.Biochim. Biophys. Ada 411, 263–281.
Parsegian V. A., Rand R. P. and Rau D. C. 1995 Macromolecules and water: probing with osmotic stress.Meth. Enzymol 259, 43–94.
Perry J. W. and Oka T. 1980 Regulation of ornithine decarboxylase in cultured mouse mammary gland by the osmolarity in the cellular environment.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 629, 24–35.
Pierard A., Glansdorff N., Mergeay M. and Wiame J. M. 1965 Control of the biosynthesis of carbamoyl phosphate inEscherichia coli.J. Mol. Biol. 14, 23–36.
Posas F., Camps M. and Arino J. 1995 The PPZ protein phosphatases are important determinants of salt tolerance in yeast cells.J. Biol. Chem. 270, 13036–13041.
Poulin R., Wechter R. S. and Pegg A. E. 1991 An early enlargement of the putrescine pool is required for growth in L1210 mouse leukemia cells under hypoosmotic stress.J. Biol. Chem. 266, 6142–6151.
Rubenstein K. E., Streibel E., Massey S., Lapi L. and Cohen S. S. 1972 Polyamine metabolism in potassium-deficient bacteria.J. Bacteriol. 112, 1213–1221.
Sambrook J., Fritsch E. F. and Maniatis T. 1989Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, New York.
Saroja G. N. and Gowrishankar J. 1996 Roles of SpoT and FNR in NH4+ 4 assimilation and osmoregulation in GOGAT (glutamate synthase)-deficient mutants ofEscherichia coli.J. Bacteriol. 178, 4105–4114.
Shortridge V. D., Lazdunski A. and Vasil M. L. 1992 Osmoprotectants and phosphate regulate expression of phospholipase C inPseudomonas aeruginosa.Mol. Microbiol. 6, 863–871.
Singer M., Baker T. A., Schnitzler G., Deischel S. M., Goel M., Dove W., Jaacks K. J., Grossman A. D., Erickson J. W. and Gross C. A. 1989 A collection of strains containing genetically linked alternating antibiotic resistance elements for genetic mapping ofEscherichia coli.Microbiol. Rev. 53, 1–24.
Sorensen M. and Pedersen S. 1991 Cysteine, even in low concentrations, induces transient arnino acid starvation inEscherichia coli.J. Bacteriol. 173, 5244–5246.
Sutherland L., Cairney J., Elmore M. J., Booth I. R. and Higgins C. F. 1986 Osmotic regulation of transcription: induction of theproU betaine transport gene is dependent on accumulation of intracellular potassium.J. Bacteriol. 168, 805–814.
Uchida S., Garcia-Perez A., Murphy H. and Burg M. B. 1989 Signal for induction of aldose reductase in renal medullary cells by high external NaCl.Am. J. Physiol. 256, C614-C620.
Wyn Jones R. G. 1984 Phytochemical aspects of osmotic adaptation.Recent Adv. Phytochem. 18, 55–78.
Yancey P. H., Clark M. E., Hand S. C., Bowlus R. D. and Somero G. N. 1982 Living with water stress: evolution of osmolyte systems.Science 217, 1214–1222.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Umaprasad, G., Gowrishankar, J. Evidence for the existence of a novel component of biological water stress (anhydrotic stress) inEscherichia coli . J. Genet. 77, 1–11 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02933035
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02933035