Abstract
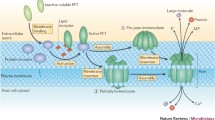
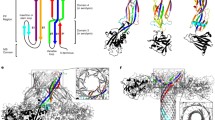
The repertoire of the cytolytic pore-forming protein toxins (PFT) comprises 81 identified members. The essential feature of these cytolysins is their capacity to provoke the formation of hydrophilic pores in the cytoplasmic membranes of target eukaryotic cells. This process results from the binding of the proteins on the cell surface, followed by their oligomerization which leads to the insertion of the oligomers into the membrane and formation of protein-lined channels. It impairs the osmotic balance of the cell and causes cytolysis. In this review the molecular aspects of a number of important PFT and their respective encoding structural genes will be briefly described.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abrami L., Fivaz M., Decroly E., Seidah N.G., François J., Thomas G., Leppla S., Buckley J.T., van der Goot F.G.: The poreforming toxin proaerolysin is processed by furin.J.Biol.Chem. 273, 32656–32661 (1988).
Aktories K., Just I.:Bacterial Protein Toxins, Handbook of Experimental Pharmacology, Vol. 145. Springer-Verlag, Berlin (Germany) 2000.
Alouf J.E.: Streptococcal toxins (streptolysin O, streptolysin S, erythrogenic toxin).Pharmacol.Ther. 11, 211–270 (1980).
Alouf J.E.: Introduction to the family of the structurally related cholesterol-binding cytolysins (sulfhydryl-activated toxins), pp. 443–456 in J.E. Alouf, J.H. Freer (Eds):The Comprehensive Sourcebook of Bacterial Protein Toxins. Academic Press, London 1999.
Alouf J.E.: Cholesterol-binding cytolytic protein toxins.Internat.J.Med.Microbiol. 290, 351–356 (2000).
Alouf J.E.: Pore-forming bacterial protein toxins, pp. 1–14 in F.G. van der Goot (Ed.):Pore Forming Toxins. Springer-Verlag, Berlin (Germany) 2001.
Alouf J.E., Freer J.H.:The Comprehensive Sourcebook of Bacterial Protein Toxins. Academic Press, London 1999.
Alouf J.E., Palmer M.: Streptolysin O, pp. 459–473 in J.E. Alouf, J.H. Freer (Eds):The Comprehensive Sourcebook of Bacterial Protein Toxins. Academic Press, London 1999.
Alouf J.E., Dufourcq J., Siffert O., Thiaudière E., Geoffroy C.: Interaction of staphylococcal δ-toxin and synthetic analogues with erythrocytes and phospholipid vesicles. Biological and physical properties of the amphipathic peptides.Eur.J.Biochem. 183, 381–390 (1989).
Baida G., Budarina Z.I., Kuzmin P., Solonin A.S.: Complete nucleotide sequence and molecular characterization of hemolysin II gene fromBacillus cereus.FEMS Microbiol.Lett. 180, 7–14 (1999).
Bayley H.: Toxin structure part of a hole?Curr.Biol. 7, R763-R767 (1997).
Bernheimer A.W., Rodbart M.: The effect of nucleic acids and carbohydrates on the formation of streptolysin S.J.Exp.Med. 88, 149–168 (1948).
Bernheimer A.W., Rudy B.: Interactions between membranes and cytolytic peptides.Biochim.Biophys.Acta 864, 123–141 (1986).
Bernheimer A.W., Avigad L.S., Kim K.-S.: Comparison of metridiolysin from the sea anemone with thiol-activated cytolysins from bacteria.Toxicon 17, 69–75 (1979).
Bhakdi S., Tranum-Jensen J.: Mechanism of complement cytolysis and the concept of channel-forming proteins.Philos.Trans.Roy.Soc.London Ser. B 306, 311–324 (1984).
Bhakdi S., Tranum-Jensen J.: Damage to cell membranes by pore-forming bacterial cytolysins.Progr.Allergy 40, 1–43 (1988).
Bhakdi S., Bayley H., Valeva A., Walev I., Walker B., Kehoe M., Palmer M.: Staphylococcal α-toxin, streptolysin-O, andEscherichia coli hemolysin: prototypes of pore-forming bacterial cytolysins.Arch.Microbiol. 165, 73–79 (1996).
Billington S.J., Jost B.H., Songer J.G.: Thiol-activated cytolysins: structure, function and role in pathogenesis.FEMS Microbiol.Lett. 182, 197–205 (2000).
Braun V., Hertle R.: The family ofSerratia andProteus cytolysins, pp. 349–361 in J.E. Alouf, J.H. Freer (Eds):The Comprehensive Sourcebook of Bacterial Protein Toxins. Academic Press, London 1999.
