Abstract
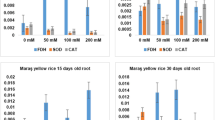
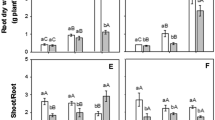
The effect of NaCl at sublethal concentration was observed on germinating seeds of salt-sensitive and -resistant rice cultivars with respect to the level of proline regulatory enzymes and the growth of seedlings on different days of early germination period. The two enzymes of proline biosynthesis and catabolism, Δ-pyrroline-5-carboxylate reductase and L-proline dehydrogenase, were taken into consideration to observe the effects of 100 mM NaCl on their activities in both rice cultivars. The activity of Δ-pyrroline-5-carboxylate reductase in salt-resistant cultivar was increased twice after 5 d in 100 mM NaCl. Simultaneously, the activity of L-proline dehydrogenase was decreased significantly. High activities of Δ-pyrroline-5-carboxylate reductase may be regarded as a biological marker for screening the sensitive and resistant cultivars of rice seed under NaCl-salinity.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arnon, D.I., Hoagland, D.R.: The water culture method for growing plants without soil. - Univ. Calif. Agr. Exp. Circ.347: 1–39, 1938.
Aspinall, D., Paleg, L.G.: Proline accumulation — physiological aspects. - In: Paleg, L.G., Aspinal, D. (ed.): The Physiology and Biohemistry of Drought Resistance in Plants. Pp. 206–211. Academic Press, Sydney 1981.
Bates, L.S., Waldren, R.P., Teare, I.D.: Rapid determination of free proline in water-stress studies. -Plant Soil39: 205–210, 1973.
Hoffman, G.J.: Alleviating salinity stress. - In: Arhin.C.F., Taylor,H.M. (ed.): Modifying the Rood Environment to Reduce Crop Stress. Pp. 305–343. American Society of Agricultural Engineers, St. Joseph 1981.
Huber, W.: Über den Einfluss von NaCl- oder Abscisinsä'urebehandlung auf den Protein- Metabolismus und einige weitere Enzyme des Aminosäurestoffwechsels in Keimlingen vonPennisetum typhoides. - Planta121: 225–235, 1974.
Laliberte, G., Hellebust, A.J.: Pyrroline-5-carboxylate reductase inChlorella autotrophica andChlorella saccharophila in relation to osmoregulation. - Plant Physiol.91: 917–923, 1989.
Lowry, O.H., Rosebrough, N.J., Farr, A.L., Randall, R.J.: Protein measurement with the Folin-phenol reagent. - J. biol. Chem.193: 265–275, 1951.
Mezl, V.A., Knox, W.E.: Properties and analysis of a stable derivative of pyrroline-5-carboxylic acid for use in metabolic studies. - Anal. Biochem.74: 430–440, 1976.
Rena, A., Splittstoesser, W.E.: L-proline dehydrogenase and pyrroline-5-carboxylate reductase from pumpkin cotyledons. -Phytochemistry14: 657–661, 1975.
Sudhakar, C., Reddy, P.S., Veeranjaneyulu, K.: Biochemical changes during early seedling growth of horsegram(Dolichos biflorus L.) subjected to salt-stress. - Indian J. exp. Biol.25: 479–482, 1987.
Treichel, S.: The influence of NaCl on proline accumulating cell suspension cultures ofMesembryanthemum nodiflorum and other halophytes. - Physiol. Plant.67: 173–181, 1986.
Yoshio, K., Tsuyoshi, O., Yasuhiko, Y., Shigeho, I.: Proline in osmoregulation ofBrevibacterium lactofermentum. - Agr. biol. Chem.53: 2475–2479, 1989.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Roy, D., Bhunia, A., Basu, N. et al. Effect of nacl- salinity on metabolism of proline in salt- sensitive and salt- resistant cultivars of rice. Biol Plant 34, 159–162 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02925814
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02925814