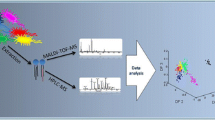
Abstract
High-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) and gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS) were used to analyze the phospholipids and fatty acids of fourArcobacter species (becoming routinely isolated from a wide variety of food sources, especially of animal origin) to provide information for the identification within these species. Phospholipid differences were observed in the HPLC profiles. GC-MS analysis provided a complete fatty acid composition for each arcobacter that after pattern recognition analysis allows taxonomic classification of each species.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- DAD:
-
diode array detector
- FA:
-
fatty acid(s)
- FAB:
-
fast atom bombardment
- FAME(s):
-
fatty acid methyl ester(s)
- GC:
-
gas chromatography
- HPLC:
-
high-performance liquid chromatography
- MS:
-
mass spectrometry
- NIST:
-
National Institute of Standards and Technology
- PCA:
-
principal component analysis
- TIC:
-
total ion current
References
Basile F., Beverly M.B., Abbas-Hawks C., Mowry C.D., Voorhees K.J., Hadfield T.L.: Direct mass spectrometric analysis ofin situ thermally hydrolyzed and methylated lipids from whole bacterial cells.Anal.Chem.70, 1555–1562 (1998).
Bastyns K., Cartuyvels D., Chapelle S., Vandamme P., Goossens H., De Wachter R.: A variable 23S rRNA region is useful discriminating target for genus-specific and species-specific PCR amplification inArcobacter species.Syst.Appl.Microbiol.18, 353–356 (1995).
Beebe K.R., Pell R.J., Seasholtz M.B.:Chemometrics: a Practical Guide. John Wiley & Sons, New York 1999.
Beverly M.B., Voorhees K.J., Hadfield T.L.: Direct mass spectrometric analysis ofBacillus spores.Rap.Com.Mass Spectrom.13, 2320–2326 (1999).
Buyer J.S.: Identification of bacteria from single colonies by fatty acid analysis.J.Microbiol.Meth.48, 259–265 (2002).
Červenka L., Malíková Z., Zachová I., Vytřasová J.: The effect of acetic acid, citric acid, and trisodium citrate in combination with different levels of water activity on the growth ofArcobacter butzleri in culture.Folia Microbiol.49, 8–12 (2004).
Cronan J.E.: Phospholipis modifications in bacteria.Curr.Opin.Microbiol.5, 202–205 (2002).
Donachie S.P., Bowman J.P., On S.L.W., Alam M.:Arcobacter halophilus sp.nov., the first obligate halophile in the genusArcobacter.Internat.J.Syst.Bacteriol.Evol.Microbiol.55, 1271–1277 (2005).
Fenselau C.:Mass Spectrometry for the Characterization of Microorganisms, pp. 8–17. Maple Press, York (PA) 1994.
Gattinger A., Schloter M., Munch J.C.: Phospholipid, etherlipid and phospholipid fatty acid fingerprints in selected euryarchaeontal monocultures for taxonomical profiling.FEMS Microbiol.Lett.213, 133–139 (2002).
Harmon K.M., Wesley I.V.: Identification ofArcobacter isolates by PCR.Lett.Appl.Microbiol.23, 241–244 (1996).
Harmon K.M., Wesley I.V.: Multiplex PCR for the identification ofArcobacter and differentiation ofArcobacter butzleri from other arcobacters.Vet.Microbiol.58, 215–227 (1997).
Harrington P.B.:RESOLVE Tutorial. Colorado School of Mines, Golden (USA) 1990.
Harrington C.S., On S.L.W.: Extensive 16S ribosomal RNA gene sequence diversity inCampylobacter hyointestinalis strains: taxonomic and applied implications.Internat.J.Syst.Bacteriol.49, 1171–1175 (1999).
Hochel I., Viocha D., Škvor J., Musil M.: Development of an indirect competitive ELISA for detection ofCampylobacter jejuni subsp.jejuni O:23 in foods.Folia Microbiol.49, 579–586 (2004).
Houf K., Tutenel A., De Zutter L., Van Hoof J., Vandamme P.: Development of a multiplex PCR assay for the simultaneous detection and identification ofArcobacter butzieri, Arcobacter cryaerophius andArcobacter skirrowii.FEMS Microbiol. Lett.193, 89–94 (2000).
Houf K., On S.L.W., Coenye T., Mast J., Van Hoof J., Vandamme P.:Arcobacter cibarius sp.nov., isolated from broiler carcasses.Internat.J.Syst.Bacteriol.Evol.Microbiol.55, 713–717 (2005).