Buckley A.T.: The channel-forming toxin aerolysin, pp. 362–372 in J.E. Alouf, J.H. Freer (Eds):The Comprehensive Sourcebook of Bacterial Protein Toxins. Academic Press, London 1999.
Carr A., Sledjeski D.D., Podbielski A., Boyle M.D., Kreikemeyer B.: Similarities between complement-mediated and streptolysin S-mediated hemolysis.J.Biol.Chem. 276, 41790–41796 (2001).
Comai M., Della-Serra M., Coariola M., Werner S., Colin D., Prevost G., Menestrina G.: Protein engineering modulates the transport properties and ion selectivity of the pores formed by staphylococcal γ-hemolysins in lipid membranes.Mol.Microbiol. 44, 1251–1267 (2002).
Coote J.: The RTX toxins of Gram-negative bacterial pathogens, modulators of the host immune response.Rev.Med.Microbiol. 7, 53–62 (1996).
Dourmashkin R.R., Rosse W.F.: Morphologic changes in the membranes of red blood cells undergoing hemolysis.Am.J.Med. 41, 699–710 (1966).
Dufourcq J., Castano S., Talbot J.-C.: δ-Toxin related hemolytic toxins and peptidic analogues, pp. 386–401 in J.E. Alouf, J.H. Freer (Eds):The Comprehensive Sourcebook of Bacterial Protein Toxins. Academic Press, London 1999.
Fivaz M., Abrami L., Tsitrin Y., van der Gott F.G.: Aerolysin fromAeromonas hydrophila and related toxins, pp. 35–52 in F.G. van der Goot (Ed.):Pore-Forming Toxins. Springer-Verlag, Berlin (Germany) 2001.
Flanagan J., Collin N., Timoney J., Mitchell T., Mumford J.A., Chanter N.: Characterization of the hemolytic activity ofStreptococcus equi.Microb.Pathog. 24, 211–221 (1998).
Freer J.H., Birkbeck T.H.: Possible conformation of δ-lysin, a membrane-damaging peptide ofStaphylococcus aureus.J.Theor.Biol. 94, 535–540 (1982).
Gilbert R.J., Jimenez J.L., Chen S., Tickle I.J., Rossjohn J., Parker M., Andrew P.W., Saibil H.R.: Two structural transitions in membrane pore formation by pneumolysin, the pore-forming toxin ofStreptococcus pneumoniae.Cell 97, 647–655 (1999).
Ginsburg I.: Is streptolysin S of group A streptococci a virulence factor?Acta Pathol.Microbiol.Scand. 107, 1051–1059 (1999).
Glaser P., Sakamoto H., Bellalou J., Ullman A., Danchin A.: Secretion of cyclolysin, the calmodulin-sensitive adenylatecyclasehemolysin bifunctional protein ofBordetella pertussis.EMBO J. 7, 3997–4004 (1988).
van der Goot F.G.: Plasticity of the transmembrane β-barrel.Trends Microbiol. 8, 89–90 (2000).
van der Goot F.G.:Pore-forming Toxins. Springer-Verlag, Berlin (Germany) 2001.
Gouaux E.: Channel-forming toxins: tales of transformation.Curr.Opin.Struct.Biol. 7, 566–573 (1997).
Gouaux E.: α-Hemolysin fromStaphylococcus aureus: an archetype of β-barrel, channel-forming toxins.J.Struct.Biol. 121, 110–122 (1998).
Gouaux E., Hobaugh M., Song L.: α-Hemolysin, γ-hemolysin, and leukocidin fromStaphylococcus aureus: distant in sequence but similar in structure.Protein Sci. 6, 2631–2635 (1997).
Humar D., Datta V., Bast D.J., Beali B., De Azavedo J.C., Nizet V.: Streptolysin S and necrotizing infections produced by group G streptococcus.Lancet 359, 124–129 (2002).
Hunter S.E.C., Brown G.J.E., Oyston P.C.F., Titball R.W.: Molecular genetics of β-toxin ofClostridium perfringens reveals sequence homology with α-toxin, γ-toxin and leukocidin ofStaphylococcus aureus.Infect.Immun. 61, 3958–3965 (1993).
König B., Köller M., Prevost G., Piemont Y., Alouf J.E., Schreiner A., König W.: Activation of human effector cells by different bacterial toxins (leukocidin, alveolysin, and erythrogenic toxin A): generation of interleukin-8.Infect.Immun. 62, 4831–4837 (1994).
König B., Prévost G., König W.: Composition of staphylococcal bi-component toxin determines pathophysiological reactions.J.Med.Microbiol. 46, 479–485 (1997).
Ladant D., Ullmann A.:Bordetella pertussis adenylate cyclase: a toxin with multiple talents.Trends Microbiol. 7, 172–176 (1999).
Lally E.T., Hill R.B., Kieba I.R., Korostoff J.: The interaction between RTX toxins and target cells.Trends Microbiol. 7, 356–361 (1999).
Lesieur C., Vecsey-Semin B., Abrami L., Fivaz M., van der Goot F.G.: Membrane insertion: the strategy of toxins.Mol.Membr.Biol. 14, 45–64 (1997).
Locht C.: Molecular aspects ofBordetella pertussis pathogenesis.Internat.Microbiol. 2, 137–144 (1999).
Loridan C., Alouf J.E.: Purification of RNA-core induced streptolysin S, and isolation and hemolytic characterization of the carrier-free toxin.J.Gen.Microbiol. 132, 305–307 (1986).
Ludwig A., Goebel W.: The family of the multigene encoded RTX toxins, pp. 330–338 in J.E. Alouf, J.H. Freer (Eds):The Comprehensive Sourcebook of Bacterial Protein Toxins. Academic Press, London 1999.
Lund T., de Buyser M.L., Granum P.E.: A new cytotoxin fromBacillus cereus that may cause necrotic enteritis.Mol.Microbiol. 38, 254–261 (2000).
Lysons R.J., Kent K.A., Bland A.P., Sellwood R., Robinson W.F., Frost A.J.: A cytotoxic hemolysin fromTreponema hyodysenteriae, a probable virulence determinant in swine dysentery.J.Med.Microbiol. 34, 97–102 (1991).
Marchlewicz B.A., Duncan J.: Properties of a hemolysin produced by group B streptococci.Infect.Immun. 30, 805–813 (1980).
Mayer M.M.: Mechanism of cytolysis by complement.Proc.Nat.Acad.Sci.USA 69, 2954–2958 (1972).
Menestrina G., Vécsey-Semjén B.: Biophysical methods and model membranes for the study of bacterial pore-forming toxins, pp. 287–309 in J.E. Alouf, J.H. Freer (Eds):The Comprehensive Sourcebook of Bacterial Protein Toxins. Academic Press, London 1999.
Menestrina G., Mackman N., Holland I.B., Bhakdi S.:Escherichia coli hemolysin forms voltage-dependent ion channels in membranes.Biochim.Biophys.Acta 905, 109–117 (1987).
Menestrina G., Dalla Serra M., Pederzolli C., Bregante M., Gambale F.: Bacterial hemolysins and leucotoxins affect target cells by forming large exogenous pores into their plasma membrane:Escherichia coli hemolysin A a case example.Biosci.Rep. 15, 543–551 (1995).
Menestrina G., Dalla-Serra M., Prevost G.: Mode of action of β-barrel toxins of the staphylococcal γ-hemolysin family.Toxicon 39, 1661–1672 (2001).
Morgan P.J., Andrew P.W., Mitchell T.J.: Thiol-activated cytolysins.Rev.Med.Microbiol. 7, 221–229 (1996).
Muir S., Koopman M.B.H., Libby S.J., Joens L.A., Heffron F., Kusters J.H.: Cloning and expression of aSerpula (Treponema)hyodysenteriae hemolysin gene.Infect.Immun. 60, 529–535 (1992).
Nizet V., Beall B., Bast D.B., Vivekananda D., Kilburn L., Low D.E., de Azavedo J.C.S.: Genetic locus for streptolysin S production by group A streptococcus.Infect.Immun. 68, 4245–4254 (2000).
Olson R., Nariya H., Yokota K., Kamio Y., Gouaux E.: Crystal structure of staphyloccal LukF delineates conformational changes accompanying formation of a transmembrane channel.Nature Struct.Biol. 6, 134–140 (1999).
Parker M.W., Buckley J.T., Postma J.P., Tucker A.D., Leonard K., Pattus F., Tsernoglou D.: Structure of theAeromonas toxin proaerolysin in its water-soluble and membrane-channel tates.Nature 367, 292–295 (1994).
Pedelacq J.D., Maveyraud L., Prevost G., Baba-Loussa L., Gonzalez A., Courcelle E., Shepard W., Monteil H., Samama J.P., Mourey L.: The structure of aStaphylococcus aureus leucocidin component (LukF-PV) reveals the fold of the water-soluble species of a family of transmembrane pore-forming toxins.Structure 7, 277–287 (1999).
Prévost G.: The bi-component staphylococcal leucocidins and γ-hemolysins (toxins), pp. 402–418 in J.E. Alouf, J.H. Freer (Eds):The Comprehensive Sourcebook of Bacterial Protein Toxins. Academic Press, London 1999.