Kabeya H., Maruyama S., Morita Y., Kubo M., Yamamoto K., Arai S., Izumi T., Kobayashi Y., Katsube Y., Mikami T.: Distribution ofArcobacter species among livestock in Japan.Vet.Microbiol.93, 153–158 (2003a).
Kabeya H., Kobayashi Y., Maruyama S., Mikami T.: One-step polymerase chain reaction-based typing ofArcobacter species.Internat.J.Food Microbiol.81, 163–168 (2003b).
Logan E.F., Neill S.D., Mackie D.P.: Mastitis in dairy cows associated with an aerotolerantCampylobacter.Vet.Res.110, 229–230 (1982).
Mansfield L.P., Forsythe S.J.:Arcobacter butzleri andA. cryaerophilus — newly emerging human pathogens.Rev.Med.Microbiol.11, 161–170 (2000).
McClung C.R., Patriquin D.G.: Isolation of a nitrogen-fixingCampylobacter species from the roots ofSpartina alternifloraLoisel.Can.J.Microbiol.26, 881–886 (1980).
MIDI (Microbial Diagnostics), Newark (Delaware); http://www.midi-inc.com (1999).
Miketová P., Moore I.M., Pasvogel A., Khailova L., Schram K.H., Hunter J.J., Kaemingk K.L.: Determination of phospholipids as biomarkers of brain tissue damage in acute lymphoblastic leukemia patients.Sci.Pap.Univ.Pardubice Ser.A8, 73–91 (2002).
Olsen G.J., Overbeek R., Larsen N., March T.O., McCaughey J., Maciukenas M.A., Kuan W.M., Macke T.J., Xing Y., Woese C.R.: The ribosomal data base project.Nucl.Acids Res.20, 2199–2220 (1992).
Phillips C.A.: Arcobacters as emerging human foodborne pathogens.Food Control12, 1–6 (2001a).
Philips C.A.:Arcobacter spp. in food: isolation, identification and control.Trends Food Sci.Technol.12, 263–275 (2001b).
Šabatková Z., Pazlarová J., Demnerová K.: Sample processing effect on polymerase chain reaction used for identification ofCampytobacter jejum.Fona Microbiol.49, 693–698 (2004).
Vandamme P., Falsen E., Rossau R., Hoste B., Segers P., Tytgat R., De Ley J.: Revision ofCampylobacter, Helicobacter, andWolinella taxonomy: emendation of generic descriptions and proposal ofArcobacter gen.nov.Internat.J.Syst.Bacteriol.41, 88–103 (1991).
Vandamme P., Vancanneyt M., Pot B., Mels L., Hoste B., Dewettinck D., Vlaes L., Van Den Borre C., Higgins R., Hommez J., Kersters K., Butzler J.P., Goosens H.: Polyphasis taxonomic study of the emended genusArcobacter withArcobacter butzleri comb.nov. andArcobacter skirrowii sp.nov., an aerotolerant bacterium isolated from veterinary specimen.Internat.J.Syst.Bacteriol.42, 344–356 (1992).
Vandenberg O., Dediste A., Houf K., Ibekwem S., Souayah H., Cadranel S., Douat N., Zissis G., Butzler J.P., Vandamme P.:Arcobacter species in humans.Emerg.Infect.Dis.10, 1863–1867 (2004).
Vytřasová J., Pejchalová M., Harsová K., Binová S.: Isolation ofArcobacter butzleri, Arcobacter cryaerophilus in samples of meats and from meat-processing plants by a culture technique and detection by PCR.Folia Microbiol.47, 227–232 (2002).
Wesley I.V., Baetz A.L., Larson D.J.: Infection of cesarean-derived celostrum-deprived 1-day-old piglets withArcobacter butzleri, Arcobacter cryaerophilus, andArcobacter skirrowii.Infect.Immun.64, 2295–2299 (1996).
Zelles L.: Fatty acids patterns of microbial phospholipids and lipopolysacharides, pp. 80–93 in F. Schinner, R. Ohlinger, E. Kandeler, R. Margesin (Eds):Methods in Soil Biology, Springer-Verlag, New York 1995.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This work was partially supported by the office of Vice President for Research and Graduate Studies at theUniversity of Arizona, Tucson (Arizona) and byMinistry of Education, Youth and Sports of the Czech Republic, project no. 253 100 002.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jelínek, D., Miketová, P., Khailová, L. et al. Identification ofArcobacter species using phospholipid and total fatty acid profiles. Folia Microbiol 51, 329–336 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02931826
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02931826