Prévost G., Mourey L., Colin D.A., Menestrina G.: Staphylococcal pore-forming toxins, pp. 53–83 in F.G. van der Goot (Ed.):Pore-Forming Toxins. Springer-Verlag, Berlin (Germany) 2001.
Rossjohn J., Feil S.C., McKinstry W.J., Tweten R.K., Parker M.W.: Structure of a cholesterol-binding, thiol-activated cytolysin and a model of its membrane form.Cell 89, 685–692 (1997).
Salyers A., Whitt D.D.:Bacterial Pathogenesis: a Molecular Approach, 2nd ed. American Society for Microbiology Press, Washington (DC) 2002.
Šebo P., Ladant A.: Repeat sequences in theBordetella pertussis adenylate cyclase toxin can be recognized as alternative carboxy-terminal secretion signals by theEscherichia coli α-hemolysin translocator.Mol.Microbiol. 9, 999–1009 (1993).
Šebo P., Glaser P., Sakamoto H., Ullmann A.: High-level synthesis of active adenylate cyclase toxin ofBordetella pertussis in a reconstructedEscherichia coli system.Gene 104, 19–24 (1991).
Sekiya K., Satoh R., Danbara H., Futaesaku Y.: Electron microscopic evaluation of a two-step theory of pore-formation by streptolysin O.J.Bacteriol. 178, 6998–7002 (1996).
Sellman B.R., Kagan B.L., Tweten R.K.: Generation of a membrane-bound, oligomerized pre-pore complex is necessary for pore formation byClostridium septicum α-toxin.Mol.Microbiol. 23, 551–558 (1997).
Shatursky O., Heuck A.P., Shepard L.A., Rossjohn J., Parker M.W., Johnson A.E., Tweten R.K.: The mechanism of membrane insertion for a cholesterol-dependent cytolysin: a novel paradigm for pore-forming toxins.Cell 99, 293–299 (1999).
Shinoda S.: Hemolysins ofVibrio cholerae and otherVibrio species, pp. 373–385 in J.E. Alouf, J.H. Freer (Eds):The Comprehensive Sourcebook of Bacterial Protein Toxins. Academic Press, London 1999.
Song L., Hobaugh M.R., Shustak C., Cheley S., Bayley H., Gouaux J.E.: Structure of staphylococcal α-hemolysin, a heptameric transmembrane pore.Science 274, 1859–1866 (1996).
Staali L., Monteil H., Colin D.A.: The staphylococcal pore-forming lenkotoxins open Ca2+ channels in the membrane of human polymorphonuclear neutrophils.J.Membr.Biol. 162, 209–216 (1998).
Steiner K., Malke H.: Dual control of streptokinase and streptolysin S production by thecovRS andfasCAX two-component regulators inStreptococcus dysgalactiae subsp,equisimilis.Infect.Immun. 70, 3627–3636 (2002).
Sugawara N., Tomita T., Kamio Y.: Assembly ofStaphylococcus aureus γ-hemolysin into a pore-forming ring-shaped complex on the surface of human erythrocytes.FEBS Lett. 410, 333–337 (1997).
Tweten R., Parker M., Johnson A.E.: The cholesterol-dependent cytolysins, pp. 15–33 in F.G. van der Goot (Ed.):Pore-forming Toxins. Springer-Verlag, Berlin (Germany) 2001.
Valeva A., Palmer M., Bhakdi S.: Staphylococcal α-toxin: formation of the heptameric pore is partially cooperative and proceeds through multiple intermediate stages.Biochemistry 36, 13298–13304 (1997).
Vandana S., Raje. M, Krishnasastry M.V.: The role of the amino terminus in the kinetics and assembly ofα-hemolysin ofStaphylococcus aureus.J.Biol.Chem. 272, 24858–24863 (1997).
Welch R.A.: RTX structure and function: a story of numerous anomalies and few analogies in toxin biology, pp. 85–111 in F.G. van der Goot (Ed.):Pore-forming Toxins. Springer-Verlag, Berlin (Germany) 2001.
Woltjes J., Legdeur-Velthuis H., de Graaf J.: Detection and characterization of hemolysin production inStreptococcus mutans.Infect.Immun. 31, 850–855 (1981).
Zitzer A., Palmer M., Weller U., Wassenaar T., Biermann C., Tranum-Jensen J., Bhakdi S.: Mode of primary binding of target membranes and pore formation induced byVibrio cytolysin (hemolysin).Eur.J.Biochem. 247, 209–216 (1997).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alouf, J.E. Molecular features of the cytolytic pore-forming bacterial protein toxins. Folia Microbiol 48, 5–16 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02931271
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02931271